特点
栈——先进后出
队列——后进先出
思路
1. 快速得到最大值的栈
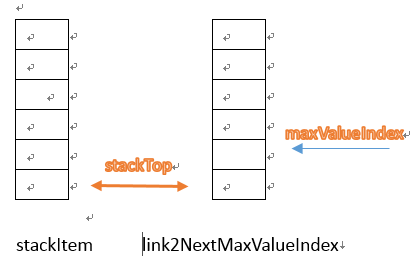
结构
- 需要两个数组:一个数组stackItem保存栈的元素,另一个数组link2NextMaxValueIndex保存下一个最大值的位置
- 两个指针:一个为stackTop指向栈顶,另一个为maxValueIndex指向最大值的下标
操作
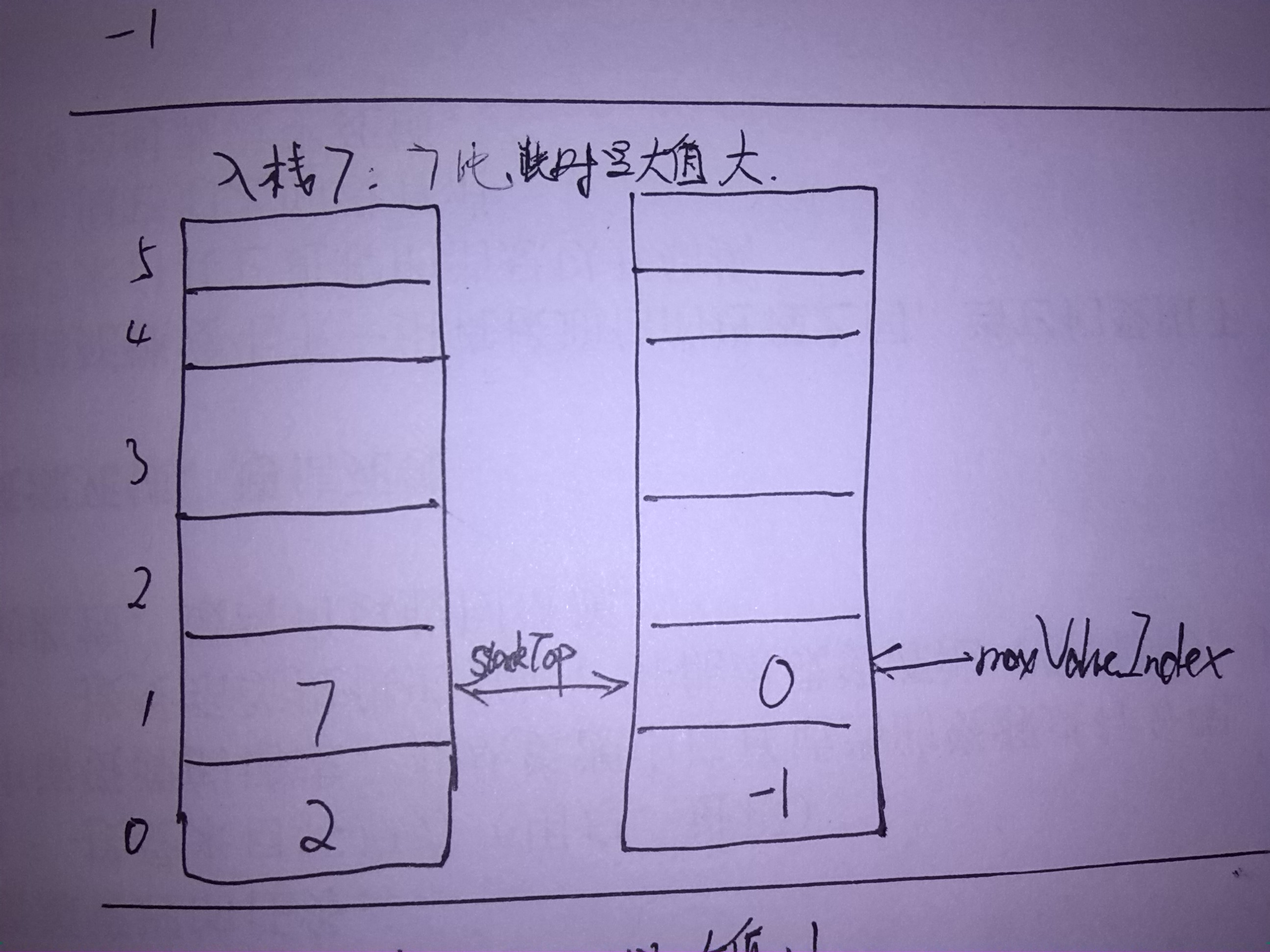
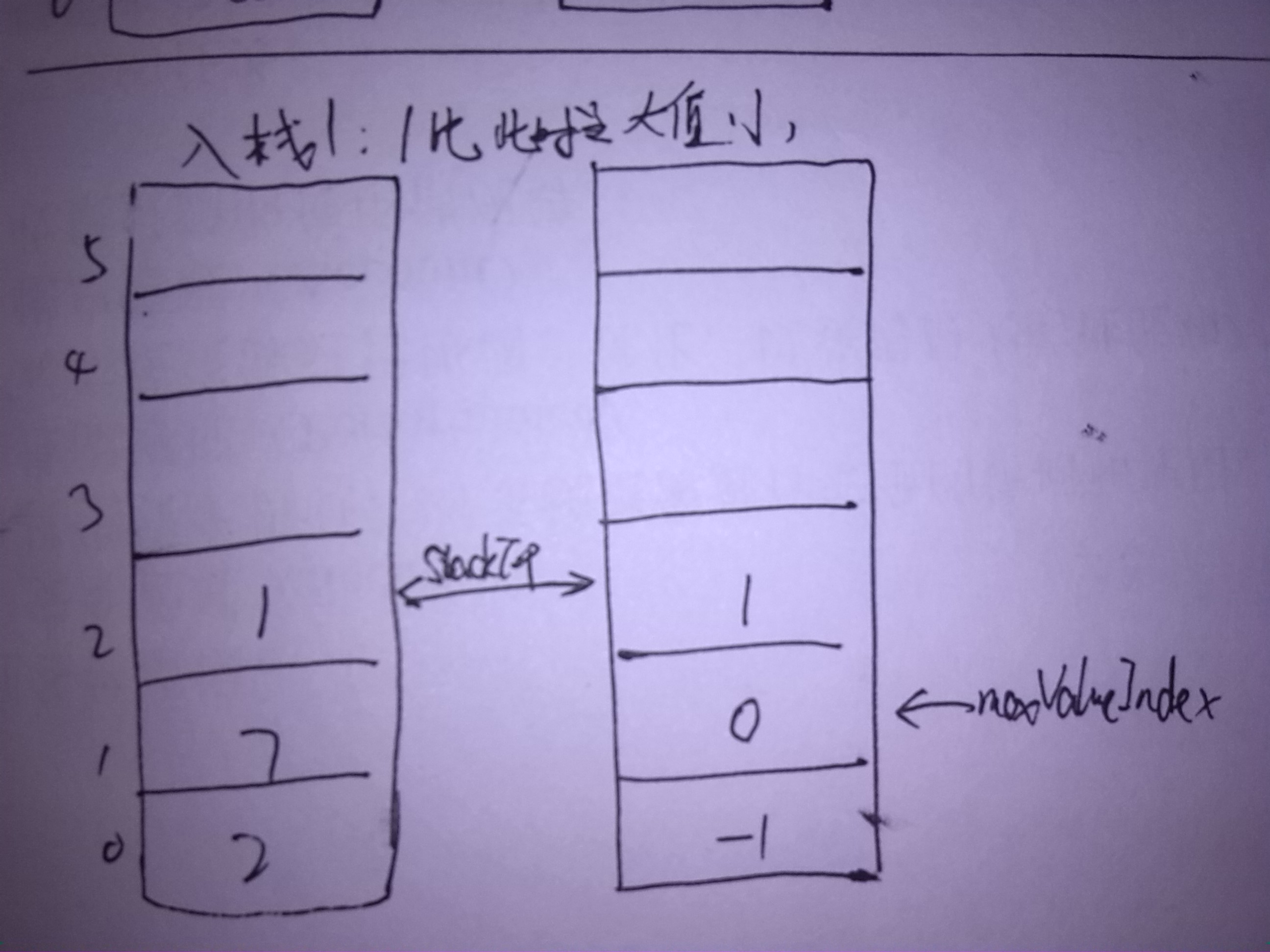
- 插入时:比较插入元素与最大值的大小,如果比最大值还大呢,link2NextMaxValueIndex指向原来最大值的位置(即maxValueIndex),而maxValueIndex变为现在插入元素的位置;否则link2NextMaxValueIndex指向-1
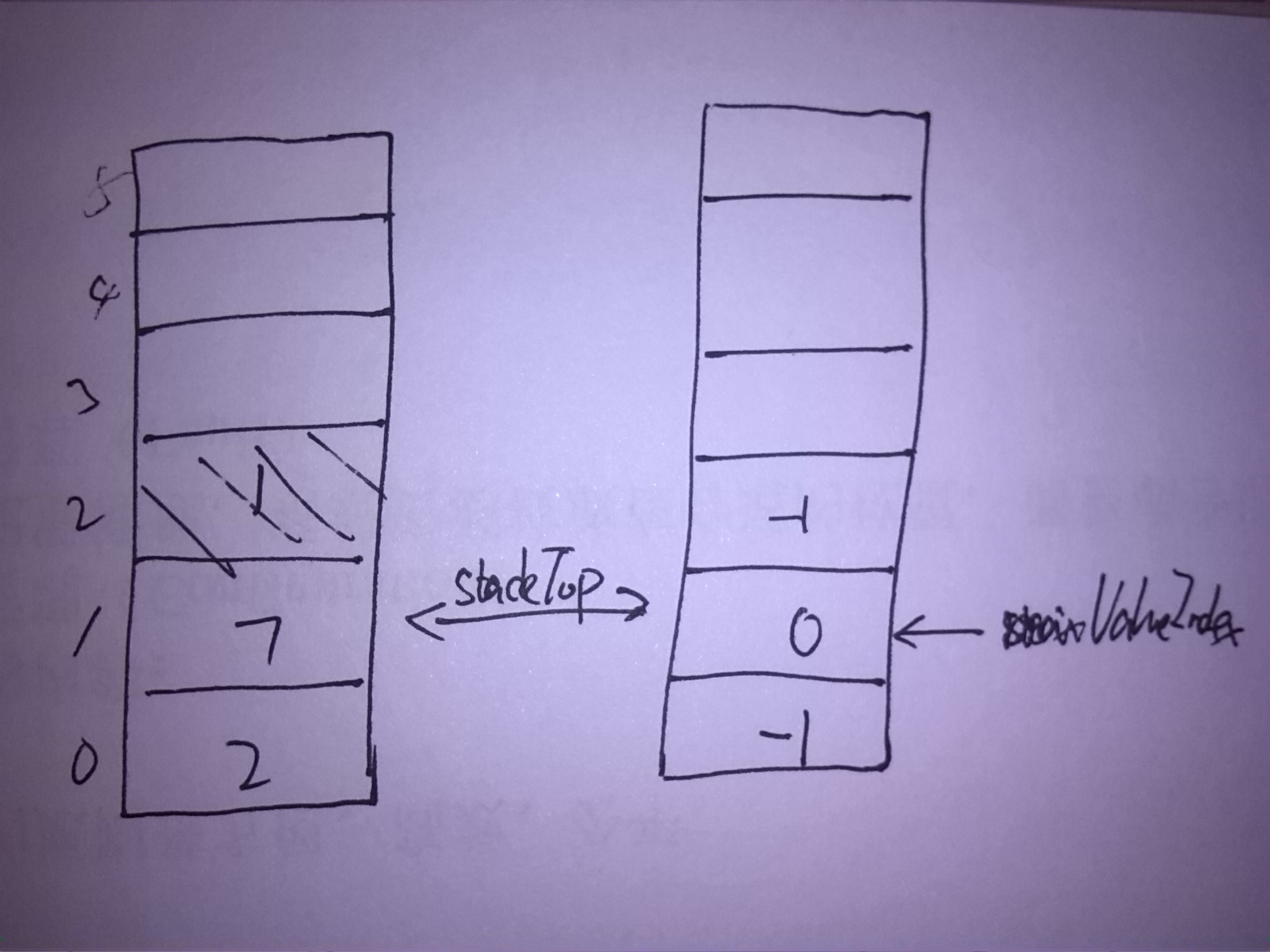
- 删除时:删除元素的位置出,如果maxValueIndex与当前位置相同,此时maxValueIndex为link2NextMaxValueIndex[satckTop]
- 返回栈的最大元素
图示
以入栈2 7 1,出栈为例:


代码
#include <iostream> #include <climits> #define MAX 100 using namespace std; class stack { public: stack() : stackTop(-1), maxValueIndex(-1) {} void push(int val); int pop(); int max(); int size() { return stackTop + 1; } int empty() { return stackTop < 0 ? 