一:准备
1.二测排序
其中1说明了自定义类型
2与3说明了shuffle阶段的分区与分组,同时说明了程序的写法。

2.RawComparator class

3.二次排序的要点
组合key,key是一个组合的字段,自定义数据类型
实现WritableComparable
保证原来的分区不变,自定义分区规则
继承Patitioner
保证原来的分组不变,自定义分组规则
继承RawComparator
4.输入的数据

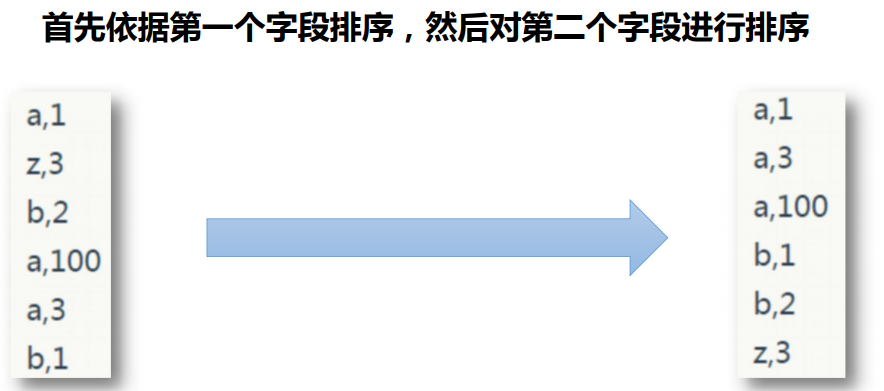
5.需求
平时的只有一次排序,就是第一个会排序,但是输出的结果中第二个没有排序处理。
现在希望。在第一个key排序之后,后面的key也可以排序出来。
二:第一次排序
3.输出第一排序的程序
MAPPER--------------
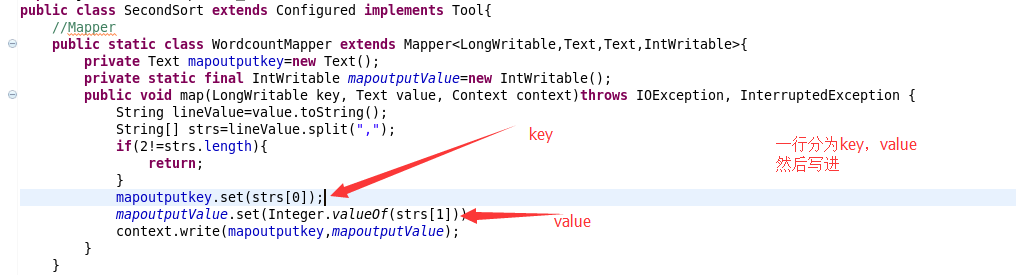
REDUCER------------

4.结果

三:二次排序
5.map和reduce程序
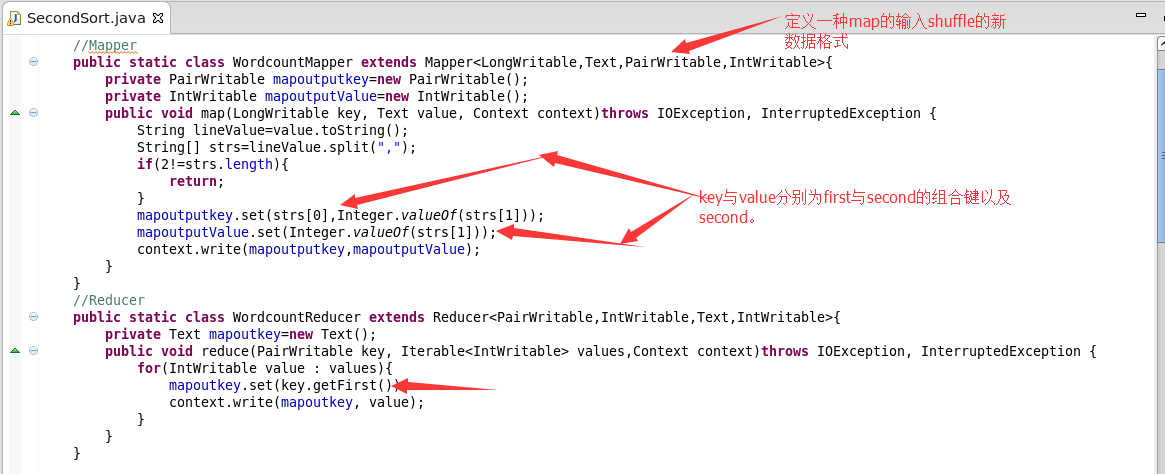
6.自定义类型的程序
需要实现接口WritableComparable
输入String,int。
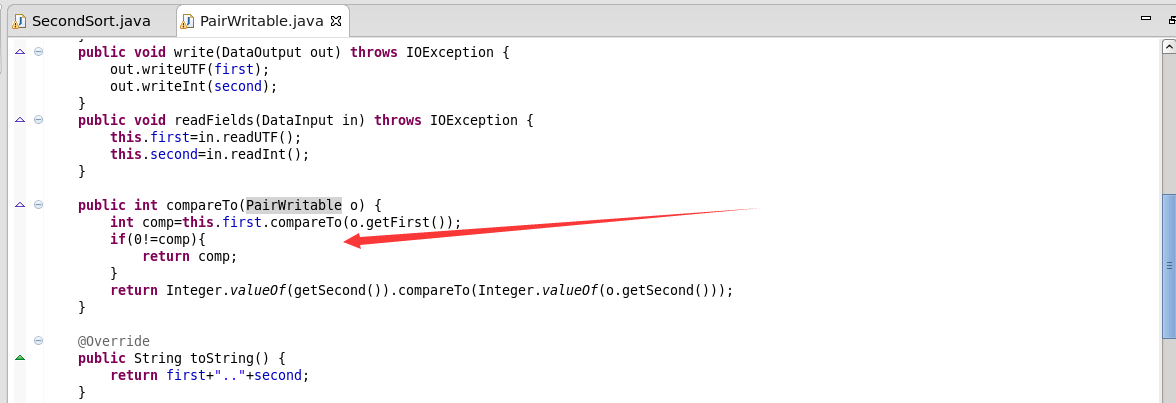
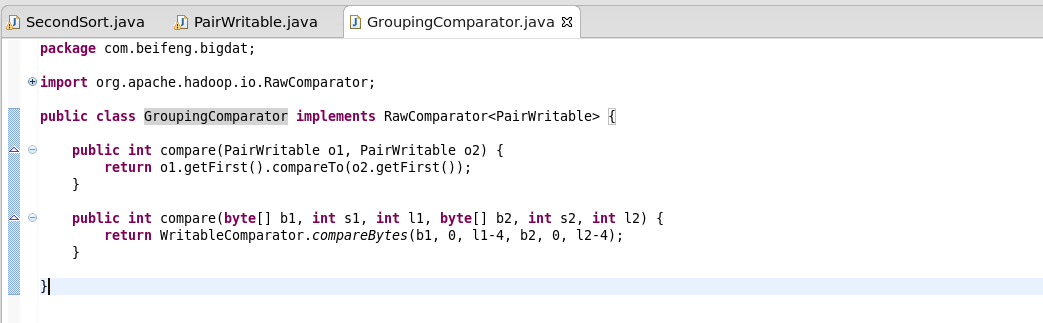
7.自定义分组比较器
需要实现RawComparator
两个函数都是相同的意思,都是在返回first的比较结果。
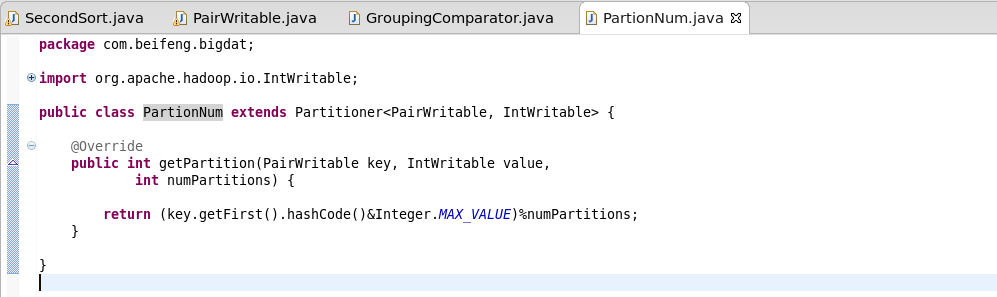
8.定义分区规则
继承Patitioner
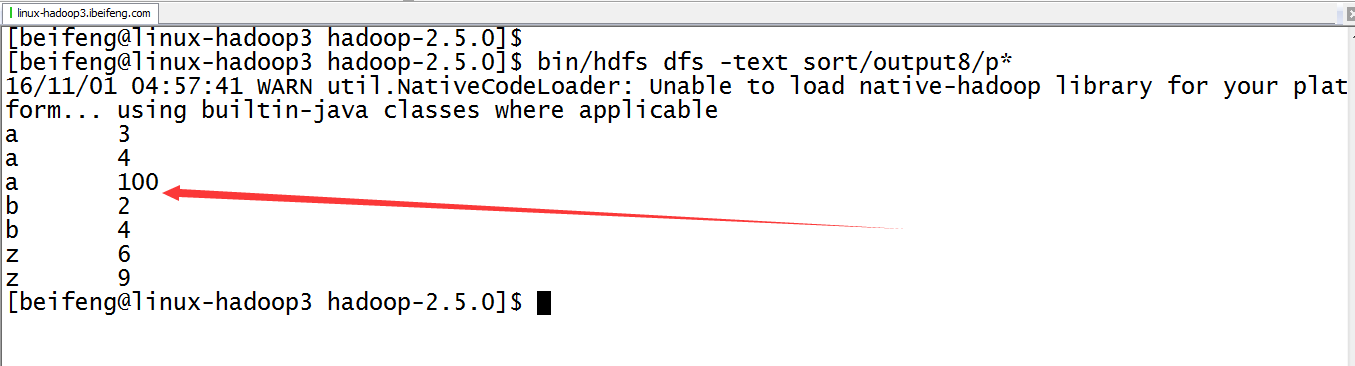
9.运行结果
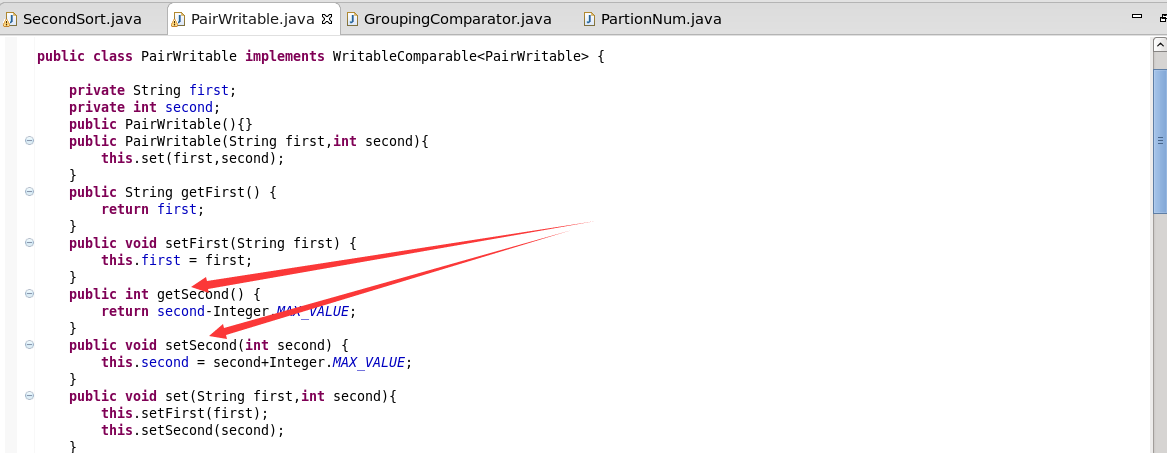
四:优化点
例如分区就属于优化,但是这里说的是正负数的优化。
五:重新整理
1.项目结构
2.程序代码
RealSecondSort.class
package com.senior.sort;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.Partitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper.Context;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
import com.senior.network.WebPvCount;
import com.senior.network.WebPvCount.WebPvCountMapper;
import com.senior.network.WebPvCount.WebPvCountReducer;
public class RealSecondSort extends Configured implements Tool{
