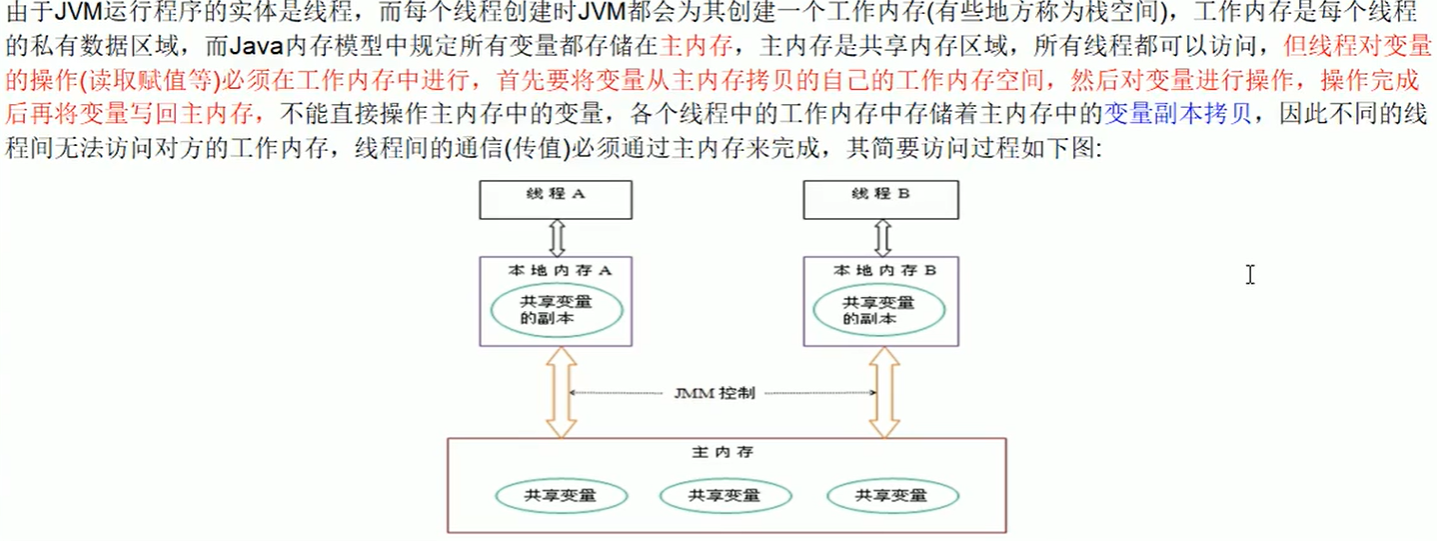
一、volatile
volatile是java虚拟机提供的轻量级的同步机制;
三大特性:保证可见性,不保证原子性,禁止指令重排
JMM(Java内存模型)-->(三大特性:可见性,原子性,有序性)
- 可见性

验证可见性代码
//volatile可以保证可见性,及时通知其他线程,主物理内存的值已经被修改
protected static void seeOKByVolatile() {
MyData myData = new MyData();
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " come in");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
myData.addTO60();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " updated number value:" + myData.number);
},"AAA").start();
//第二个线程就是我们main线程
while(myData.number == 0) {
//main线程一直在这里等待循环,直到number值不在等于0
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " mission is over,main get number value:" + myData.number);
}
- 不保证原子性
class MyData{
volatile int number = 0;
public void addTO60(){
this.number = 60;
}
//number ++在多线程环境下是非线程安全的
public void addPlusPlus() {
number ++;
}
//默认是0
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();
public void addMyAtomic() {
atomicInteger.getAndIncrement();
}
}
/**
* 1验证volatile的可见性
* 1.1,假如int number = 0;number变量之前根本没有添加volatile关键字修饰,没有可见性
* 1.2,添加了volatile,可以解决可见性问题
* 2验证volatile不保证原子性
* 2.1,原子性指的是不可分割,完整性,也即某个线程正在做某个具体业务时,中间不可以被加塞或者被分割,需要整体完整。
* 要么同时成功,要么同时失败。
* 2.2,volatile不保证原子性的案例演示
* 2.3,why
* 2.4,如何解决原子性?
* *加Synchronized
* *使用我们juc下的atomicInteger
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class VolatileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// seeOKByVolatile();
MyData myData = new MyData();
for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
new Thread(() ->{
for (int j = 1; j <= 1000; j++) {
myData.addPlusPlus();
myData.addMyAtomic();
}
},"线程" + i).start();
}
//需要等待上面20个线程都全部计算完成后,再用main线程取得最终的结果
while(Thread.activeCount() > 2) {
Thread.yield();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " int type, finally number value:" + myData.number);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " AtomicInteger type, finally number value:" + myData.atomicInteger);
}
}
- 禁止指令重排

