Java keywords are also known as reserved words. Keywords are particular words which act as a key to a code. These are predefined words by Java so it cannot be used as a variable or object name.
List of Java Keywords
-
abstract
abstract class Employee{
abstract void work();
}aaabstract is used to declare abstract class. It can have abstract and non-abstract method.
-
boolean
boolean is used to declare a variable ad a boolean type. It can hold True and False Only.
-
break is used to break loop or switch statement. It breaks the current flow of the program.
-
byte
byte is used to declare a variable that can hold an 8-bit data values.
-
case
switch(expression){
case value1:
//code to be executed
break;
case value2:
//code to be executed
break;
default:
//code to ececuted if all cases are not matched
}case is used to with the switch statements to mark blocks of test.
-
catch
try{
//code that may throw an exception
}catch(Exception_class_name ref){
}catch is used to catch the exception generated by try statement.
-
char
char is used to declare a variable that can hold unsigned 16-bit Unicode characters.
-
class
class is used to declare a class.
-
continue
continue is used to continue to the loop (skips the remaining code).
-
default
default is used to specify the default block of code in a switch statement.
-
do
do{
//code to executed
}while(condition);do is used to declare a do-while loop.
-
double
double is used to declare a variable that hold a 64-bit floating -point numbers.
-
else
else is used to indicate the alternative branches in an if statement.
-
enum
public class EnumExample1{
//defining the enum inside the class
public enum Season{
WINTER,SPRING,SUMMER,FALL
}
//main method
public static void main(String[] args){
//traversing the num
for(Season s: Season.values()){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}enum (enumerate) is used to fixed set of constants.
-
extends
public Subclass-name extends Superclass-name{
//methods and fields
}extends is used to indicate that a class derived from another class.
-
final
-
final variable
public class Bike9{
final int speedlimit = 90; //final variable
public void run(){
speedlimit = 400;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Bike9 obj = new Bike9();
obj.run();
}
}C:UsersdreamDesktopMarkdownn学习Java基础 est>javac Bike9.java
Bike9.java:5: error: cannot assign a value to final variable speedlimit
speedlimit = 400;
^
1 error
-
final method
class Bike{ final void run(){ //final method System.out.println("running"); } } class Honda extends Bike{ void run(){ System.out.println("running safely with 100kmph"); } static void main(String args[]){ Honda honda= new Honda(); honda.run(); } }C:UsersdreamDesktopMarkdownn学习Java基础 est>javac Bike.java Bike.java:8: error: run() in Honda cannot override run() in Bike void run(){ ^ overridden method is final 1 error-
final class
final class Bike{} class Honda1 extends Bike{ void run(){System.out.println("running safely with 100kmph");} public static void main(String args[]){ Honda1 honda= new Honda1(); honda.run(); } }C:UsersdreamDesktopMarkdownn学习Java基础 est>javac Bike.java Bike.java:20: error: cannot inherit from final Bike class Honda1 extends Bike{ ^ 1 errorfinal is used to indicate a variable, method, or class. these would be restrict to use.
-
-
finally
finally is used to indicate a block of code in a try-catch structure. the block is always executed.
-
float
float is used to declare a variable that can hold a 32-bit floating-point number
-
for
for(initialization;condition;Increment/Decrement){ //statement or code to be executed }for is used to start a for loop
-
if
if is used to test condition, it executes the if block if condition is true.
-
implements
interface printable{ void print(); } class A6 implements printable{ // implements interface public void print(){ System.out.println("Hello"); } public static void main(String args[]){ A6 obj = new A6(); obj.print(); } }C:UsersdreamDesktopMarkdownn学习Java基础 est>java A6 Hello
implements is used to implement an interface.
-
import
import makes class and interfaces available and accessible to the current source code.
-
instanceof
class Simple1{ public static void main(String[] args){ Simple1 s = new Simple1(); System.out.println(s instanceof Simple1);//true } }C:UsersdreamDesktopMarkdownn学习Java基础 est>java Simple1 true
instanceof is used to test whether the object is an instance of the specified class or interface
-
int
int is used to declare a variable that can hold a 32-bit signed integer
-
interface
interface is used to declare a interface. It can have only static constants and abstract method.
