一:
1.API

2.构造函数的程序
注意这集中构造函数的特点。
同时,字段separator的使用。
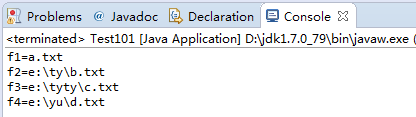
1 import java.io.File; 2 3 public class Test101 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 //f1 6 File f1=new File("a.txt"); 7 //f2 8 File f2=new File("e:\ty","b.txt"); 9 //f3 10 File d=new File("e:\tyty"); 11 File f3=new File(d,"c.txt"); 12 //separator 13 File f4=new File("e:"+File.separator+"yu"+File.separator+"d.txt"); 14 // 15 System.out.println("f1="+f1); 16 System.out.println("f2="+f2); 17 System.out.println("f3="+f3); 18 System.out.println("f4="+f4); 19 } 20 }
3.结果
二:增删改查
1.常见的方法
1,创建。
boolean createNewFile():在指定位置创建文件,如果该文件已经存在,则不创建,返回false。
和输出流不一样,输出流对象一建立创建文件。而且文件已经存在,会覆盖。
boolean mkdir():创建文件夹。
boolean mkdirs():创建多级文件夹。
2,删除。
boolean delete():删除失败返回false。如果文件正在被使用,则删除不了返回falsel。
void deleteOnExit();在程序退出时删除指定文件。
3,判断。
boolean exists() :文件是否存在.
isFile():
isDirectory();
isHidden();
isAbsolute();
4,获取信息。
getName():
getPath():
getParent():
getAbsolutePath()
long lastModified()
long length()
2.程序
1 import java.io.File; 2 import java.io.IOException; 3 4 import javax.swing.plaf.synth.SynthSeparatorUI; 5 /** 6 * 文件的创建,删除,判断,获取 7 * @author Administrator 8 * 9 */ 10 public class Test102 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 12 getMethod(); 13 } 14 //createNewFile,mkdir,mkdirs,isDirectory,isFile,isAbsolute,exists 15 public static void mkMethod() throws IOException{ 16 File f=new File("a.txt"); 17 //System.out.println(f.createNewFile()); 18 System.out.println(f.exists()); 19 System.out.println(f.canExecute()+"..."); 20 System.out.println(f.mkdir()); //true 21 System.out.println(f.isDirectory()); //true 22 System.out.println(f.isFile()); //false 23 System.out.println(f.isAbsolute()); 24 } 25 //delete 26 public static void deMethod() throws IOException{ 27 File f=new File("a.txt"); 28 System.out.println(f.delete()); 29 } 30 //getPath,getAbsolutePath,getParent,getName 31 public static void getMethod() throws IOException{ 32 File f=new File("b.txt"); 33 System.out.println(f.getPath()); 34 System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath()); 35 System.out.println(f.getParent()); 36 System.out.println(f.getName()); 37 } 38 }
3.renameTo的程序
1 import java.io.File; 2 3 public class Test103 { 4 /** 5 * reNameTo 6 * 相当于剪切复制 7 */ 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 File f1=new File("a.txt"); 10 File f2=new File("b.txt"); 11 System.out.println(f1.renameTo(f2)); 12 } 13 }
三:列表
1.罗列全部的列表
注意的是list与listFile的区别
1 import java.io.File; 2 /** 3 * list与listFile的区别 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 public class Test104 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 //listFileMethod(); 10 listMethod(); 11 } 12 public static void listFileMethod(){ 13 File f=new File("E:\Summary6\demo1"); 14 File[] dir=f.listFiles(); 15 for(File file : dir){ 16 System.out.println(file.getName()+"..."+file.length()); 17 } 18 } 19 public static void listMethod(){ 20 File f=new File("E:\Summary6\demo1"); 21 String[] str=f.list(); 22 for(String s : str){ 23 System.out.println(s); 24 } 25 } 26 }
2.过滤需要的文件夹
注意:留下的是经过过滤条件筛选后的文件