public class ReSortSeqDemo {
int a = 0;
boolean flag = false;
public void method1() {
a = 1;
flag = true;
}
public void method2() {
if(flag) {
a = a + 5;
System.out.println("a的值是:"+ a);
}
}
}
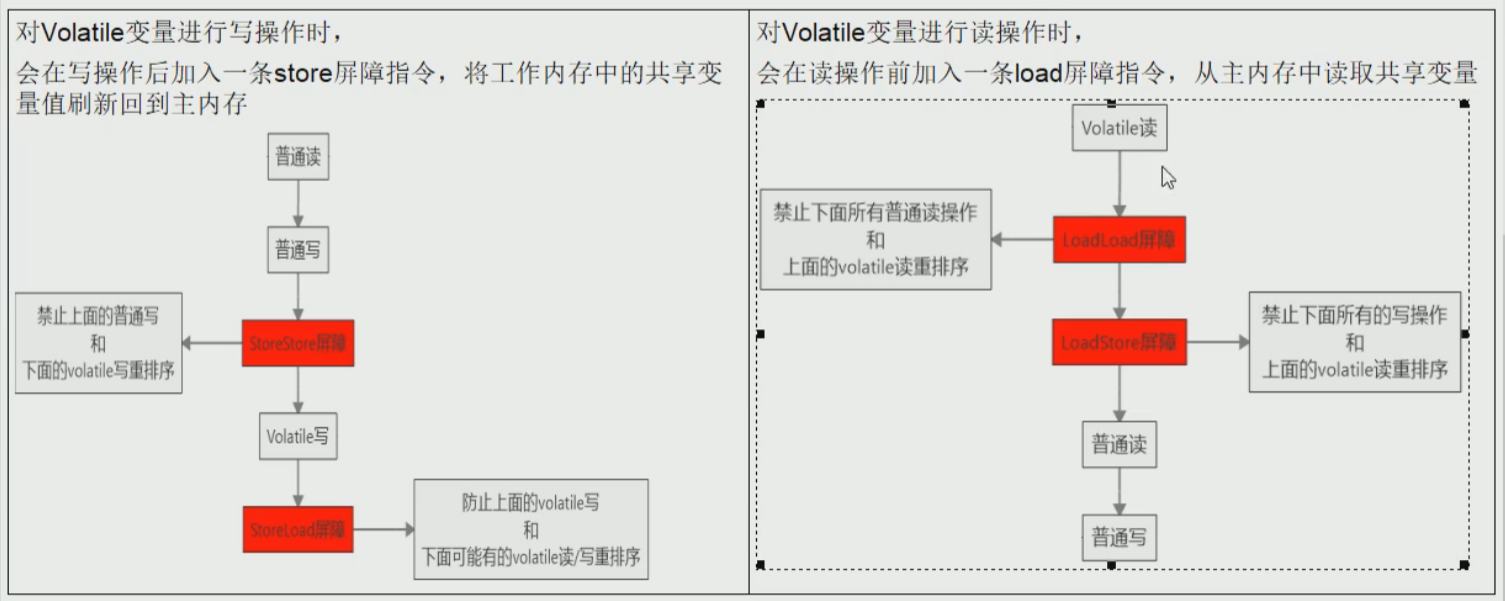
同时开启多个线程执行method1和method2,可能method1中的flag=true先执行,然后就执行method2,那么a此时就是5,之后才执行a=1,这就是指令重排了,那么为了禁止指令重排,为了防止flag=true先执行,那么就用volatile修饰。
禁止指令重排小结




