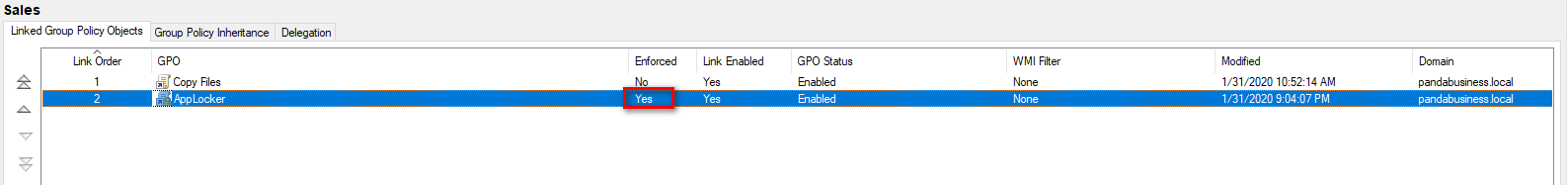
AppLocker can help you:
- Define rules based on file attributes that persist across app updates, such as the publisher name (derived from the digital signature), product name, file name, and file version. You can also create rules based on the file path and hash.
- Assign a rule to a security group or an individual user.
- Create exceptions to rules. For example, you can create a rule that allows all users to run all Windows binaries, except the Registry Editor (regedit.exe).
