摘要:在NS3的学习中,PHY MAC中总有一些常数,需要理解才能修改。如帧间间隔等。那么,本文做个简单分析,帮助大家理解。针对802.11标准中MAC协议。
void WifiMac::Configure80211b (void) { SetSifs (MicroSeconds (10)); SetSlot (MicroSeconds (20)); SetEifsNoDifs (MicroSeconds (10 + 304)); SetPifs (MicroSeconds (10 + 20)); SetCtsTimeout (MicroSeconds (10 + 304 + 20 + GetDefaultMaxPropagationDelay ().GetMicroSeconds () * 2)); SetAckTimeout (MicroSeconds (10 + 304 + 20 + GetDefaultMaxPropagationDelay ().GetMicroSeconds () * 2)); }
304是怎么来的呢??
1、PHY
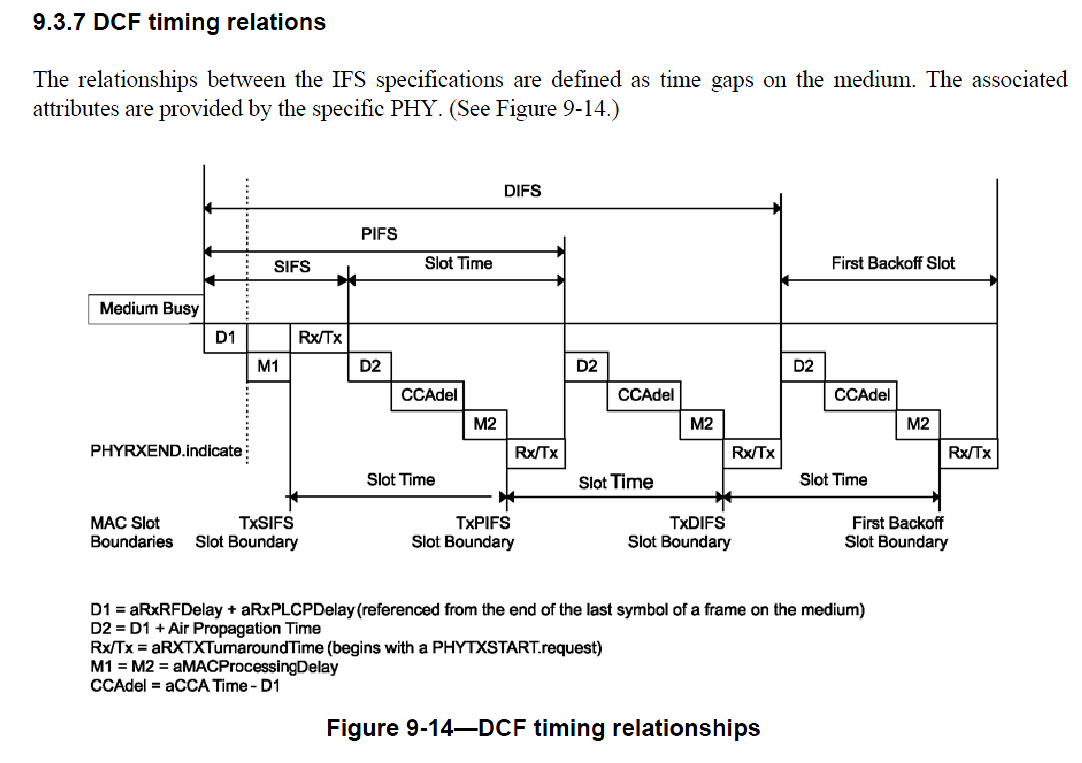
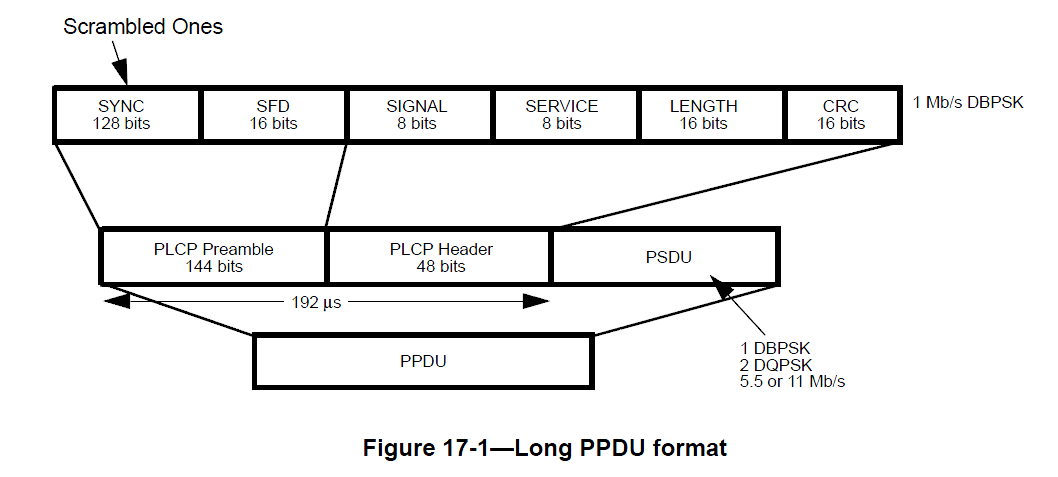
采用DSSS,1Mbps模式下。在802.11-2012中,17.2.2.3节中,有PPDU format规定了帧格式。如下图:
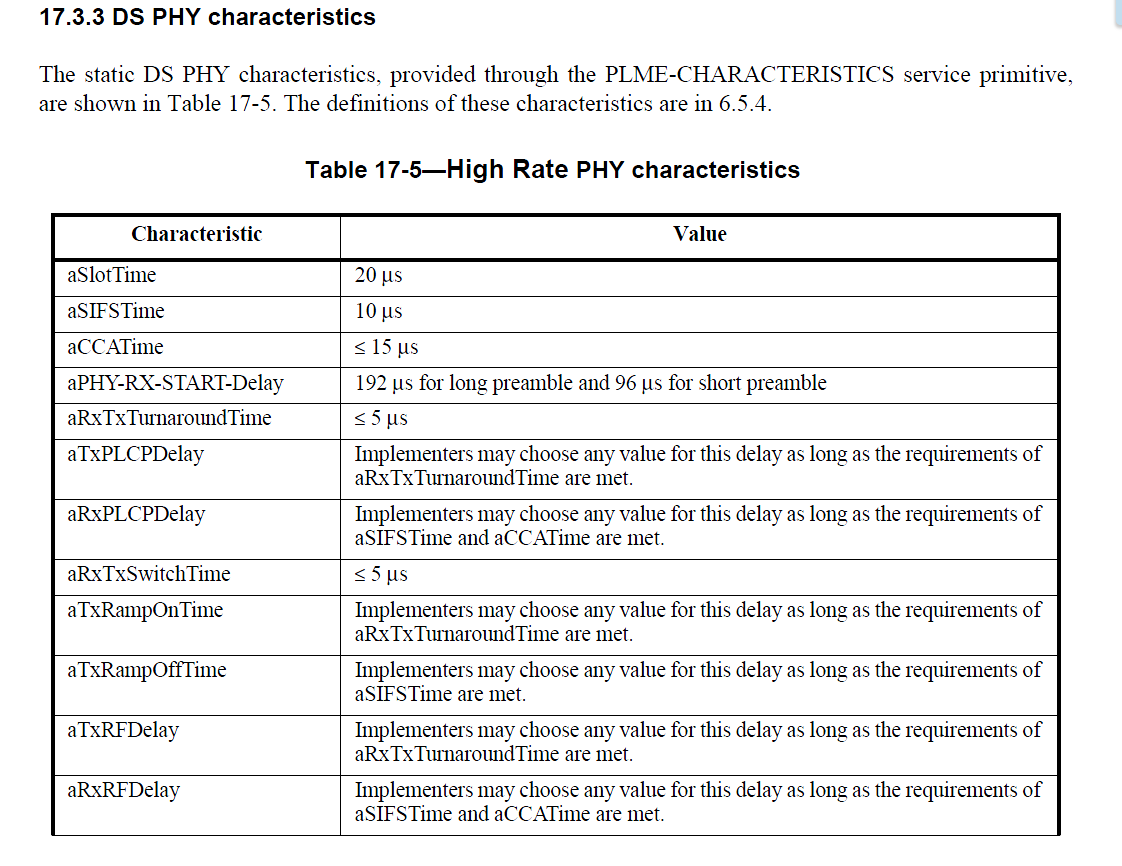
其中,大家比较关心的2个参数就是 PLCP Preamble 和 PLCP Header,分别为144bits和48bits。也就是192us,英文为192 MicroSeconds。
计算时间的相关代码,在NS3中 wifi-phy.cc中,代码如下:
uint32_t WifiPhy::GetPlcpHeaderDurationMicroSeconds (WifiMode payloadMode, WifiPreamble preamble) { switch (payloadMode.GetModulationClass ()) { case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_OFDM: { switch (payloadMode.GetBandwidth ()) { case 20000000: default: // (Section 18.3.3 "PLCP preamble (SYNC))" and Figure 18-4 "OFDM training structure"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012) // also (Section 18.3.2.4 "Timing related parameters" Table 18-5 "Timing-related parameters"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012) // We return the duration of the SIGNAL field only, since the // SERVICE field (which strictly speaking belongs to the PLCP // header, see Section 18.3.2 and Figure 18-1) is sent using the // payload mode. return 4; case 10000000: // (Section 18.3.2.4 "Timing related parameters" Table 