二、多线程下的单例模式


public class SingletonDemo {
private volatile static SingletonDemo instance = null;
private SingletonDemo() {
System.out.println("构造器被调用");
}
public static SingletonDemo getInstance() {
if(instance == null) {
synchronized (SingletonDemo.class) {
if(instance == null) {
instance = new SingletonDemo();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
三、CAS(CompareAndSet)比较并交换
public class CASDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(5);
System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(5, 2021) + " current data:" + atomicInteger.get());
System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(5, 2021) + " current data:" + atomicInteger.get());
}
}
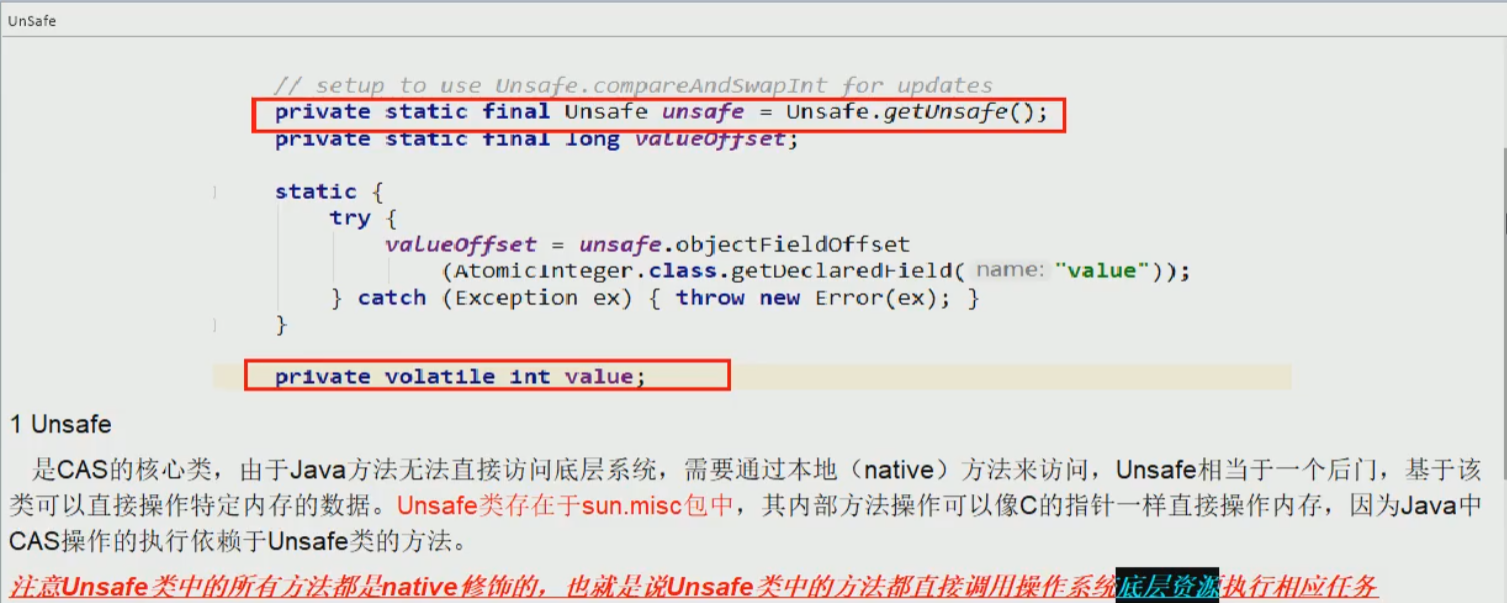
底层原理(unsafe的理解)unsafe位于rt.jar/sun/misc/unsafe.class---自旋

