E. A and B and Lecture Rooms
time limit per test2 seconds
memory limit per test256 megabytes
inputstandard input
outputstandard output
A and B are preparing themselves for programming contests.
The University where A and B study is a set of rooms connected by corridors. Overall, the University has n rooms connected by n - 1 corridors so that you can get from any room to any other one by moving along the corridors. The rooms are numbered from 1 to n.
Every day А and B write contests in some rooms of their university, and after each contest they gather together in the same room and discuss problems. A and B want the distance from the rooms where problems are discussed to the rooms where contests are written to be equal. The distance between two rooms is the number of edges on the shortest path between them.
As they write contests in new rooms every day, they asked you to help them find the number of possible rooms to discuss problems for each of the following m days.
Input
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the number of rooms in the University.
The next n - 1 lines describe the corridors. The i-th of these lines (1 ≤ i ≤ n - 1) contains two integers ai and bi (1 ≤ ai, bi ≤ n), showing that the i-th corridor connects rooms ai and bi.
The next line contains integer m (1 ≤ m ≤ 105) — the number of queries.
Next m lines describe the queries. The j-th of these lines (1 ≤ j ≤ m) contains two integers xj and yj (1 ≤ xj, yj ≤ n) that means that on the j-th day A will write the contest in the room xj, B will write in the room yj.
Output
In the i-th (1 ≤ i ≤ m) line print the number of rooms that are equidistant from the rooms where A and B write contest on the i-th day.
Examples
inputCopy
4
1 2
1 3
2 4
1
2 3
output
1
inputCopy
4
1 2
2 3
2 4
2
1 2
1 3
output
0
2
Note
in the first sample there is only one room at the same distance from rooms number 2 and 3 — room number 1.
【题解】
假设要求两个点为x,y且(d[y]>=d[x])
求出两个点的最近公共祖先z,那么有两种情况
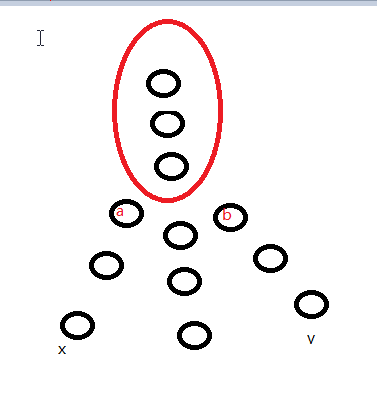
1.当(d[x]=d[y])那么就是(n-size[z]+size[z]-size[a]-size[b])如图(1)
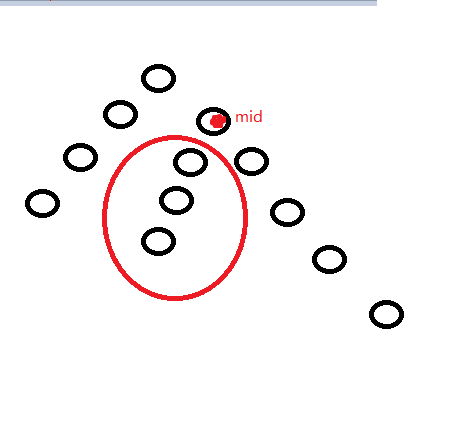
2.当(d[x]!=d[y])那么就是(size[mid]-size[y])如图(2)
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
const int SIZE=510000;
int ver[SIZE*2],nxt[SIZE*2],head[SIZE],en=0,size[SIZE],d[SIZE]= {0},f[SIZE][20],t;
inline void AddEdge(int from,int to) {
ver[++en]=to,nxt[en]=head[from],head[from]=en;
}
void dfs(int x,int fa) {
size[x]=1;
d[x]=d[fa]+1;
for(int i=head[x]; i; i=nxt[i]) {
int y=ver[i];
if(d[y])continue;
f[y][0]=x;
for(int j=1; j<=t; j++)f[y][j]=f[f[y][j-1]][j-1];
dfs(y,x);
size[x]+=size[y];
}
}
int LCA(int x,int y) {
if(d[x]>d[y])swap(x,y);
for(int i=t; i>=0; i--)
if(d[f[y][i]]>=d[x])
y=f[y][i];
if(x==y)return x;
for(int i=t; i>=0; i--)
if(f[y][i]!=f[x][i])
y=f[y][i],x=f[x][i];
return f[x][0];
}
int climb(int x,int y) {
int t=0;
while(y) {
if(y&1)x=f[x][t];
y>>=1;
t++;
}
return x;
}
int main() {
int n,x,y,m;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1; i<n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
AddEdge(x,y);
AddEdge(y,x);
}
t=(int)(log(n)/log(2))+1;
dfs(1,0);
scanf("%d",&m);
for(int i=1; i<=m; i++) {
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
int z=LCA(x,y);
int k=d[x]+d[y]-2*d[z];
if(k&1)puts("0");
else if(x==y)printf("%d
",n);
else if(d[x]==d[y]) {
int R=climb(y,(k>>1)-1);
int L=climb(x,(k>>1)-1);
printf("%d
",n-size[z]+size[z]-size[L]-size[R]);
} else {
if(d[x]>d[y])swap(x,y);
int v=climb(y,k>>1);
int u=climb(y,(k>>1)-1);
printf("%d
",size[v]-size[u]);
}
}
return 0;
}