记一下java流处理的操作
1.去重,按照billTypeCode去重
list = list.stream().collect(
Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toCollection(
() -> new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparing(o -> o.getBillTypeCode()))), ArrayList::new));
排序:
List<DictValue> sortedDictValues = dictValues.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(DictValue::getOrderNum))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
2.求和
Double sum = workDoc.getItemList().stream().mapToDouble(e -> e.getAllocatedQuantity().doubleValue()).reduce(0, Double::sum);
Integer ageSum = persons .stream() .reduce(0, (sum, p) -> sum += p.age, (sum1, sum2) -> sum1 + sum2);
3.遍历赋值
list.stream().forEach(e -> e.setStatus("30"));
4.过滤
List<ItemInfo> itemone = new ArrayList<>(itemInfos);
itemone = itemone.stream().filter(o -> matnr.equals(o.getItemCode())).collect(Collectors.toList());
5.map: stream().map()可以让你转化一个对象成其他的对象
List<String> lineList = itemCodeNoExistList.stream().map(ShopOrderExcelDto::getLine).collect(Collectors.toList());
6.把list转化为map,key是id,value是实体,如果存在重复的key,取第一个实体
Map<Integer, Person> mapp = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getId, Function.identity(),(k1, k2) -> k1));
7.取值去重
List<String> targetFactoryCode = targetLocationList.stream().map(Location::getFactoryCode).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
8.分组,对于list中的对象按照名字分组,返回一个map<String,List>
Map<String,List<Person>> m = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(l->l.getName()));

9.分组,返回一个Map<Boolean,List>,如果分组了,就是list的size>1,则是true,否则是false
Map<Boolean,List<Person>> m = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(p->p.getName().equals("haha")));

10.groupingBy()提供第二个参数,表示downstream,即对分组后的value作进一步的处理,返回map<String,Set>
Map<String,Set<Person>> m = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(l->l.getName(),Collectors.toSet()));

11.分组,返回value集合中元素的数量
Map<String,Long> m = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(l->l.getName(),Collectors.counting()));
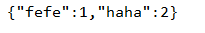
12.分组,对value集合中元素求和
Map<String,Integer> m = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(l->l.getName(),Collectors.summingInt(Person::getId)));

13.分组,并取value集合中某个元素最大的实体,在这里先按照name分组,然后取id最大的的实体,注意value是Optional的
Map<String,Optional<Person>> m = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(l->l.getName(),Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Person::getId))));

14.分组,并通过mapping对value字段进行处理
Map<String,Set<Integer>> m = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(l->l.getName(),Collectors.mapping(Person::getId,Collectors.toSet())));
15.对于list集合的空指针问题java8的处理方式:如果list不为空,那就赋值给newList,否则重新new一个list
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = null;
List<String> newList = Optional.ofNullable(list).orElse(Lists.newArrayList());
newList.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x));
}
16.循环
IntStream.range(1, 4) .forEach(System.out::println); // 相当于 for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) {} // 1 // 2 // 3
17.原始类型聚合操作
reduce方法接受标识值和BinaryOperator累加器。此方法可用于构造一个新的 Person,其中包含来自流中所有其他人的聚合名称和年龄:reduce方法接受三个参数:标识值,BiFunction累加器和类型的组合器函数BinaryOperator。由于初始值的类型不一定为Person,我们可以使用这个归约函数来计算所有人的年龄总和:CollectionUtils.subList:截取list