Bash scripting techniques
BASH SCRIPTING I/O
-
I/O - File vs. terminal vs. network
-
Input from a terminal
read -p "Enter your name:" name; echo "Hi," $name -
Input from a file
input="filePathNaMme"while IFS=read -r f1 f2 f3 f4 -
Input from the network
while read -r inline < /dev/ttyS1
-
ERROR HANDLING
-
Error handling
-
"$?" is the exit status of a script we just ran
if ["$?"="0"] then
-
ARRAYS
bashArray = (val1, val2, val3)
OR
declare -a bashArray = (val1, val2, val3)
for i in 1 2 3
do
echo ${bashArray[$i]}
done
ENCODING/DECODING
-
locale - shows local related environment variables
-
Can change assignment of LANG for local character encoding
- Allows bash to accept special characters (i.e. LANG=da_DK.UTF-8)
-
Can use openssl or base64 to encode and decode strings(base64)
Encoding:
echo string | base64OR
base64 <<< stringDecoding:
echo string | base64 --decodeOR
base64 -d <<< string
BASH: PUTTING IT ALL TOGEHTER
-
Port scanner in bash
#!/bin/bash target=$1 minPort=$2 maxPort=$3 function scanports { for ((counter=$minPort; counter<=$maxPort; counter++)) do (echo >/dev/tcp/$target/$counter) > /dev/null 2>&1 && echo "$counter open" done } scanports -
Run the follow command on Kali Linux
bash portscan.sh 10.0.0.7 21 80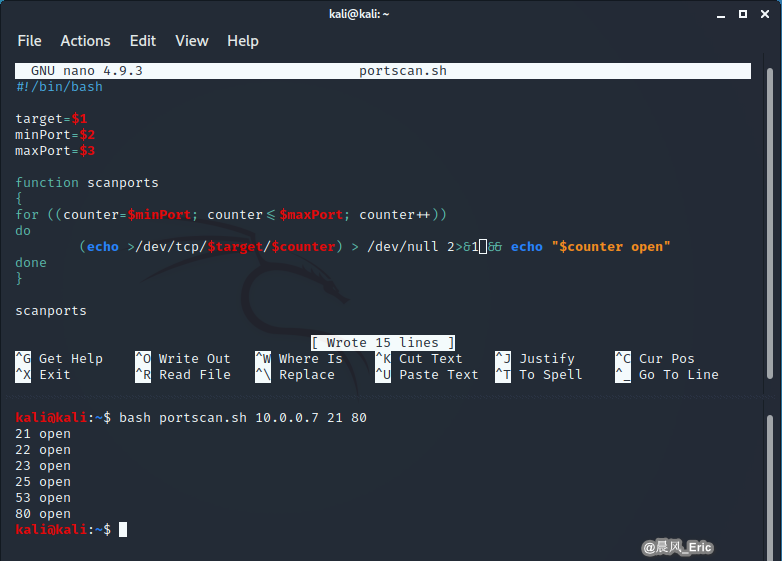
QUICK REVIEW
- Redirecting input from stdin and output to stdout is the most common bash I/O technique
- Bash scripts can be used with Linux pipes
- Arrays can be useful, but aren't supported in older shells (make sure you're running bash and not sh)