1 import java.io.File; 2 import java.io.FilenameFilter; 3 4 public class Test105 { 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 filterMethod(); 8 } 9 public static void filterMethod(){ 10 File dir=new File("e:\"); 11 String[] arr=dir.list(new FilenameFilter(){ 12 @Override 13 public boolean accept(File dir, String name) { 14 15 return name.endsWith(".rrr"); 16 } 17 }); 18 for(String name:arr){ 19 System.out.println(name); 20 } 21 } 22 }
3.listRoot:打印盘符
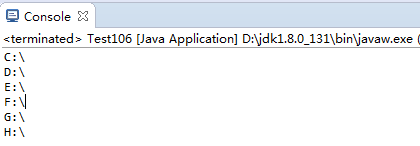
1 import java.io.File; 2 3 public class Test106 { 4 /** 5 * listRoot:打印盘符 6 * @param args 7 */ 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 File[] f=File.listRoots(); 10 for(File str : f){ 11 System.out.println(str); 12 } 13 } 14 }
4.效果
5.循环打印
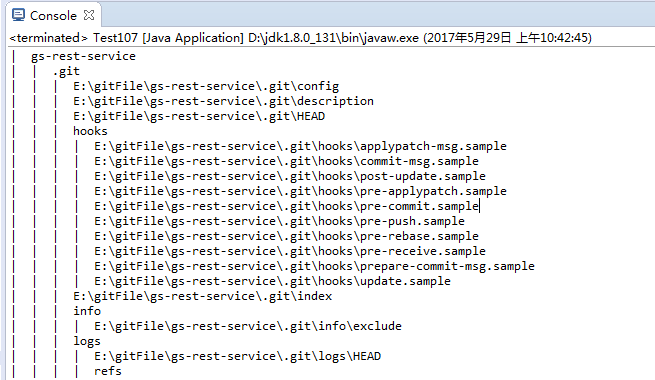
1 import java.io.File; 2 3 /** 4 * 循环打印文件夹下的文件,以及下一层的文件夹中的文件 5 */ 6 public class Test107 { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 showMethod(); 9 } 10 public static void showMethod(){ 11 File dir=new File("E:\gitFile\gs-rest-service"); 12 loopMethod(dir,0); 13 } 14 public static void loopMethod(File dir,int level){ 15 System.out.println(getLevel(level)+dir.getName()); 16 level++; 17 File[] files = dir.listFiles(); 18 for(int x=0; x<files.length; x++) 19 { 20 if(files[x].isDirectory()) 21 loopMethod(files[x],level); 22 else 23 System.out.println(getLevel(level)+files[x]); 24 } 25 } 26 public static String getLevel(int level){ 27 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 28 sb.append("| "); 29 for(int x=0; x<level; x++) 30 { 31 sb.insert(0,"| "); 32 } 33 return sb.toString(); 34 } 35 }
6.效果
四:打印流
1.介绍
打印流主要包括字节打印流与字符打印流
相对而言字符打印流更加常用。
2.字节打印流:
PrintStream
构造函数可以接收的参数类型:
1,file对象。File
2,字符串路径。String
3,字节输出流。OutputStream
3.字符打印流:
PrintWriter
构造函数可以接收的参数类型:
1,file对象。File
2,字符串路径。String
3,字节输出流。OutputStream
4,字符输出流,Writer。
4.程序
1 import java.io.BufferedReader; 2 import java.io.FileWriter; 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 5 import java.io.PrintWriter; 6 7 /** 8 * 关于printWriter的使用 9 */ 10 public class Test108 { 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 13 BufferedReader bufr=new BufferedReader( 14 new InputStreamReader(System.in)); 15 PrintWriter out=new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("acb.txt"),true); 16 String line=null; 17 while((line=bufr.readLine())!=null){ 18 if(line.equals("over")) 19 break; 20 out.println(line); 21 } 22 bufr.close(); 23 out.close(); 24 } 25 26 }
五:properties特性
1.介绍
Properties是hashtable的子类。
也就是说它具备map集合的特点。而且它里面存储的键值对都是字符串。
是集合中和IO技术相结合的集合容器。
该对象的特点:可以用于键值对形式的配置文件。
那么在加载数据时,需要数据有固定格式:键=值。
2.设置与获取
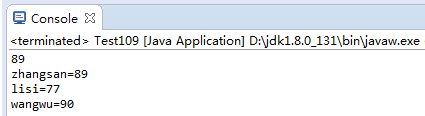
1 import java.util.Properties; 2 import java.util.Set; 3 public class Test109 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Properties pro=new Properties(); 6 //set 7 pro.setProperty("zhangsan", "89"); 8 pro.setProperty("lisi", "77"); 9 pro.setProperty("wangwu","90"); 10 //get 11 System.out.println(pro.getProperty("zhangsan")); 12 //特有的获取方法 13 Set<String> value=pro.stringPropertyNames(); 14 for(String name : value){ 15 System.out.println(name+"="+pro.getProperty(name)); 16 } 17 } 18 }
3.运行效果
4.将文件中的值存放到properties集合中
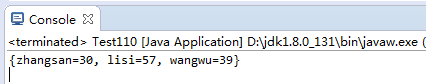