18-5 "Timing-related parameters"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012) return 8; case 5000000: // (Section 18.3.2.4 "Timing related parameters" Table 18-5 "Timing-related parameters"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012) return 16; } } //Added by Ghada to support 11n case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_HT: { //IEEE 802.11n Figure 20.1 switch (preamble) { case WIFI_PREAMBLE_HT_MF: // L-SIG return 4; case WIFI_PREAMBLE_HT_GF: //L-SIG return 0; default: // L-SIG return 4; } } case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_ERP_OFDM: return 4; case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_DSSS: if (preamble == WIFI_PREAMBLE_SHORT) { // (Section 17.2.2.3 "Short PPDU format" and Figure 17-2 "Short PPDU format"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012) return 24; } else // WIFI_PREAMBLE_LONG { // (Section 17.2.2.2 "Long PPDU format" and Figure 17-1 "Short PPDU format"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012) return 48; } default: NS_FATAL_ERROR ("unsupported modulation class"); return 0; } } uint32_t WifiPhy::GetPlcpPreambleDurationMicroSeconds (WifiMode payloadMode, WifiPreamble preamble) { switch (payloadMode.GetModulationClass ()) { case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_OFDM: { switch (payloadMode.GetBandwidth ()) { case 20000000: default: // (Section 18.3.3 "PLCP preamble (SYNC))" Figure 18-4 "OFDM training structure" // also Section 18.3.2.3 "Modulation-dependent parameters" Table 18-4 "Modulation-dependent parameters"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012) return 