//Mapper
public static class SortMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text,PariWritable,IntWritable>{
private PariWritable mapoutkey=new PariWritable();
private IntWritable mapoutvalue=new IntWritable();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String valueStr=value.toString();
String strs[]=valueStr.split(",");
mapoutkey.set(strs[0],Integer.valueOf(strs[1]));
mapoutvalue.set(Integer.valueOf(strs[1]));
context.write(mapoutkey, mapoutvalue);
}
}
//Reducer
public static class SortReducer extends Reducer<PariWritable,IntWritable,Text,IntWritable>{
private Text outkey=new Text();
@Override
protected void reduce(PariWritable key, Iterable<IntWritable> value,Context context)throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for(IntWritable str : value){
outkey.set(key.getFirst());
context.write(outkey, str);
}
}
}
//Driver
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf=this.getConf();
Job job=Job.getInstance(conf,this.getClass().getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(RealSecondSort.class);
//input
Path inpath=new Path(args[0]);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, inpath);
//output
Path outpath=new Path(args[1]);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outpath);
//map
job.setMapperClass(SortMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(PariWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
//shuffle*************************************
job.setPartitionerClass(PartitionNum.class);
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(GroupingComparator.class);
//shuffle*************************************
//reduce
job.setReducerClass(SortReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
//submit
boolean isSucess=job.waitForCompletion(true);
return isSucess?0:1;
}
//Main
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Configuration conf=new Configuration();
args=new String[]{
"hdfs://linux-hadoop01.ibeifeng.com:8020/user/beifeng/mapreduce/wordcount/inputSortData",
"hdfs://linux-hadoop01.ibeifeng.com:8020/user/beifeng/mapreduce/wordcount/outputSortData2"
};
int status=ToolRunner.run(new RealSecondSort(), args);
System.exit(status);
}
}
PariWritable.java
这个地方使用的接口可以看看下面的说明。
package com.senior.sort;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
public class PariWritable implements WritableComparable<PariWritable>{
private String first;
private Integer second;
public PariWritable(){}
public PariWritable(String first,Integer second){
set(first,second);
}
//set get
public String getFirst() {
return first;
}
public void setFirst(String first) {
this.first = first;
}