1 : 0; } private: int stackItem[MAX]; int link2NextMaxValueIndex[MAX]; int stackTop; int maxValueIndex; }; void stack::push(int val) { ++stackTop; if(stackTop == MAX) { cout << "The stack has been full!" << endl; return; } else { stackItem[stackTop] = val; if(max() < val) { link2NextMaxValueIndex[stackTop] = maxValueIndex; maxValueIndex = stackTop; } else link2NextMaxValueIndex[stackTop] = -1; } } int stack::pop() { int ret; if(stackTop == -1) { cout << "The stack is empty!" << endl; return -1; } else { ret = stackItem[stackTop]; if(stackTop == maxValueIndex) maxValueIndex = link2NextMaxValueIndex[stackTop]; --stackTop; return ret; } } int stack::max() { if(maxValueIndex >= 0) return stackItem[maxValueIndex]; else return INT_MIN; } int main() { stack s; cout << "s.empty():" << s.empty() << endl; s.push(3); s.push(4); cout << "s.top():" << s.pop() << endl; cout << "s.top():" << s.pop() << endl; cout << "s.top():" << s.pop() << endl; cout << "s.size():" << s.size() << endl; cout << "s.empty():" << s.empty() << endl; }
结果

2. 快速得到最大值的队列
两个栈可以实现队列(参考),就用刚才的栈实现队列
代码
#include <iostream> #include <climits> #define MAX 100 using namespace std; class stack { public: stack() : stackTop(-1), maxValueIndex(-1) {} void push(int val); int pop(); int max(); int size() { return stackTop + 1; } int empty() { return stackTop < 0 ? 1 : 0; } private: int stackItem[MAX]; int link2NextMaxValueIndex[MAX]; int stackTop; int maxValueIndex; }; class queue { public: void enQueue(int val); int deQueue(); int size() { return stackIn.size() + stackOut.size(); } private: stack stackIn; stack stackOut; }; void stack::push(int val) { ++stackTop; if(stackTop == MAX) { cout << "The stack has been full!" << endl; return; } else { stackItem[stackTop] = val; if(max() < val) { link2NextMaxValueIndex[stackTop] = maxValueIndex; maxValueIndex = stackTop; } else link2NextMaxValueIndex[stackTop] = -1; } } int stack::pop() { int ret; if(stackTop == -1) { cout << "The stack is empty!" << endl; return -1; } else { ret = stackItem[stackTop]; if(stackTop == maxValueIndex) maxValueIndex = link2NextMaxValueIndex[stackTop]; --stackTop; return ret; } } int stack::max() { if(maxValueIndex >= 0) return stackItem[maxValueIndex]; else return -100; } void queue::enQueue(int val) { stackIn.push(val); } int queue::deQueue() { if(stackOut.empty() and !stackIn.empty()) { while(!stackIn.empty()) stackOut.push(stackIn.pop()); } return stackOut.pop(); } int main() { stack s; cout << "s.empty():" << s.empty() << endl; s.push(3); s.push(4); cout << "s.top():" << s.pop() << endl; cout << "s.top():" << s.pop() << endl; cout << "s.top():" << s.pop() << endl; cout << "s.size():" << s.size() << endl; cout << "s.empty():" << s.empty() << endl; queue q; q.enQueue(1); q.enQueue(2); q.enQueue(3); cout << "q.size()" << q.size() << endl; q.deQueue(); cout << "q.size()" << q.size() << endl; }
结果
