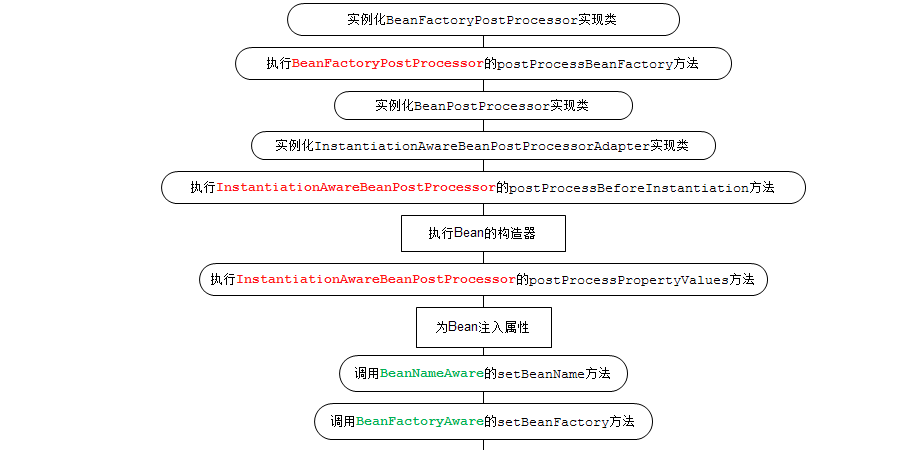

从网上偷的一张图
总结如下:
分为2个阶段,实例化前后,初始化前后
1 实例化前-postProcessBeforeInstantiation 这个方法基本没啥大用
2 实例化中-通过反射实例化
3 填充属性-也是通过beanPostProcessor做的(@Resource @Autowired 处理这两个注解的beanPostProcessor是不同的)
4 执行beanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization (@PostConstruct注解就是在这里执行的)
5 执行initializingBean的afterPropertiesSet
6 调用init-method
7 执行beanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization (AOP就是在这里做的)
AbstractAutoProxyCreator# postProcessAfterInitialization
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (bean != null) { Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName); if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) { return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey); } } return bean; }