1.前言:
将测试数据全部敲入数据库非常繁琐,而且如果与合作伙伴一起开发,部署,那么他们肯定也不想把时间花在一个一个录入数据的繁琐过程中,这时候,创建一个批量录入数据的脚本(population script)就非常有必要。
2.代码:
假设在models.py中定义的数据为下面:
from django.db import models
# Create your models here.
class Category(models.Model):
name=models.CharField(max_length=128,unique=True)
class Meta:
verbose_name_plural="Categories"
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class Page(models.Model):
category=models.ForeignKey(Category,on_delete=models.CASCADE)
title=models.CharField(max_length=128)
url=models.URLField()
views=models.IntegerField(default=0)
def __str__(self):
return self.title
populate.py如下(仅供参考):
import os # In your live server environment, you’ll need to tell your WSGI application what settings # file to use. Do that with os.environ: #reference source:https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.1/topics/settings/ os.environ.setdefault('DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE','tango_with_django_project.settings') import django django.setup() from rango.models import Category,Page #If you’re using components of Django “standalone” – for example, writing a Python script # which loads some Django templates and renders them, or uses the ORM to fetch some data – # there’s one more step you’ll need in addition to configuring settings. # After you’ve either set DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE or called configure(), you’ll need to call # django.setup() to load your settings and populate Django’s application registry. # reference source:https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.1/topics/settings/ def populate(): python_pages=[ {"title":"official", "url":"http://docs.python.org"}, {"title":"How to think like a computer scientis", "url":"http://ww.greenteapress.com/thinkpy"}, {"title":"learn python in 10 minites", "url":"http://www.korokithakis.net/tutorials/python"} ] django_pages=[ {"title":"Official Django tutorial", "url":"https://docs.jangoproject.com/en/1.9/intro"}, {"title":"Django Rocks", "url":"http://www.djangorocks.com" }, {"title":"HOw to tango with django", "url":"http://www.tangowithdjango.com"} ] other_pages=[ {"title":"Bottle", "url":"http://bottlepy.org"}, {"title":"Flask", "url":"http://flask.pocoo.org"}, {"title":"Bold test", "url":"http://boldtest.org"} ] cats={"Python":{"pages":python_pages}, "Django":{"pages":django_pages}, "Other Frameworks":{"pages":other_pages}} def add_page(cat,title,url,views=0): p=Page.objects.get_or_create(category=cat,title=title,url=url,views=views)[0] # p.url=url # p.views=views p.save() return p def add_cat(name): c=Category.objects.get_or_create(name=name)[0] c.save() return c for cat,cat_data in cats.items(): c=add_cat(cat) for p in cat_data['pages']: add_page(c,p["title"],p['url']) for c in Category.objects.all(): for p in Page.objects.filter(category=c): print("-{0}-{1}".format(str(c),str(p))) if __name__=="__main__": print("starting rango population script") populate()
3.代码要点
(1)在独立运行django的代码时,而不是通过 python manage.py runserver的方式运行时,必须使用django.setup()来引入Django项目的设置,而在引入设置之前还要指明 环境变量DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE用的是本项目的settings。
设置环境变量在python中常用os.environ,它返回一个字典类型,里面包含了所有环境变量的键值对,所以在这里使用字典的内置方法setdefault,将环境变量
'DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE' 设置为'tango_with_django_project.settings'(本项目的settings.py)。
参考:https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.1/topics/settings/#envvar-DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE
(2)get_or_create方法:(官方文档定义https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.1/ref/models/querysets/#get-or-create如下)
get_or_create(defaults=None, **kwargs) A convenience method for looking up an object with the given kwargs (may be empty if your model has defaults for all fields),
creating one if necessary. Returns a tuple of (object, created), where object is the retrieved or created object and created is a boolean specifying whether a new
object was created. This is meant to prevent duplicate objects from being created when requests are made in parallel, and as a shortcut to boilerplatish code.
在这里,需要注意的是,如果在创建model instance时,仅在model有默认值的情况下可以不输入任何kwargs,否则必须至少输入一个值(field,如这里page的category,或者Category的name),然后该方法会带着这个值先去找有没有该值下的model instance,如果没有则创建一个新的,返回(object,created),这里object 是新创建的对象的reference,created为True.
4.运行查看
运行python populate.py:
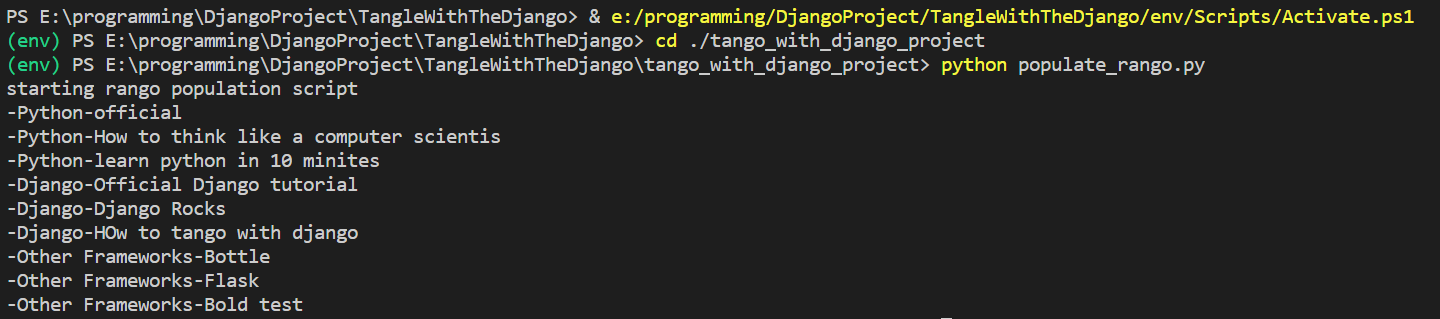
然后登陆admin页面查看:

可以看到,数据全部被读入数据库。