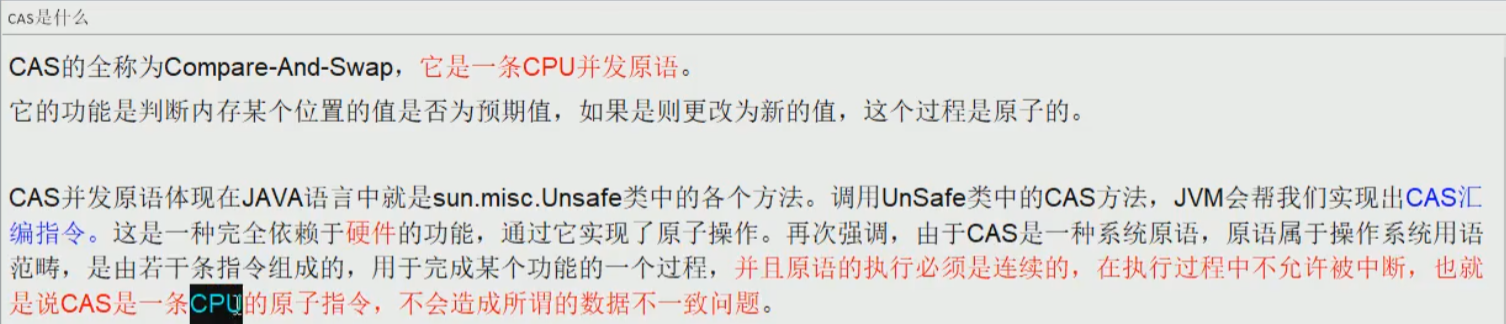
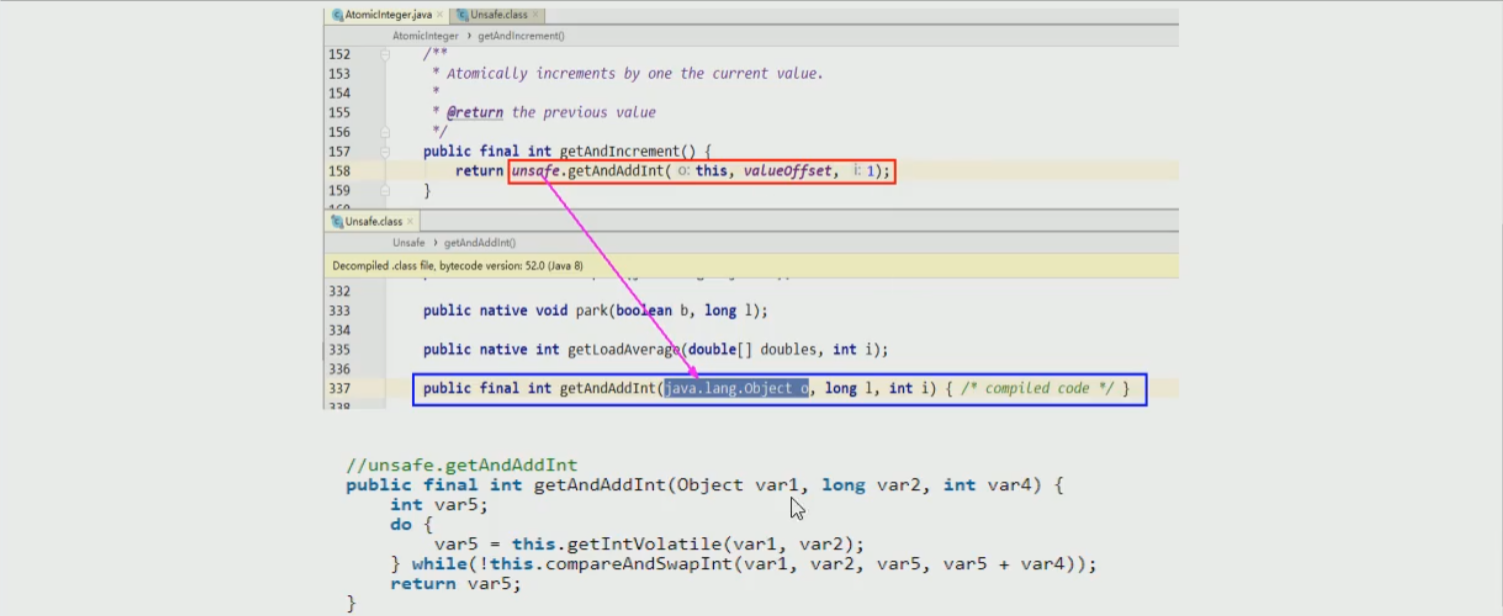