public Integer getSecond() {
return second-Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
public void setSecond(Integer second) {
this.second = second+Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
public void set(String first, Integer second) {
this.first=first;
this.second=second;
}
//
public void readFields(DataInput input) throws IOException {
this.first=input.readUTF();
this.second=input.readInt();
}
public void write(DataOutput output) throws IOException {
output.writeUTF(first);
output.writeInt(second);
}
public int compareTo(PariWritable o) {
int comp=this.first.compareTo(o.getFirst());
if(0!=comp){
return comp;
}
return Integer.valueOf(getSecond()).compareTo(Integer.valueOf(o.getSecond()));
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PariWritable [first=" + first + ", second=" + second + "]";
}
}
PartitionNum.java
package com.senior.sort;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
public class PartitionNum extends Partitioner<PariWritable, IntWritable> {
@Override
public int getPartition(PariWritable key, IntWritable value, int num) {
return (key.getFirst().hashCode()&Integer.MAX_VALUE)%num;
}
}
GroupingComparator.java
关于程序中的一点仔细看下面的一个部分,就可以很好的理解了。
package com.senior.sort;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.RawComparator;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
public class GroupingComparator implements RawComparator<PariWritable> {
public int compare(PariWritable o1, PariWritable o2) {
return o1.getFirst().compareTo(o2.getFirst());
}
public int compare(byte[] b1, int arg1, int l1, byte[] b2, int arg4,int l2) {
return WritableComparator.compareBytes(b1, 0, l1-4, b2, 0, l2-4);
}
}
3.效果
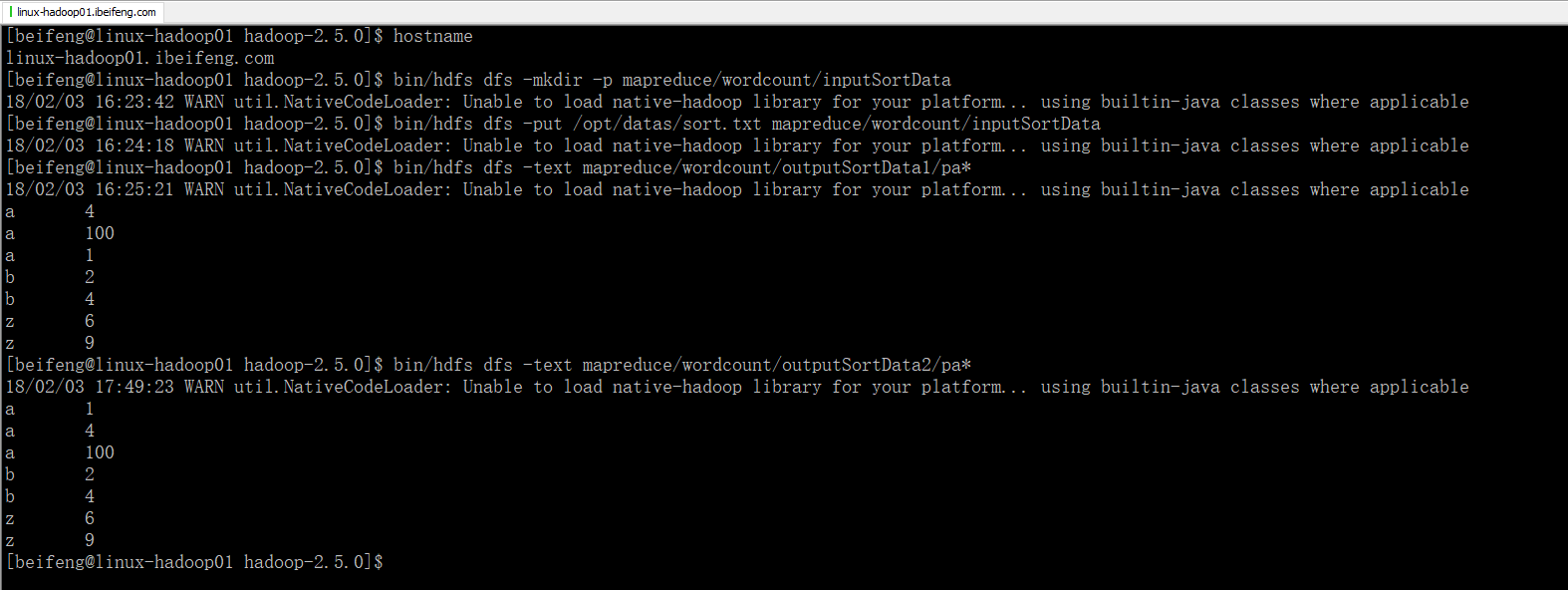
六:Hadoop的序列化
1.说明
在上面的程序中使用到了序列化,在整理的过程中对这一块进行整理一番。
2.序列化的功能
- 排列紧凑:尽量减少带宽,加快数据交换速度
- 处理快速:进程间通信需要大量的数据交互,使用大量的序列化机制,必须减少序列化和反序列的开支
- 跨语言:可以支持不同语言间的数据交互啊,如C++
- 可扩展:当系统协议升级,类定义发生变化,序列化机制需要支持这些升级和变化
3.Writable
public interface Writable {
void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException;
void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException;
}
4.其他接口
public interface RawComparator<T> extends Comparator<T> {
public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1, byte[] b2, int s2, int l2);
}
class MyGrouper implements RawComparator<StartEndDate> {
@Override
public int compare(StartEndDate o1, StartEndDate o2) {
return (int)(o1.getStartDate().getTime()- o2.getEndDate().getTime());
}
@Override
public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1, byte[] b2, int s2, int l2) {
int compareBytes = WritableComparator.compareBytes(b1, s1, 8, b2, s2, 8);
return compareBytes;
}
}