16; case 10000000: // (Section 18.3.3 "PLCP preamble (SYNC))" Figure 18-4 "OFDM training structure" // also Section 18.3.2.3 "Modulation-dependent parameters" Table 18-4 "Modulation-dependent parameters"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012) return 32; case 5000000: // (Section 18.3.3 "PLCP preamble (SYNC))" Figure 18-4 "OFDM training structure" // also Section 18.3.2.3 "Modulation-dependent parameters" Table 18-4 "Modulation-dependent parameters"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012) return 64; } } case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_HT: { //IEEE 802.11n Figure 20.1 the training symbols before L_SIG or HT_SIG return 16; } case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_ERP_OFDM: return 16; case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_DSSS: if (preamble == WIFI_PREAMBLE_SHORT) { // (Section 17.2.2.3 "Short PPDU format)" Figure 17-2 "Short PPDU format"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012) return 72; } else // WIFI_PREAMBLE_LONG { // (Section 17.2.2.2 "Long PPDU format)" Figure 17-1 "Long PPDU format"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012) return 144; } default: NS_FATAL_ERROR ("unsupported modulation class"); return 0; } } double WifiPhy::GetPayloadDurationMicroSeconds (uint32_t size, WifiTxVector txvector) { WifiMode payloadMode=txvector.GetMode(); NS_LOG_FUNCTION (size << payloadMode); switch (payloadMode.GetModulationClass ()) { case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_OFDM: case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_ERP_OFDM: { // (Section 18.3.2.4 "Timing related