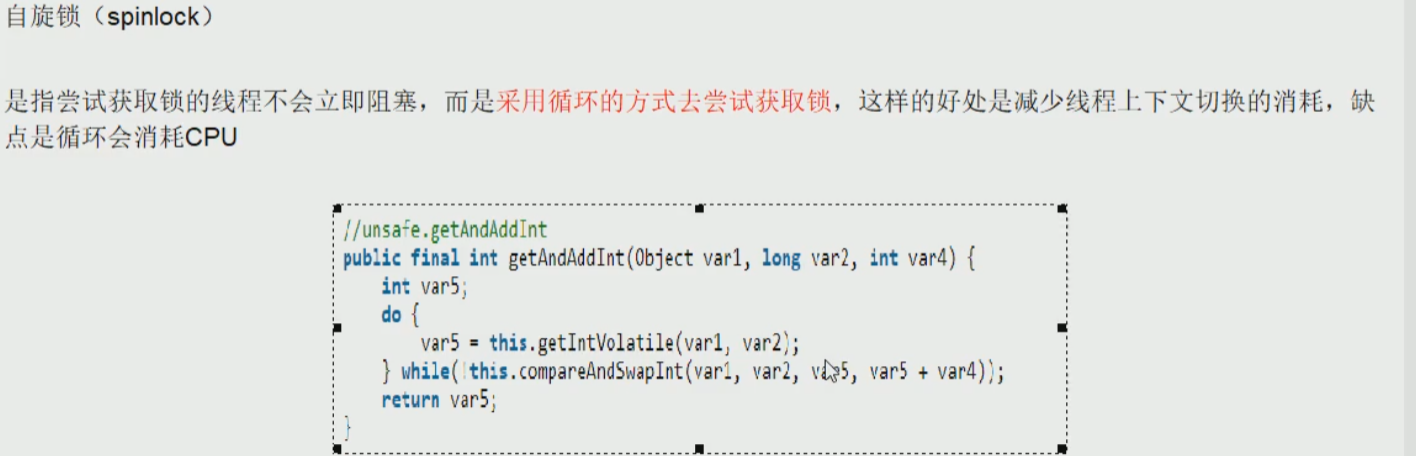
- 调用getAndIncrement(),实则是调用getAndAddInt(),然后打开该方法的源码;
- 首先是通过getIntVolatile()取得主内存的值var5,然后调用compareAndSwapInt()方法,意思就是比较当前对象var1和内存地址偏移量var2下的值和var5做比较,如果相等,那么执行var5+var4,否则的话,继续循环;直到相等为止,退出循环。
- 退出循环的条件是this.compareAndSwapInt()方法返回true(也是值相等,而且已经var5+var4加完了),然后取反,则退出do-while循环。

