给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
进阶:
- 你可以在
O(n log n)时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序吗?
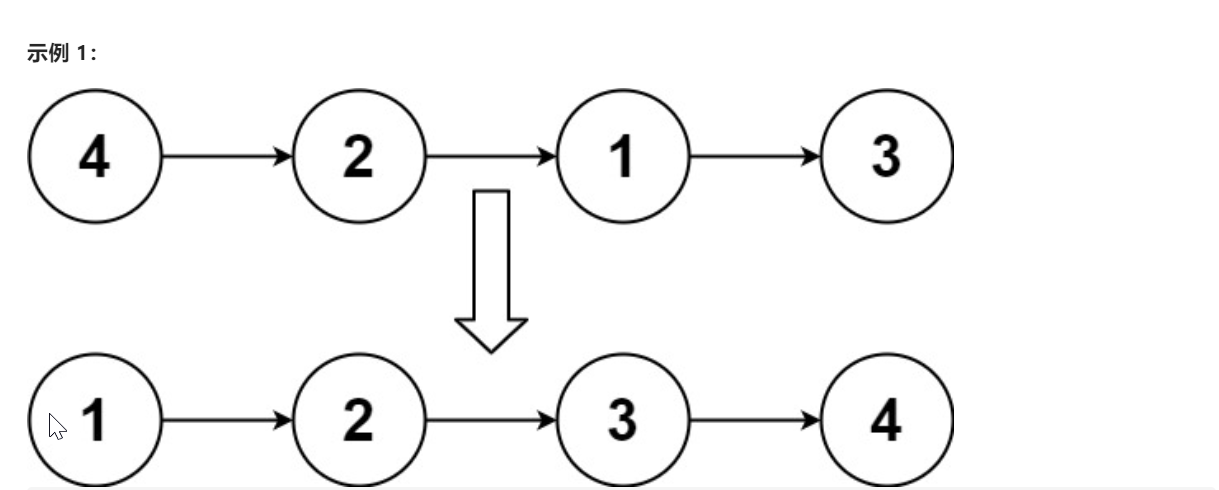
输入:head = [4,2,1,3] 输出:[1,2,3,4]
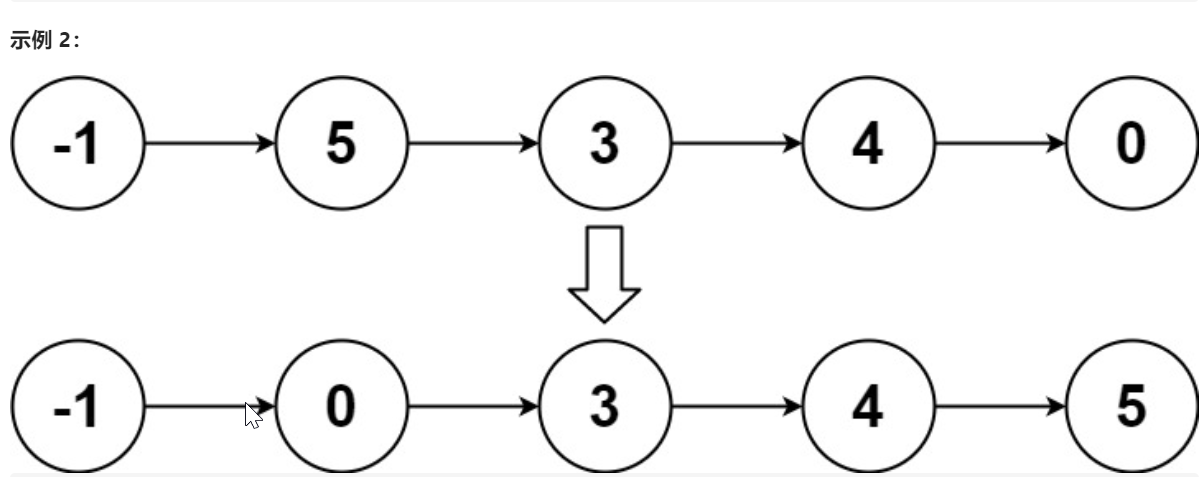
输入:head = [-1,5,3,4,0] 输出:[-1,0,3,4,5]
示例 3:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]
/* * 148. Sort List * 题意:链表排序 * 难度:Medium * 分类:Linked List, Sort * 思路:快慢指针把链表分成两半,在merge两个链表 * 快排方法自己不会写,记下思路 * 快排尝试直接以ListNode互相交换位置,节点间的指向会乱掉的,当递归子情况的时候会修改指针,父方法不知道子调用做了哪些操作 * https://www.cnblogs.com/morethink/p/8452914.html * Tips:空间复杂度不是O(1)的,但是几个高票答案都是这样写的,面试给出这样的代码应该也够了 */
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) { return head; } ListNode slow = head; //记一下 ListNode fast = head.next; while (fast != null && fast.next != null) { //把链表分成两半 slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } ListNode l2 = sortList(slow.next); slow.next = null; //别忘了这要断开 ListNode l1 = sortList(head); return mergeList(l1, l2); } public ListNode mergeList(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode res = new ListNode(0); ListNode head = res; while (l1 != null && l2 != null) { if (l1.val < l2.val) { res.next = l1; l1 = l1.next; res = res.next; } else { res.next = l2; l2 = l2.next; res = res.next; } } if (l1 != null) { res.next = l1; } if (l2 != null) { res.next = l2; } return head.next; }
public ListNode sortList2(ListNode head) { //链表快排 //采用快速排序 quickSort(head, null); return head; } public void quickSort(ListNode head, ListNode end) { if (head != end) { ListNode node = partion(head, end); quickSort(head, node); quickSort(node.next, end); } } public ListNode partion(ListNode head, ListNode end) { ListNode p1 = head, p2 = head.next; //p1指的是小于pivot的索引 //走到末尾才停 while (p2 != end) { //head到p1间是小于pivot的数,p1与p2间都是大于pivot的数 if (p2.val < head.val) { //lc922 类似的思想, 把小于的值放到该放的位置上 p1 = p1.next; int temp = p1.val; p1.val = p2.val; p2.val = temp; } p2 = p2.next; } //与pivot交换下位置 int temp = p1.val; p1.val = head.val; head.val = temp; return p1; //返回 }
调用堆排序简单
class Solution { public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if (head == null) return null; PriorityQueue<ListNode> heap = new PriorityQueue<ListNode>(new Comparator<ListNode>(){ @Override public int compare(ListNode o1, ListNode o2){ return o1.val < o2.val ? -1 : 1; } }); ListNode node = head; while(node!= null) { ListNode next = node.next; heap.add(node); node = next; } ListNode newHead = heap.poll(); ListNode current = newHead; while(!heap.isEmpty()) { ListNode p = heap.poll(); current.next = p; current =p; } current.next = null; return newHead; } }