3.3单例模式中的懒汉实现双重检查锁定内存模型

1 package net.xdclass; 2 3 public class SingletonLazy { 4 // 这里注释了前面三种都调用此变量,第四种需要注释 5 // private static SingletonLazy instance; 6 7 /** 8 * 构造函数私有化 9 */ 10 11 private SingletonLazy() {} 12 13 14 /* 15 * 单例对象的方法 16 */ 17 public void process() { 18 System.out.println("方法调用成功"); 19 } 20 21 22 23 /** 24 * 第一种方式: 25 * 对外暴露一个方法获取类的对象 26 * 27 * 线程不安全,多线程下存在安全问题,所以不会被采用的 28 */ 29 // public static SingletonLazy geyInstance() { 30 // if(instance == null) { 31 // instance = new SingletonLazy()(); 32 // } 33 // return instance; 34 // } 35 36 37 /*第二种实现方式: 38 * 通过加锁synchronized 保证单例 39 * 采用synchronized 对方法加锁有很大的性能开销 40 * 解决方法:锁力度不要这么大 41 */ 42 // public static synchronized SingletonLazy getInstance() { 43 // if(instance == null) { 44 //A、B线程来到这里存在问题 45 // instance = new SingletonLazy(); 46 // } 47 // return instance; 48 // } 49 // 50 51 52 53 54 /* 55 * 第三种实现方式: 56 * 57 * DCL 双重检查锁定 (doubule-checked-locking),在多线程情况下保持高性能 58 * 59 * 这是否安全,instance = new SingletonLazy();并不是原子性操作 60 * 1.分配空间给对象 61 * 2.在空间内创建对象 62 * 3.将对象赋值给引用instance 63 * 64 * 假如线程1-》3-》2顺序,会把值写入主内存,其他线程就会读取到instance最新的值,但是这个是不完全的对象 65 * (指令重排) 66 * 67 */ 68 // public static SingletonLazy getInstance() { 69 // if(instance == null) { 70 // //A、B 71 // 72 // synchronized(SingletonLazy.class) { 73 // if(instance == null) { 74 // instance = new SingletonLazy(); 75 // } 76 // } 77 // } 78 // return instance; 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 /* 86 * volatile 是java提供的关键词,可以禁止指令重排 87 * 88 */ 89 private static volatile SingletonLazy instance; 90 public static SingletonLazy getInstance() { 91 //第一重检查 92 if(instance == null) { 93 //A、B 锁定 94 95 synchronized(SingletonLazy.class) { 96 //第二重检查 97 if(instance == null) { 98 instance = new SingletonLazy(); 99 } 100 } 101 } 102 return instance; 103 104 105 } 106 107 108 109 110 }


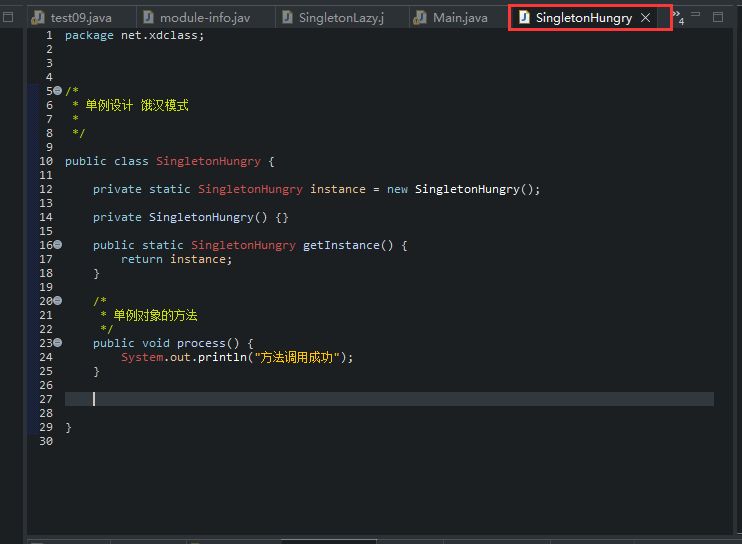
1 package net.xdclass; 2 3 4 5 /* 6 * 单例设计 饿汉模式 7 * 8 */ 9 10 public class SingletonHungry { 11 12 private static SingletonHungry instance = new SingletonHungry(); 13 14 private SingletonHungry() {} 15 16 public static SingletonHungry getInstance() { 17 return instance; 18 } 19 20 /* 21 * 单例对象的方法 22 */ 23 public void process() { 24 System.out.println("方法调用成功"); 25 } 26 27 28 29 }