-
long
long is used to declare a variable that can hold a 64-bit signed integer.
-
native
native is used to specify that a method is implemented in native code using JNI(Java Native Interface)
-
new
new is used to create an instance of the class or array.
-
null
null is used to indicate that a reference does not refer to anything.
-
package
//save as Simple.java package mypack; public class Simple{ public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println("Wellcome to Package"); } }C:UsersdreamDesktopMarkdownn学习Java基础 est>javac -d . Simple.java
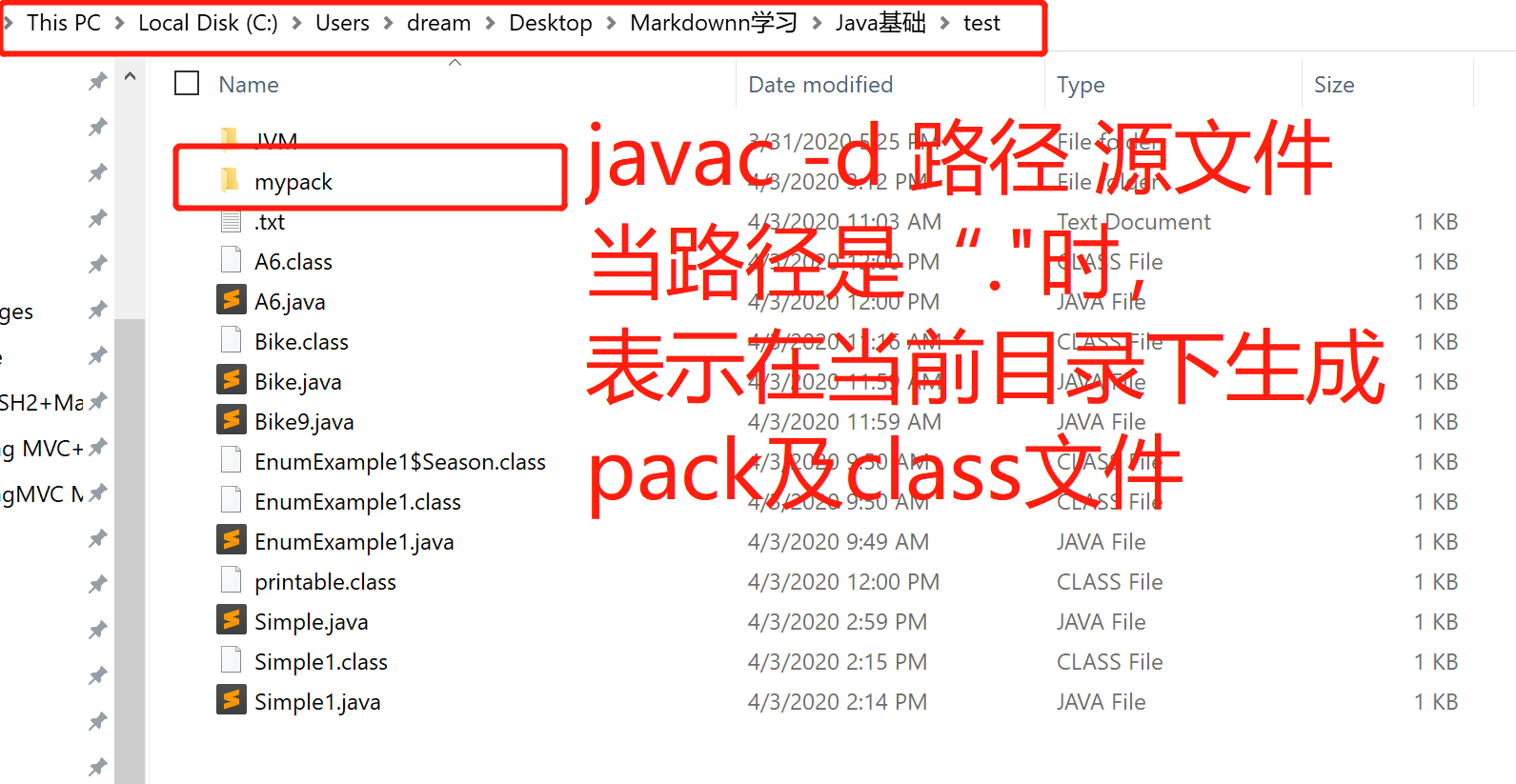
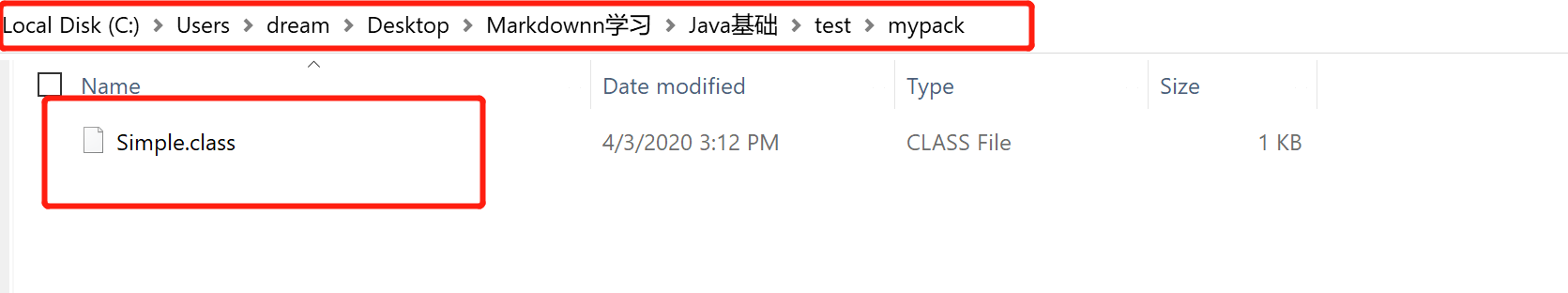
C:UsersdreamDesktopMarkdownn学习Java基础 est>java mypack.Simple Wellcome to Package
package is used to declare a Java package that includes the classes.
-
private
private is an access modifier. it is used to indicate that a method or variable may be accessed only in the class in which it is declared.
-
protected
protected is an access modifier. it can be assigned to variables, methods, and inner classes.
-
public
public is an access modifier. it is used to indicate that an item is accessible anywhere.
-
return
return is used to return from a method when its execution is complete.
-
short
short is used to declare a variable that can hold a16-bit integer.
-
static
static is used to indicate that a variable, method, block, or nested class belong to class area than heap memory(where store instance of class).
-
strictfp
strictfp class A{} //stricfp applied on classstrictfp interface M{} //stricfp applied on interfaceclass A{ strictfp void m(){} //stricfp applied on method }strictfp ensure that you will get the same result on every platform if you perform operations in the floating-point variable. it is used to applied on method, class or interface.