parameters" Table 18-5 "Timing-related parameters"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012 // corresponds to T_{SYM} in the table) uint32_t symbolDurationUs; switch (payloadMode.GetBandwidth ()) { case 20000000: default: symbolDurationUs = 4; break; case 10000000: symbolDurationUs = 8; break; case 5000000: symbolDurationUs = 16; break; } // (Section 18.3.2.3 "Modulation-dependent parameters" Table 18-4 "Modulation-dependent parameters"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012) // corresponds to N_{DBPS} in the table double numDataBitsPerSymbol = payloadMode.GetDataRate () * symbolDurationUs / 1e6; // (Section 18.3.5.4 "Pad bits (PAD)" Equation 18-11; IEEE Std 802.11-2012) uint32_t numSymbols = lrint (ceil ((16 + size * 8.0 + 6.0) / numDataBitsPerSymbol)); // Add signal extension for ERP PHY if (payloadMode.GetModulationClass () == WIFI_MOD_CLASS_ERP_OFDM) { return numSymbols * symbolDurationUs + 6; } else { return numSymbols * symbolDurationUs; } } case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_HT: { double symbolDurationUs; double m_Stbc; //if short GI data rate is used then symbol duration is 3.6us else symbol duration is 4us //In the future has to create a stationmanager that only uses these data rates if sender and reciever support GI if (payloadMode.GetUniqueName() == "OfdmRate135MbpsBW40MHzShGi" || payloadMode.GetUniqueName() == "OfdmRate65MbpsBW20MHzShGi" ) { symbolDurationUs=3.6; } else { switch (payloadMode.GetDataRate ()/ (txvector.GetNss())) { //shortGi case 7200000: case 14400000: case 21700000: case 28900000: case 43300000: case 57800000: case 72200000: case 