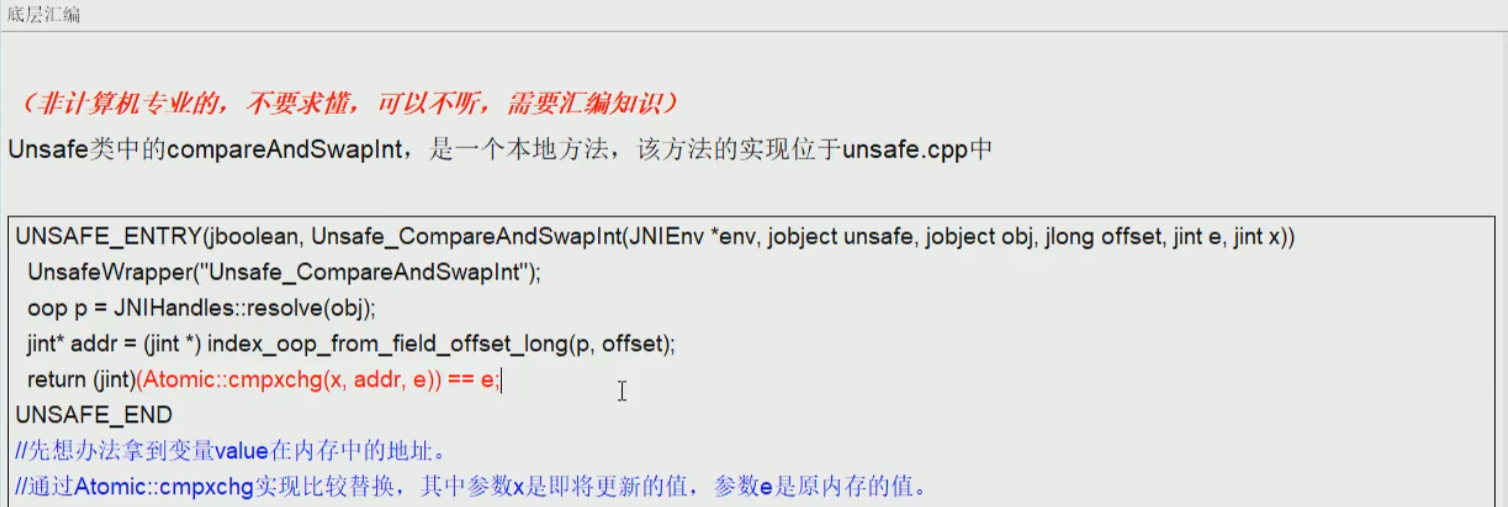

cas缺点
- 1.循环时间长,开销大

- 2.只能保证一个共享变量的原子操作

- 3.可能产生ABA问题

原子引用Demo
public class AtomicReferenceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user1 = new User("张三",13);
User user2 = new User("李四",13);
AtomicReference<User> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<User>();
atomicReference.set(user1);
System.out.println(atomicReference.compareAndSet(user1, user2) + " " + atomicReference.get().toString());
System.out.println(atomicReference.compareAndSet(user1, user2) + " " + atomicReference.get().toString());
}
}
class User{
String username;
int age;
//省略get,set,tostring
}
ABA问题的解决
public class ABADemo {
static AtomicReference<Integer> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<Integer>(100);
static AtomicStampedReference<Integer> atomicStampedReference = new AtomicStampedReference<Integer>(100, 1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("==========以下是ABA问题的产生===========");
new Thread(()->{
atomicReference.compareAndSet(100, 101);
atomicReference.compareAndSet(101, 100);
},"T1").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {//暂停1秒钟t2线程,保证t1线程完成一次ABA
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(atomicReference.compareAndSet(100, 2021) + " " + atomicReference.get());
},"T2").start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("==========以下是ABA问题的解决===========");
new Thread(()->{
int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 第一次版本号:" + stamp);
try {
//暂停1秒钟t3线程,保证t3和t4线程同时拿到1这个版本号
