1、map
map是python内置的高阶函数,它接收一个函数和一个列表,函数依次作用在列表的每个元素上,返回一个可迭代map对象。
class map(object): """ map(func, *iterables) --> map object Make an iterator that computes the function using arguments from each of the iterables. Stops when the shortest iterable is exhausted. """ def __getattribute__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return getattr(self, name). """ pass def __init__(self, func, *iterables): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ pass def __iter__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Implement iter(self). """ pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__ def __new__(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. """ pass def __next__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Implement next(self). """ pass def __reduce__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return state information for pickling. """ pass
用法举例 : 将列表li中的数值都加1, li = [1,2,3,4,5]
li = [1,2,3,4,5] def add1(x): return x+1 res = map(add1, li)
print(res) for i in res: print(i) 结果: <map object at 0x00000042B4E6D4E0> 2 3 4 5 6
2、lambda表达式
是一个表达式,可以创建匿名函数,冒号前是参数,冒号后只能有一个表达式(传入参数,根据参数表达出一个值)
nl = lambda x,y:x*y # 给出x,y参数,计算出x和y的相乘 print(nl(3,5)) pring(-----)
#和map的结合 li = [1,2,3,4,5] for i in map(lambda x:x*2, li): print(i) 结果: 15 ----- 2 4 6 8 10
3、Pool
1、多进程,是multiprocessing的核心,它与threading很相似,但对多核CPU的利用率会比threading好的多
2、可以允许放在Python程序内部编写的函数中,该Process对象与Thread对象的用法相同,拥有is_alive()、join([timeout])、run()、start()、terminate()等方法
3、multiprocessing包中也有Lock/Event/Semaphore/Condition类,用来同步进程
传统的执行多个函数的例子
import time def do_proc(n): # 返回平方值 time.sleep(1) return n*n if __name__ == '__main__': start = time.time() for p in range(8): print(do_proc(p)) # 循环执行8个函数 print("execute time is " ,time.time()-start) 结果: 0 1 4 9 16 25 36 49 execute time is 8.002938985824585
使用多进程执行函数
import time from multiprocessing import Pool def do_proc(n): # 返回平方值 time.sleep(n) print(n) return n*n if __name__ == '__main__': pool = Pool(3) # 池中最多只能放三个任务 start = time.time() p1 = pool.map(do_proc, range(8)) # 跟python的map用法相似(map连续生成8个任务的同时依次传给pool,pool依次调起池中的任务,执行完的任务从池中剔除) pool.close() # 关闭进程池 pool.join() # 等待所有进程(8个进程)的结束 print(p1) print("execute time is ", time.time() - start) 结果: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 [0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49] execute time is 3.3244528770446777
查看任务管理器:
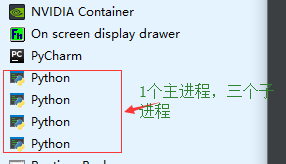
4、random
import random print(random.random()) # 生成一个0-1随机小数 print(random.uniform(10,20)) # 指定范围随机选择一个小数 print(random.randint(10,20)) # 指定范围内随机选择一个整数 print(random.randrange(0,90,2)) # 指定范围内选择一个随机偶数 print(random.choice('abcdefg')) # 指定字符串中随机选择一个字符 print(random.sample('abcdefgh'),2) # 指定字符串内随机选择2个字符 print(random.choice(['app','pear','ora'])) # 指定列表内随机选择一个值 itmes = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8] # 将列表表洗牌 random.shuffle(itmes) print(itmes)