- Use audit-only mode to deploy the policy and understand its impact before enforcing it.
- Create rules on a staging server, test them, then export them to your production environment and import them into a Group Policy Object.
- Simplify creating and managing AppLocker rules by using Windows PowerShell.
Set the AppLocker Properties to Enforce rules:

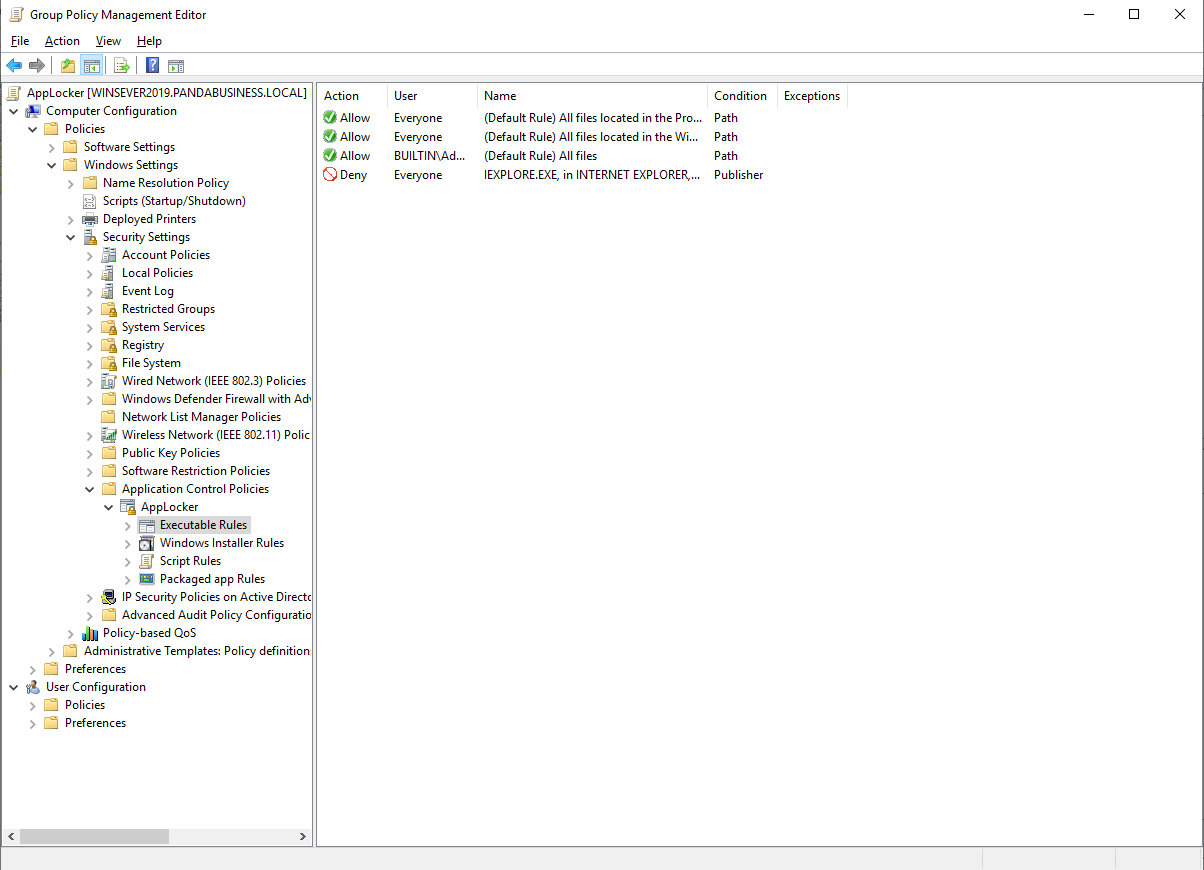
Create default rules for each item:
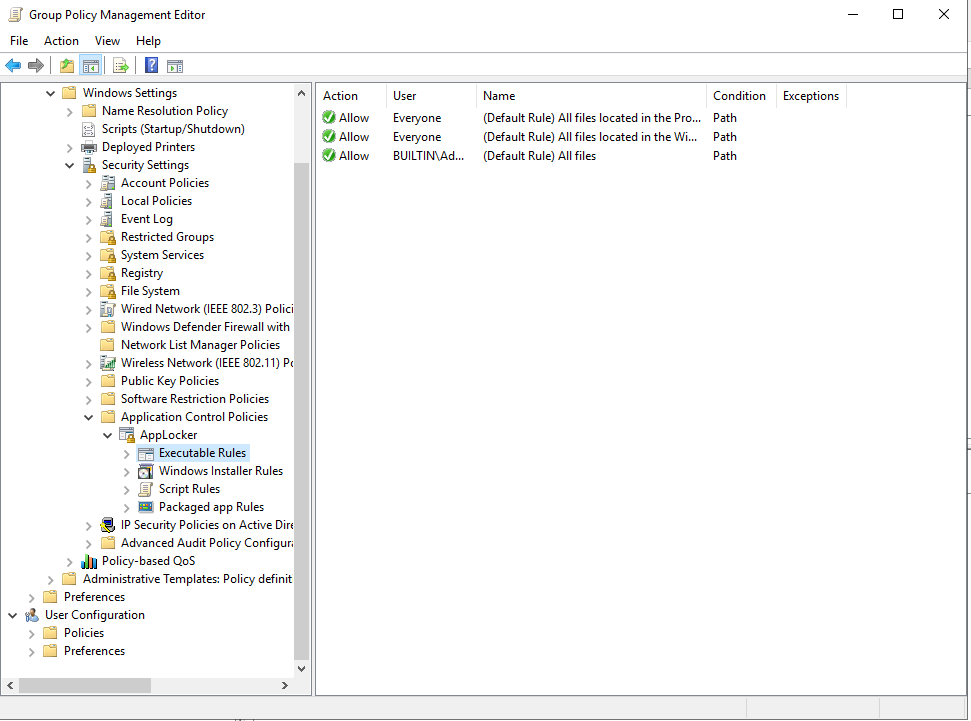
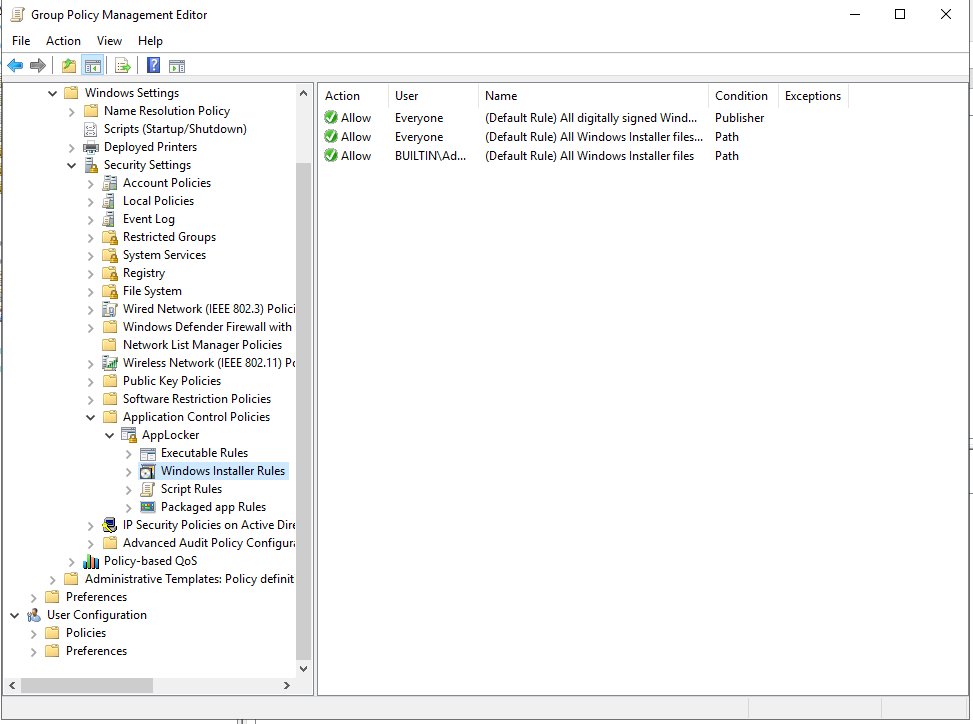
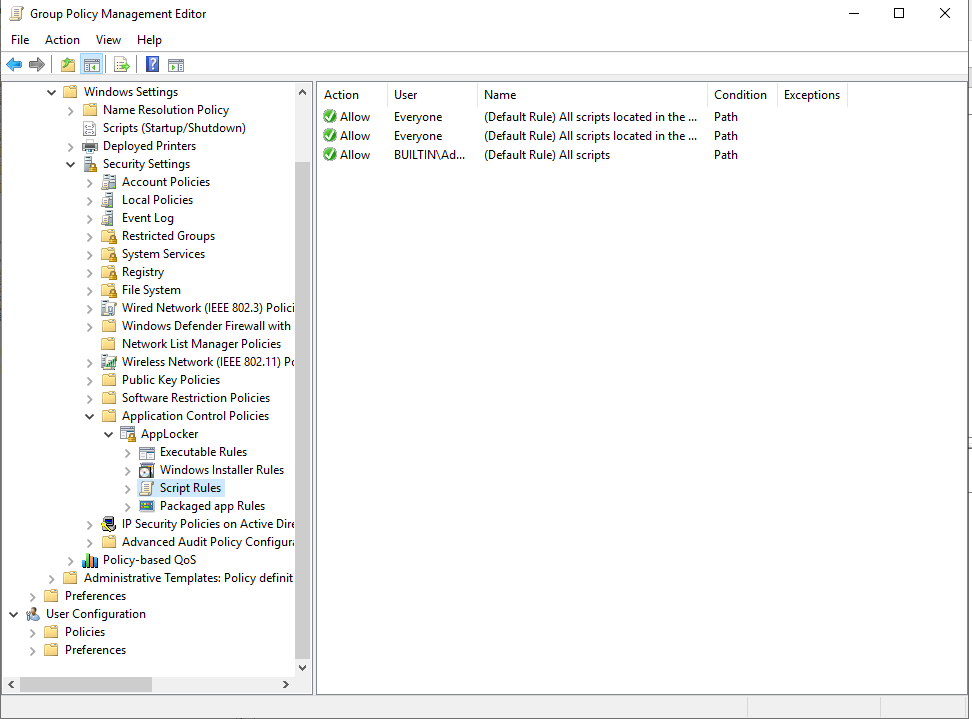