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(100, 101, atomicStampedReference.getStamp(), atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 第二次版本号:" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(101, 100, atomicStampedReference.getStamp(), atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 第三次版本号:" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
},"T3").start();
new Thread(()->{
int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 第一次版本号:" + stamp);
try {
//暂停3秒钟t4线程,保证上面的t3线程完成了一次ABA操作
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
boolean result = atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(100, 2021, stamp, stamp + 1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 修改成功否:" + result + "当前最终实际版本号:" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 当前实际最新值" + atomicStampedReference.getReference());
},"T4").start();
}
}
四、集合类不安全问题
故障现象
- 目前用了三个线程,还没有报错。
public class ContainerNotSafeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
list.add(new Random().nextInt(100));
System.out.println(list);
},"线程" + i).start();
}
}
}
- 当用了30个线程的时候,就会报错了(ConcurrentModificationException)
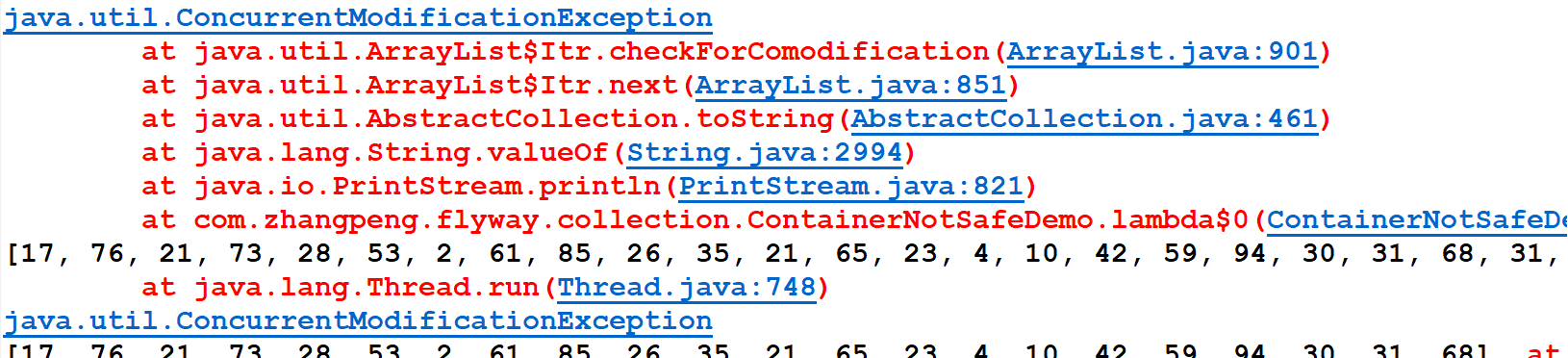
导致原因
并发争抢导致修改失败,参考我们的花名册签名情况;
一个人正在写入,另外一个同学过来争抢,导致数据不一致异常,并发修改异常。
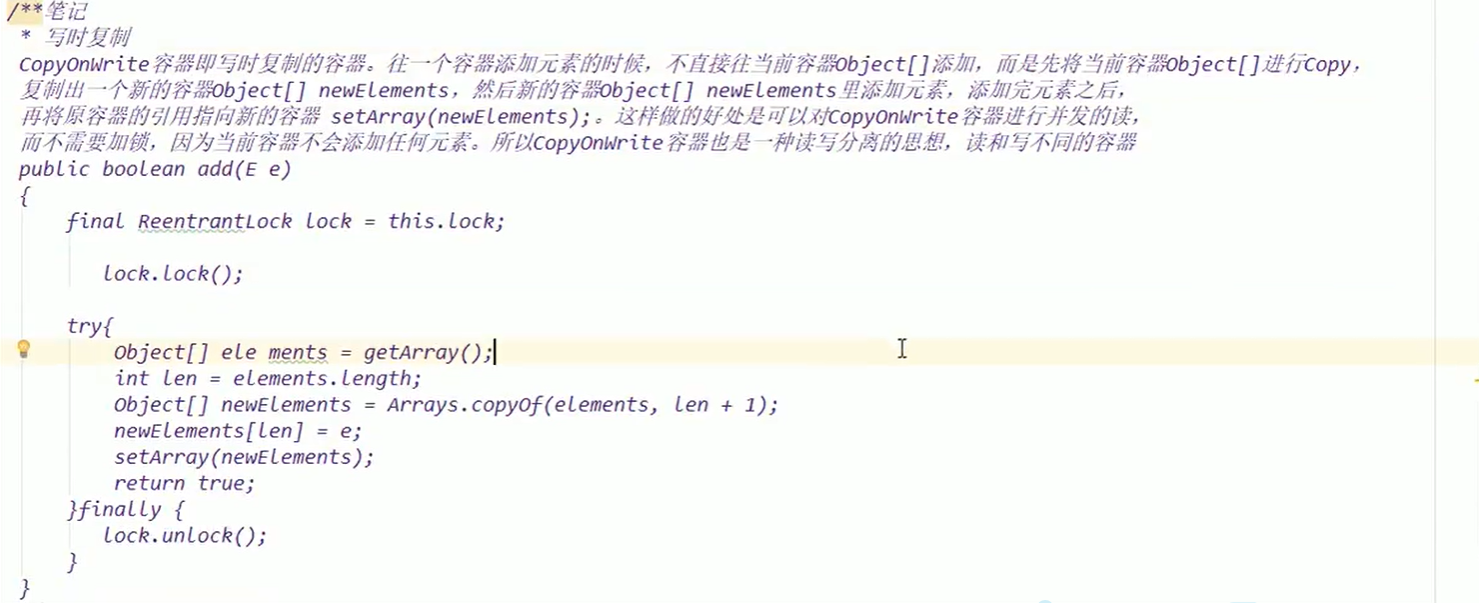
解决方案
针对List集合
- new Vector
()可以解决; - Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList
())可以解决; - new CopyOnWriteArrayList
()可以解决;
针对Set集合
- Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet
())可以解决; - new CopyOnWriteArraySet
()可以解决,底层依然是CopyOnWriteArrayList;
针对Map集合
- Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<String,String>())可以解决;
- new ConcurrentHashMap<String, String>()可以解决;
五、锁
公平锁与非公平锁
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();默认非公平锁