1 import java.io.BufferedReader; 2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 3 import java.io.FileReader; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.util.Properties; 6 public class Test110 { 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 8 BufferedReader bufr=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("info.txt")); 9 Properties pro=new Properties(); 10 String line=null; 11 while((line=bufr.readLine())!=null){ 12 String[] str=line.split("="); 13 pro.setProperty(str[0], str[1]); 14 } 15 bufr.close(); 16 System.out.println(pro); 17 } 18 }
5.运行结果
六:文件的切割与合并
1.文件的合并
1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 3 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.io.SequenceInputStream; 6 import java.util.Enumeration; 7 import java.util.Vector; 8 public class Test111 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 10 Vector<FileInputStream> vector=new Vector<FileInputStream>(); 11 vector.add(new FileInputStream("1.txt")); 12 vector.add(new FileInputStream("2.txt")); 13 vector.add(new FileInputStream("3.txt")); 14 Enumeration<FileInputStream> en=vector.elements(); 15 SequenceInputStream ss=new SequenceInputStream(en); 16 FileOutputStream fs=new FileOutputStream("4.txt"); 17 int len=0; 18 byte[] buf=new byte[1024]; 19 while((len=ss.read(buf))!=-1){ 20 fs.write(buf, 0, len); 21 } 22 ss.close(); 23 fs.close(); 24 } 25 }
2.运行效果

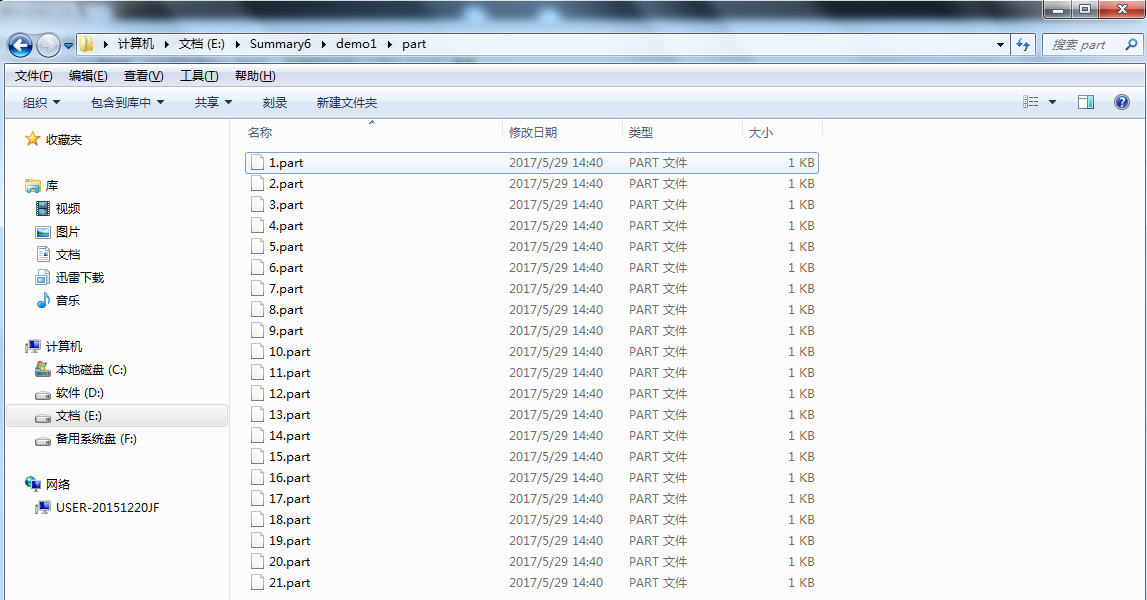
3.分割
1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 3 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 4 public class Test112 { 5 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 6 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("u.jpg"); 7 FileOutputStream fos = null; 8 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; 9 int len = 0; 10 int count = 1; 11 while((len=fis.read(buf))!=-1) 12 { 13 fos = new FileOutputStream("part\"+(count++)+".part"); 14 fos.write(buf,0,len); 15 fos.close(); 16 } 17 fis.close(); 18 } 19 }
4.运行结果
5.再进行合并
1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.io.SequenceInputStream; 5 import java.util.ArrayList; 6 import java.util.Enumeration; 7 import java.util.Iterator; 8 9 public class Test113 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 11 merge(); 12 13 } 14 public static void merge()throws IOException 15 { 16 //将ArrayList转换成Enumeration 17 ArrayList<FileInputStream> al = new ArrayList<FileInputStream>(); 18 for(int x=1; x<=21; x++) 19 { 20 al.add(new FileInputStream("part\"+x+".part")); 21 } 22 //use final ,because anonymous function 23 final Iterator<FileInputStream> it = al.iterator(); 24 Enumeration<FileInputStream> en = new Enumeration<FileInputStream>() 25 { 26 public boolean hasMoreElements() 27 { 28 return it.hasNext(); 29 } 30 public FileInputStream nextElement() 31 { 32 return it.next(); 33 } 34 }; 35 36 SequenceInputStream sis = new SequenceInputStream(en); 37 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("i.jpg"); 38 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; 39 int len = 0; 40 while((len=sis.read(buf))!=-1) 41 { 42 fos.write(buf,0,len); 43 } 44 fos.close(); 45 sis.close(); 46 } 47 48 }