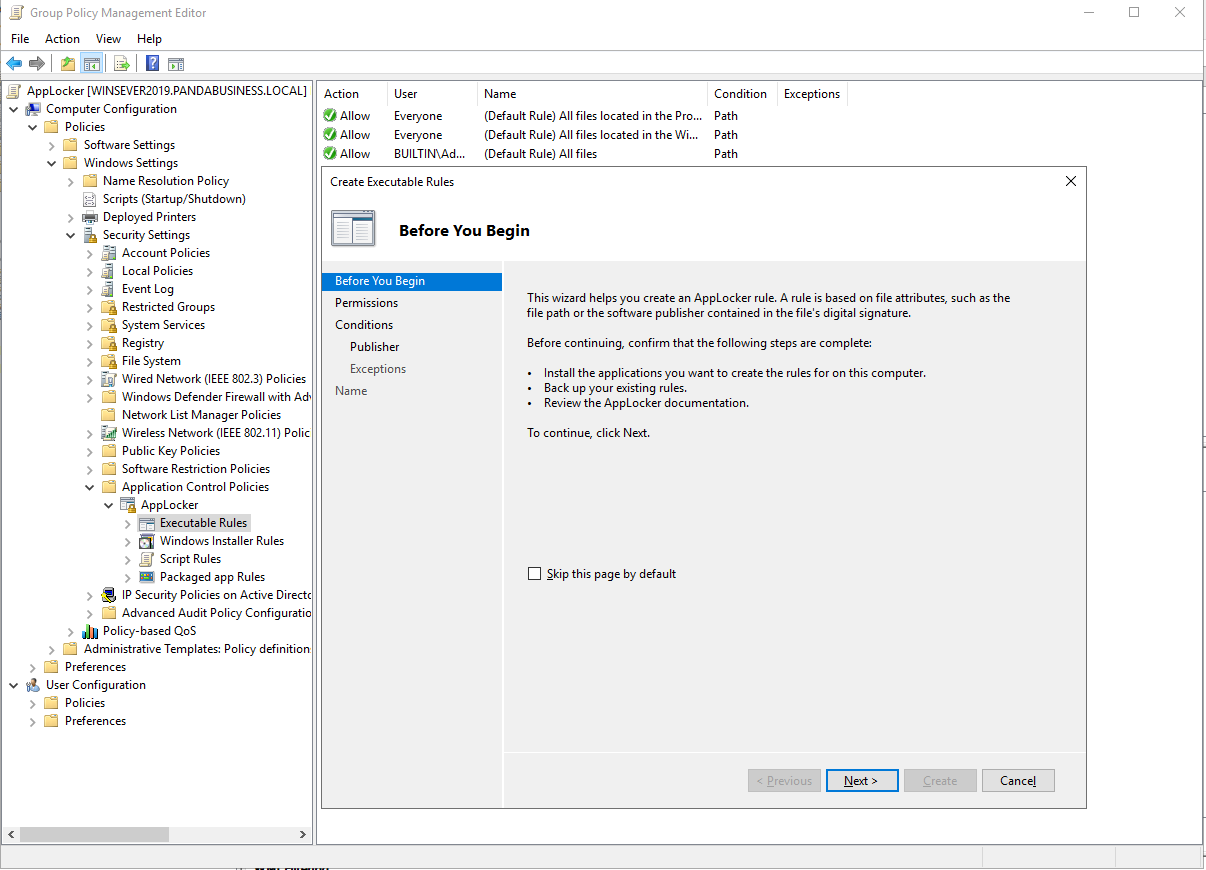
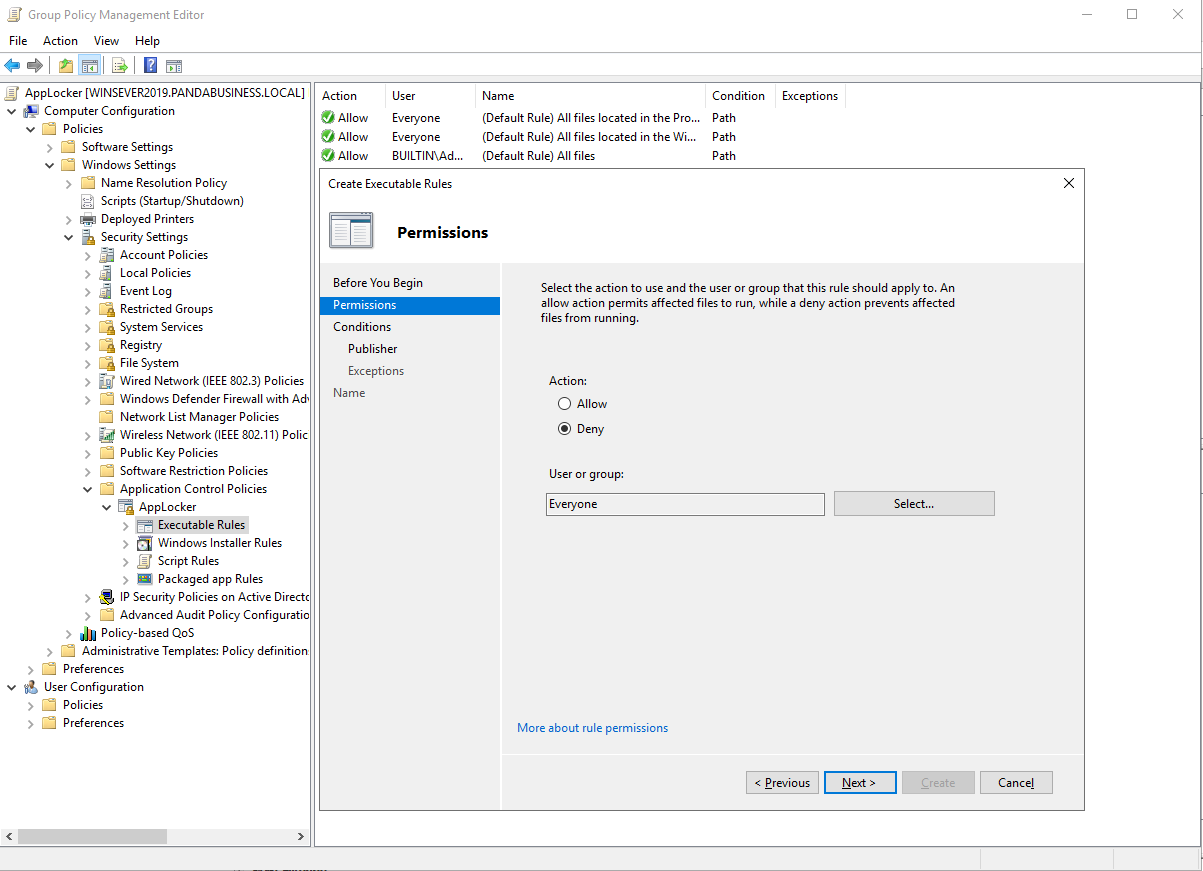
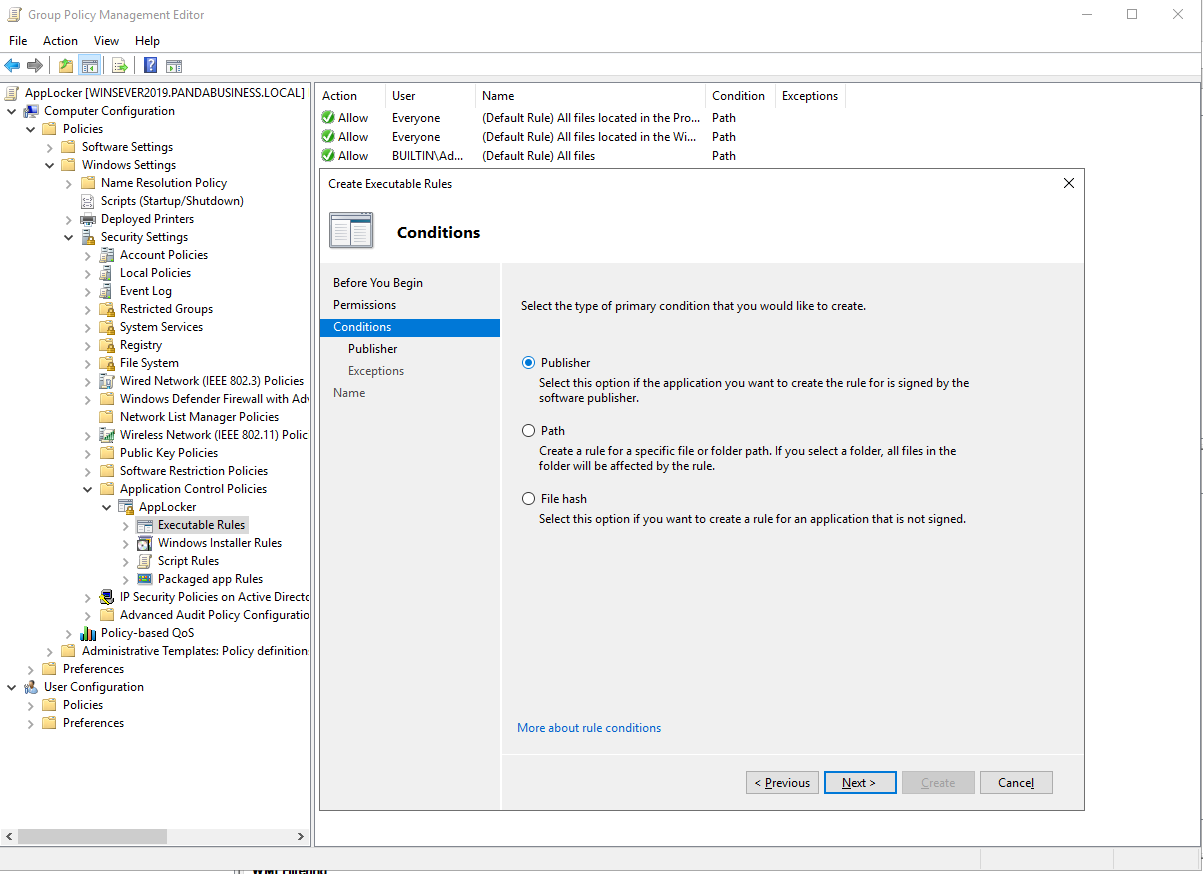
Create Executable Rules for Specific application.

Set the Application Identity Properties to Automatic Module.

Enable enforced module.