15000000: case 30000000: case 45000000: case 60000000: case 90000000: case 120000000: case 150000000: symbolDurationUs=3.6; break; default: symbolDurationUs=4; } } if (txvector.IsStbc()) m_Stbc=2; else m_Stbc=1; double numDataBitsPerSymbol = payloadMode.GetDataRate () *txvector.GetNss() * symbolDurationUs / 1e6; //check tables 20-35 and 20-36 in the standard to get cases when nes =2 double Nes=1; // IEEE Std 802.11n, section 20.3.11, equation (20-32) uint32_t numSymbols = lrint (m_Stbc*ceil ((16 + size * 8.0 + 6.0*Nes) / (m_Stbc* numDataBitsPerSymbol))); return numSymbols * symbolDurationUs; } case WIFI_MOD_CLASS_DSSS: // (Section 17.2.3.6 "Long PLCP LENGTH field"; IEEE Std 802.11-2012) NS_LOG_LOGIC (" size=" << size << " mode=" << payloadMode << " rate=" << payloadMode.GetDataRate () ); return lrint (ceil ((size * 8.0) / (payloadMode.GetDataRate () / 1.0e6))); default: NS_FATAL_ERROR ("unsupported modulation class"); return 0; } } Time WifiPhy::CalculateTxDuration (uint32_t size, WifiTxVector txvector, WifiPreamble preamble) { WifiMode payloadMode=txvector.GetMode(); double duration = GetPlcpPreambleDurationMicroSeconds (payloadMode, preamble) + GetPlcpHeaderDurationMicroSeconds (payloadMode, preamble) + GetPlcpHtSigHeaderDurationMicroSeconds (payloadMode, preamble) + GetPlcpHtTrainingSymbolDurationMicroSeconds (payloadMode, preamble,txvector) + GetPayloadDurationMicroSeconds (size, txvector); return MicroSeconds (duration); }
在函数CalculateTxDuration中,duration的计算方法。
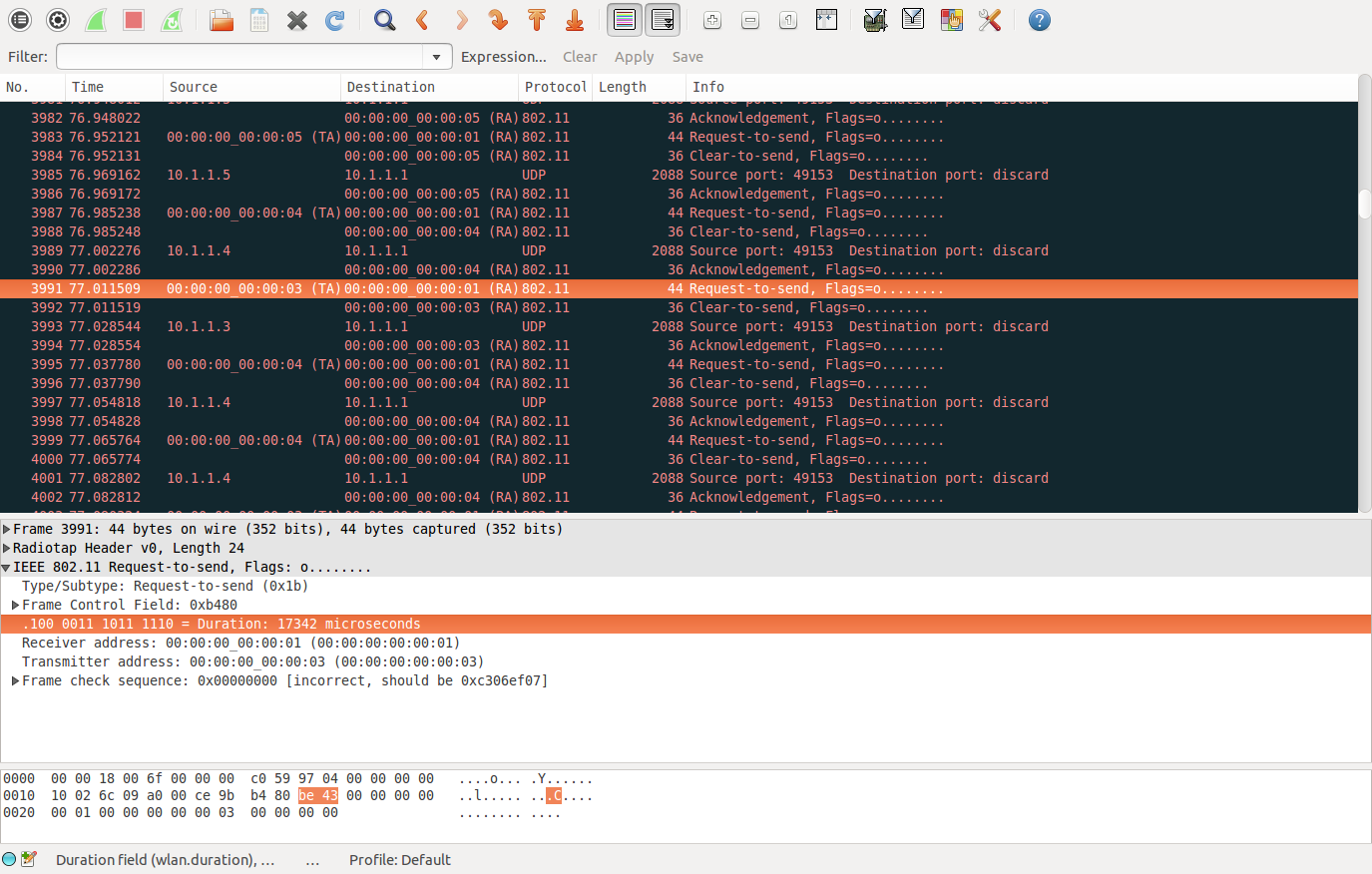
那么,假如你开启4次握手机制,那么rts的duration如何计算呢?
也就是当你生成pacp文件,用wiresharp打开时,看到rts帧中,那个duration是怎么得到的呢?
如下图中17342 是怎么得到的呢?
