一、题目描述:
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 class http_request{
5 public:
6 void funA(){cout << "call funA" << endl;}
7
8 void funB(){cout << "call funB" << endl;}
9
10 void funC(){num = 0;}
11
12 private:
13 int num;
14 };
15
16 int main()
17 {
18 http_request *p = nullptr;
19
20 p->funA();
21 p->funB();
22 p->funC();
23
24 return 0;
25 }
主要是定义一个类,然后使用这个类类型定义一个指针,并且将指针置为nullptr,访问类的成员函数,会出现什么情况。
看到这个空指针立马就会想到core dump,但是在机器上跑了下发现对于funA()、funB()的调用是对的,funC()的调用确实会core dump,Linux下跑的结果:

看到这个结果想不通为什么有的函数空指针可以调用,有的就不可以,看了下网上大家的解释,原来这个结果和this指针相关,对于类的成员函数,在类定义的时候地址就已经确定了,它不占用对象的空间,也就是说这个类的所有对象都使用的同一个函数,只不过是在具体的对象生成后去调用这个成员函数的时候,会默认传入一个this指针,存储着当前对象的地址,那么,拿到当前对象的地址,就可以操作当前对象的数据成员了,即对类数据成员的操作都本质上是this->数据成员。对于funA和funB因为只是输出语句,并没有操作类的数据成员,虽然在通过指针调用的时候传入了this指针,并且为nullptr,但是在成员函数funA、funB中并不操作数据成员,即没使用这个传入的空this指针,就没问题;但是对于funC,操作了类的数据成员,本质上为this->num = 0,而此时指针并没有指向具体的对象,this指针没有确切的空间,所以调用funC会发生core dump。
看了网上的解释后,突然感觉自己面试的时候想的好简单,看到空指针就觉得会core dump,知识盲点很多,很多东西要跑一跑才知道正确的结果。
二、二维数组中寻找给定值并输出下标
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<vector>
3 using namespace std;
4
5 typedef vector<pair<int, int> > result;
6
7 result FindPoint(int data[][5], int num, int width, int height)
8 {
9 result ret;
10 for (int i = 0; i < width; ++i)
11 {
12 for (int j = 0; j < height; ++j)
13 {
14 if (data[i][j] == num)
15 {
16 pair<int, int> val;
17 val.first = i;
18 val.second = j;
19 ret.push_back(val);
20 }
21 }
22 }
23 return ret;
24 }
25
26 int main()
27 {
28 const int width = 3;
29 const int height = 5;
30 int data[width][height] = {{4,7,9,3,0}, {3,6,90,22,1}, {80,56,3,3,3}};
31 #if 0
32 for (int i = 0; i < width; ++i)
33 {
34 for (int j = 0; j < height; ++j)
35 {
36 data[i][j] = i * j;
37 }
38 }
39 #endif
40
41 result ret = FindPoint(data, 3, width, height);
42 for(vector<pair<int, int> >::iterator i = ret.begin(); i < ret.end(); ++i)
43 {
44 cout << "[" << (*i).first << "," << (*i).second << "]" << endl;
45 }
46
47 return 0;
48 }
运行结果:
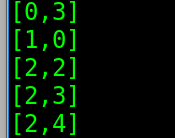
三、54张扑克牌顺序存放在vector中,乱序后输出到控制台
主要是使用STL算法中的random_shuffle()算法,可以在输入区间值的排列中任取一种,调用这个算法即可
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <vector>
3 #include <algorithm>
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 vector<int> vec;
9 for (int i = 1; i <= 54; ++i)
10 {
11 vec.push_back(i);
12 }
13 random_shuffle(vec.begin(), vec.end());
14
15 for (vector<int>::iterator i = vec.begin(); i < vec.end(); ++i)
16 {
17 cout << *i << " ";
18 }
19 cout << endl;
20
21 return 0;
22 }