- 区别


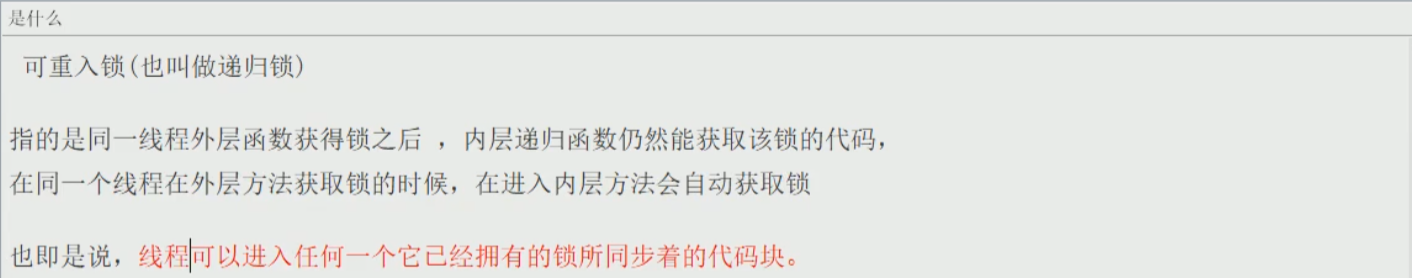
可重入锁(递归锁)
- 介绍
可重入锁最大的作用是避免死锁。
ReentrantLock和synchronized就是一个典型的可重入锁 - 代码
class Phone implements Runnable{
public synchronized void sendSMS() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " invoked sendSMS()");
sendEmail();
}
public synchronized void sendEmail() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " invoked sendEmail()");
}
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
get();
}
public void get() {
//lock.lock();加几次锁,就需要减一次锁(lock.unlock())
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " invoked get()");
set();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void set() {
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " invoked set()");
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
/**
* case1-->synchronized是典型的可重入锁;
* ********控制台输出************
* T1 invoked sendSMS()
* T1 invoked sendEmail()
* T2 invoked sendSMS()
* T2 invoked sendEmail()
* ********************
* case2-->ReentrantLock是典型的可重入锁;
* ********控制台输出************
* T4 invoked get()
* T4 invoked set()
* T3 invoked get()
* T3 invoked set()
*
*/
public class ReentrantLockDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone phone = new Phone();
new Thread(() -> {
phone.sendSMS();
},"T1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
phone.sendSMS();
},"T2").start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
Thread t3 = new Thread(phone,"T3");
Thread t4 = new Thread(phone,"T4");
t3.start();
t4.start();
}
}
自旋锁
- 介绍
- 代码(自己实现自旋锁)
/**
* TODO 实现一个自旋锁
* 自旋锁好处:循环比较获取直到成功为止,没有类似wait的阻塞;
*
* 通过CAS操作完成自旋锁,A线程先进来调用myLock方法自己持有锁5秒钟,B随后进来发现
* 当前有线程持有锁,不是null,所以只能通过自旋等待,直到A释放锁后B随后抢到。
*
* @author kakaluote
* @date 2021年6月29日 上午9:29:43
*/
public class SpinLockDemo {
AtomicReference<Thread> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<Thread>();
public void myLock(){
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(thread.getName() + " come in");
//如果设置值成功,那么退出while
while(!atomicReference.compareAndSet(null, thread)){
}
}
public void myUnLock(){
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
atomicReference.compareAndSet(thread, null);
System.out.println(thread.getName() + " invoked myUnLock()");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpinLockDemo spinLockDemo = new SpinLockDemo();
new Thread(() -> {
spinLockDemo.myLock();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
spinLockDemo.myUnLock();
},"T1").start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(() -> {
spinLockDemo.myLock();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
spinLockDemo.myUnLock();
},"T2").start();
}
}

输出解释:
T1先执行,1s后T2执行,但是T1已经执行完compareAndSet,已经成功设置值为thread,t2只能阻塞,然后T1执行5s之后,t1执行unlock,设置值为null,退出,然后t2就执行compareAndSet,1s之后,t2执行完。
独占锁(写锁)/共享锁(读锁)/互斥锁
- 介绍

- 代码
/**
* TODO 读读可以共存,读写,写读不能共存
*
* @author kakaluote 写操作:原子加独占,整个过程必须是一个完整的统一体,中间不许被分割,被打断。
* @date 2021年6月29日 下午2:13:38
*/
public class ReadWriteLockDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyCache myCache = new MyCache();
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
final int tem = i;
new Thread(() -> {
myCache.put(tem + "", tem + "");
},"线程" + i).start();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
final int tem = i;
new Thread(() -> {
myCache.get(tem + "");
},"线程" + i).start();
}
}
}
class MyCache{
private volatile Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
private ReentrantReadWriteLock rwLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
//写操作独占,不可中断
public void put(String key,Object value){
rwLock.writeLock().lock();
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 正在写入:" + key);
try {
//模拟网络拥堵
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
map.put(key, value);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 写入完成:");
}catch(Exception e){
}finally{
rwLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
public void get(String key){
rwLock.readLock().lock();
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 正在读取:");
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
Object result = map.get(key);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 读取完成:" + result);
}catch(Exception e){
}finally{
rwLock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
}
输出结果:
线程3 正在写入:3
线程3 写入完成:
线程2 正在写入:2
线程2 写入完成:
线程1 正在写入:1
线程1 写入完成:
线程4 正在写入:4
线程4 写入完成:
线程5 正在写入:5
线程5 写入完成:
线程2 正在读取:
线程1 正在读取:
线程3 正在读取:
线程5 正在读取:
线程4 正在读取:
线程3 读取完成:3
线程4 读取完成:4
线程2 读取完成:2
线程1 读取完成:1
线程5 读取完成:5