




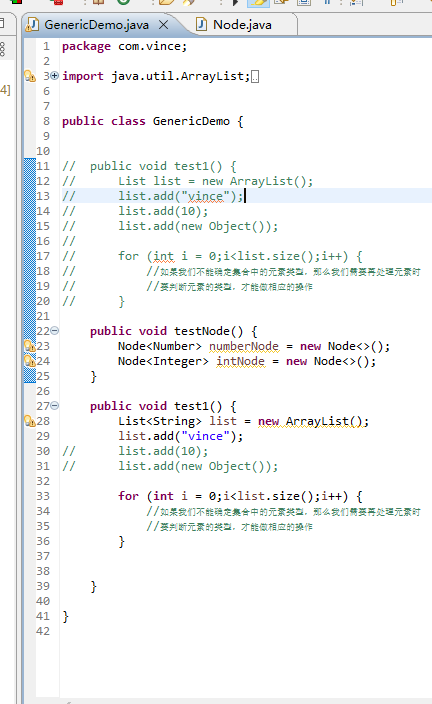
1 package com.vince; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.List; 6 7 8 public class GenericDemo { 9 10 11 // public void test1() { 12 // List list = new ArrayList(); 13 // list.add("vince"); 14 // list.add(10); 15 // list.add(new Object()); 16 // 17 // for (int i = 0;i<list.size();i++) { 18 // //如果我们不能确定集合中的元素类型,那么我们需要再处理元素时 19 // //要判断元素的类型,才能做相应的操作 20 // } 21 22 public void test1() { 23 List<String> list = new ArrayList(); 24 list.add("vince"); 25 list.add(10); 26 list.add(new Object()); 27 28 for (int i = 0;i<list.size();i++) { 29 //如果我们不能确定集合中的元素类型,那么我们需要再处理元素时 30 //要判断元素的类型,才能做相应的操作 31 } 32 33 34 } 35 36 }





解决方法:
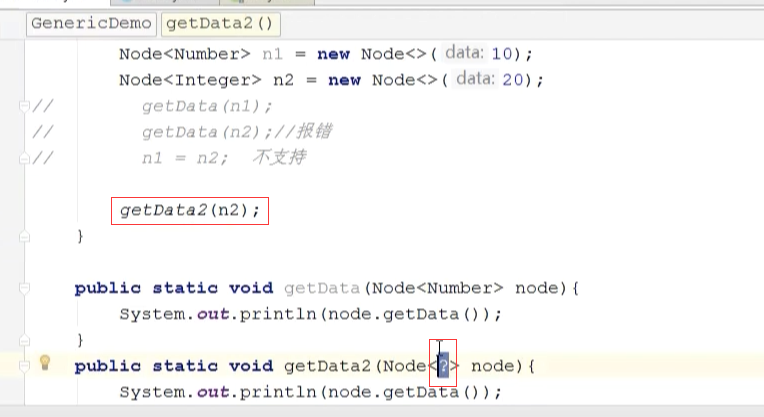

1 package com.vince; 2 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 5 import java.util.*; 6 7 /** 8 * Created by vince on 2017/6/15. 9 */ 10 public class GenericDemo { 11 12 @Test 13 public void test5(){ 14 Map<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<>(); 15 map.put(1,"vince"); 16 map.put(2,"tom"); 17 18 Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet(); 19 for(Map.Entry entry: entrySet){ 20 System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"-"+entry.getValue()); 21 } 22 23 } 24 25 @Test 26 public void test4(){ 27 String[] arrays = {"vince","jack","Tom","lily"}; 28 String[] strs = func(arrays, 0, 1); 29 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strs)); 30 } 31 32 @Test 33 public void test3(){ 34 Node<Number> n1 = new Node<>(10); 35 Node<Integer> n2 = new Node<>(20); 36 // getData(n1); 37 // getData(n2);//报错 38 // n1 = n2; 不支持 39 40 // getData2(n2); 41 42 getUpperNumberData(n1); 43 getUpperNumberData(n2); 44 45 46 } 47 48 public static void getData(Node<Number> node){ 49 System.out.println(node.getData()); 50 } 51 52 /** 53 * 使用通配符定义泛型类型,此时只能输出,不能修改 54 * @param node 55 */ 56 public static void getData2(Node<?> node){ 57 // node.setData(20); 58 System.out.println(node.getData()); 59 } 60 61 public static void getUpperNumberData(Node<? extends Number> data){ 62 //只能是Number类及其子类 63 System.out.println("data :" + data.getData()); 64 65 } 66 67 /** 68 * 泛型方法 69 * @param array 70 * @param i 71 * @param t 72 * @param <T> 73 * @return 74 */ 75 public static <T> T[] func(T[] array,int i,int t){ 76 T temp = array[i]; 77 array[i] = array[t]; 78 array[t] = temp; 79 return array; 80 } 81 82 83 84 85 @Test 86 public void test2(){ 87 Node<String> stringNode = new Node<>("vince"); 88 Node<Integer> intNode = new Node<>(10); 89 90 System.out.println(stringNode.getData()); 91 System.out.println(intNode.getData()); 92 93 } 94 @Test 95 public void test1(){ 96 List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); 97 list.add("vince"); 98 //list.add(10); 99 //list.add(new Object()); 100 101 for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { 102 //如果我们不能确定集合中的元素类型,那么我们需要在处理元素时 103 //要判断元素的类型,才能做相应的操作 104 105 } 106 } 107 }

1 package com.vince; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by vince on 2017/6/15. 5 * 泛型类 6 * T : 参数化类型,在实际使用时才会指定具体的类型 7 * 泛型只作用于编译期检查,在编译后,会被檫除 8 */ 9 public class Node<T> { 10 private T data; 11 public Node(){} 12 public Node(T data){ 13 this.data = data; 14 } 15 16 public T getData() { 17 return data; 18 } 19 20 public void setData(T data) { 21 this.data = data; 22 } 23 }