-
super
super is a reference variable which is used to refer Immediate parent class object.
-
switch
switch is used to indicate a switch statement that tests the quality of a variable against multiple values.
-
synchronized
synchronized is used to specify the critical sections or methods in multithreaded code.
-
this
this is used to refer the current object in a method or constructor.
-
throw
public class TestThrow1{ static void validate(int age){ if(age<18) throw new ArithmeticException("not valid"); else System.out.println("welcome to vote"); } public static void main(String args[]){ validate(13); System.out.println("rest of the code..."); } }throw is used to explicitly throw a custom exception.
-
throws
throws is used to declare an checked exception.
-
transient
transient is declare a variable that is transient, and will not be serialized.
-
try
try is used to start a block of code that will be tested for exceptions.
-
void
void is used to specify that a method does not have a return value.
-
volatile
volatile is used to indicate that a variable may change asynchronously.
-
while
while is used to start a while loop.
Identifiers
Java Identifiers are the name of class, package, constant, method, etc.
The two key rules of all identifiers
-
The name must not contain any white space
-
The name should not start with special characters like &(ampersand), $(dollar), _(underscore).
1. Class
public class Employee{ // Class name
}
2. Interface
interface Printable{ //Interface name
}
3. Method
public class Employee{
public void draw(){ //Method name
}
}
4. Variable
public class Employee{
int id; //Vriable name
}
5. Package
package com.casino; //Package name
public class Employee{
}
6. Constant
public class Employee{
static final int MIN_AGE = 18; //Constant name
}