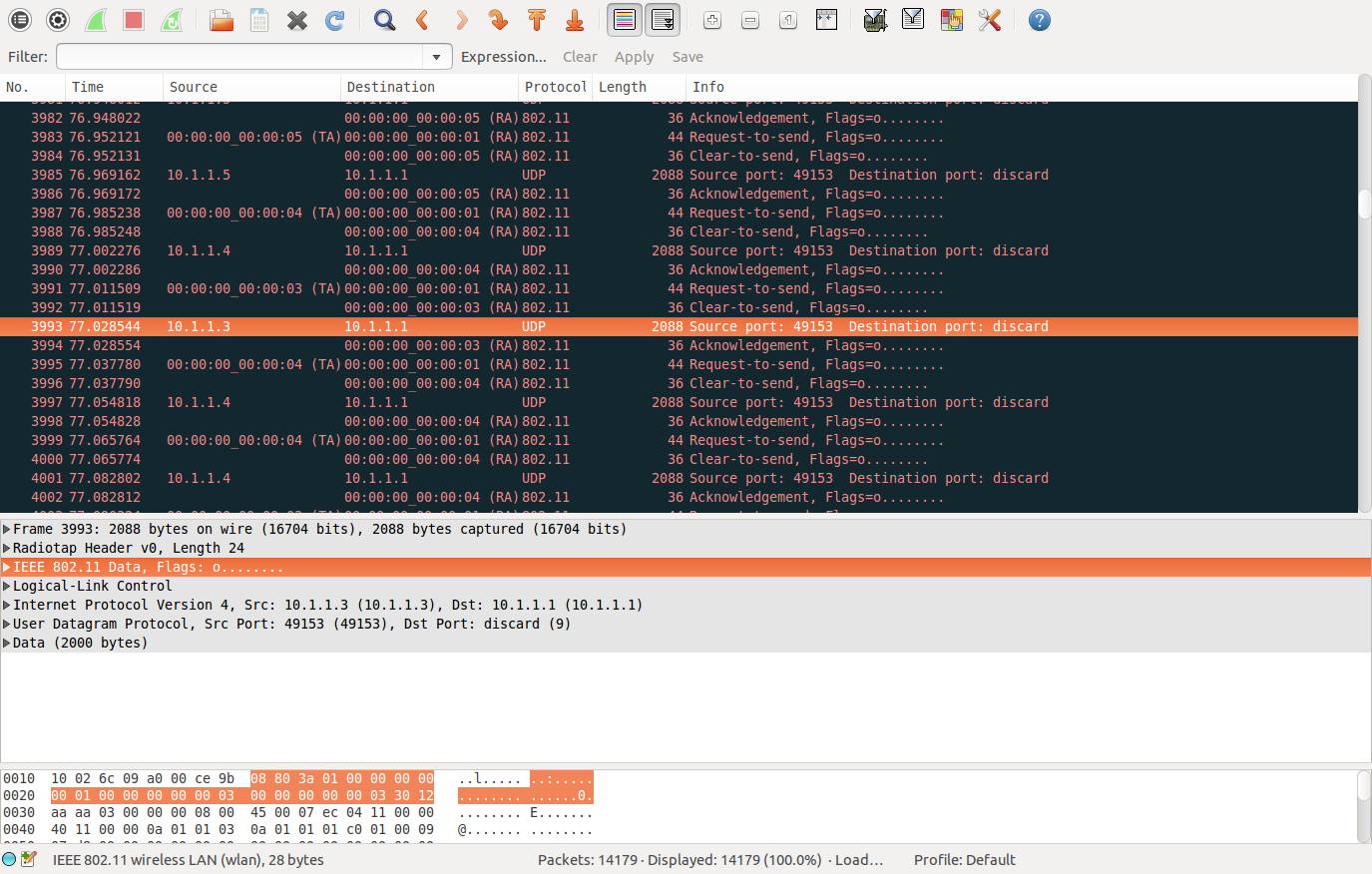
你需要知道应用层的包是如何封装的,这涉及到计算机网络的知识。这里以上面的包大小举例说明,packet =2000bytes.
