You are given two arrays A and B consisting of integers, sorted in non-decreasing order. Check whether it is possible to choose k numbers in array A and choose m numbers in array B so that any number chosen in the first array is strictly less than any number chosen in the second array.
The first line contains two integers nA, nB (1 ≤ nA, nB ≤ 105), separated by a space — the sizes of arrays A and B, correspondingly.
The second line contains two integers k and m (1 ≤ k ≤ nA, 1 ≤ m ≤ nB), separated by a space.
The third line contains nA numbers a1, a2, ... anA ( - 109 ≤ a1 ≤ a2 ≤ ... ≤ anA ≤ 109), separated by spaces — elements of array A.
The fourth line contains nB integers b1, b2, ... bnB ( - 109 ≤ b1 ≤ b2 ≤ ... ≤ bnB ≤ 109), separated by spaces — elements of array B.
Print "YES" (without the quotes), if you can choose k numbers in array A and m numbers in array B so that any number chosen in array A was strictly less than any number chosen in array B. Otherwise, print "NO" (without the quotes).
3 3
2 1
1 2 3
3 4 5
YES
3 3
3 3
1 2 3
3 4 5
NO
5 2
3 1
1 1 1 1 1
2 2
YES
In the first sample test you can, for example, choose numbers 1 and 2 from array A and number 3 from array B (1 < 3 and 2 < 3).
In the second sample test the only way to choose k elements in the first array and m elements in the second one is to choose all numbers in both arrays, but then not all the numbers chosen in A will be less than all the numbers chosen in B: 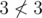 .
.
直接比较a的第k个和b的第nb-m+1个元素的大小。
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstdlib> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <iostream> 6 #include <cmath> 7 #include <queue> 8 #include <map> 9 #include <stack> 10 #include <list> 11 #include <vector> 12 #include <ctime> 13 14 using namespace std; 15 16 const int maxn = 100010; 17 18 int a[maxn]; 19 int b[maxn]; 20 int k, m; 21 int na, nb; 22 23 int main() { 24 while(~scanf("%d%d", &na, &nb)) { 25 scanf("%d%d", &k, &m); 26 for(int i = 1; i <= na; i++) { 27 scanf("%d", &a[i]); 28 } 29 for(int i = 1; i <= nb; i++) { 30 scanf("%d", &b[i]); 31 } 32 if(a[k] < b[nb-m+1]) { 33 printf("YES "); 34 } 35 else { 36 printf("NO "); 37 } 38 } 39 }