上图中可以看到:data—>udp(8)—>ip(20)—>llc(8)—>mac (28)包封装过程
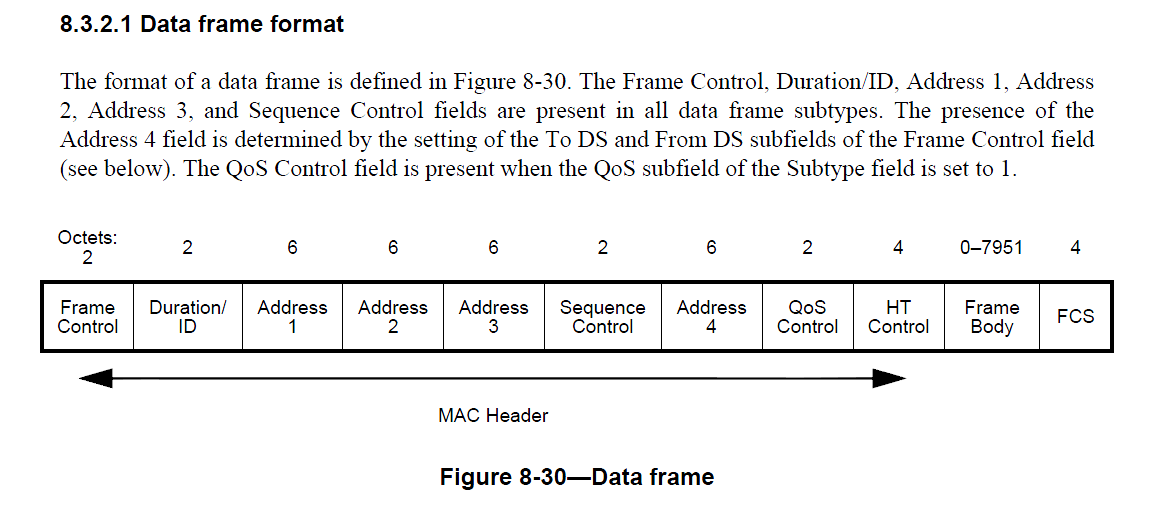
ip和udp封装包头大小,一般计算机网络书中有介绍。llc 这个没搞懂为啥是8个。mac数据帧可以看下图:
一共40字节,但是地址4,qos,ht不用。ns3中使用的是non qos mac。
好了,我们开始计算,但是还需要看一个代码在mac-low.cc:
void MacLow::SendRtsForPacket (void) { NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this); /* send an RTS for this packet. */ WifiMacHeader rts; rts.SetType (WIFI_MAC_CTL_RTS); rts.SetDsNotFrom (); rts.SetDsNotTo (); rts.SetNoRetry (); rts.SetNoMoreFragments (); rts.SetAddr1 (m_currentHdr.GetAddr1 ()); rts.SetAddr2 (m_self); WifiTxVector rtsTxVector = GetRtsTxVector (m_currentPacket, &m_currentHdr); Time duration = Seconds (0); WifiPreamble preamble; //standard says RTS packets can have GF format sec 9.6.0e.1 page 110 bullet b 2 if ( m_phy->GetGreenfield()&& m_stationManager->GetGreenfieldSupported (m_currentHdr.GetAddr1 ())) preamble= WIFI_PREAMBLE_HT_GF; else if (rtsTxVector.GetMode().GetModulationClass () == WIFI_MOD_CLASS_HT) preamble= WIFI_PREAMBLE_HT_MF; else preamble=WIFI_PREAMBLE_LONG; if (m_txParams.HasDurationId ()) { duration += m_txParams.GetDurationId (); } else { WifiTxVector dataTxVector = GetDataTxVector (m_currentPacket, &m_currentHdr); duration += GetSifs (); duration += GetCtsDuration (m_currentHdr.GetAddr1 (), rtsTxVector); duration += GetSifs (); duration += m_phy->CalculateTxDuration (GetSize (m_currentPacket, &m_currentHdr), dataTxVector, preamble); duration += GetSifs (); duration += GetAckDuration (m_currentHdr.GetAddr1 (), dataTxVector); } rts.SetDuration (duration); Time txDuration = m_phy->CalculateTxDuration (GetRtsSize (), rtsTxVector, preamble); Time timerDelay = txDuration + GetCtsTimeout (); NS_ASSERT (m_ctsTimeoutEvent.IsExpired ()); NotifyCtsTimeoutStartNow (timerDelay); m_ctsTimeoutEvent = Simulator::Schedule (timerDelay, &MacLow::CtsTimeout, this); Ptr<Packet> packet = Create<Packet> (); packet->AddHeader (rts); WifiMacTrailer fcs; packet->AddTrailer (fcs); ForwardDown (packet, &rts, rtsTxVector,preamble); }
公式就是上面这个代码中提取出来的。sifs查这个802.11-2012中上图
duration += GetSifs (); 10
duration += GetCtsDuration (m_currentHdr.GetAddr1 (), rtsTxVector); cts:14*8+192=304
duration += GetSifs (); 10
duration += m_phy->CalculateTxDuration (GetSize (m_currentPacket, &m_currentHdr), dataTxVector, preamble); 2064*8+192=16704
duration += GetSifs ();10
duration += GetAckDuration (m_currentHdr.GetAddr1 (), dataTxVector); ack:14*8+192=304
duration = 10+304+10+16704+10+304=17342
结果符合wiresharp中那个duration。