题目描述
链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/5203/B来源:牛客网
Listening to the music is relax, but for obsessive(强迫症), it may be unbearable.
HH is an obsessive, he only start to listen to music at 12:00:00, and he will never stop unless the song he is listening ends at integral points (both minute and second are 0 ), that is, he can stop listen at 13:00:00 or 14:00:00,but he can't stop at 13:01:03 or 13:01:00, since 13:01:03 and 13:01:00 are not an integer hour time.
Now give you the length of some songs, tell HH whether it's possible to choose some songs so he can stop listen at an integral point, or tell him it's impossible.
Every song can be chosen at most once.
输入描述:
The first line contains an positive integer T(1≤T≤60), represents there are T test cases. For each test case: The first line contains an integer n(1≤n≤105), indicating there are n songs. The second line contains n integers a1,a2…an (1≤ai≤109 ), the ith integer ai indicates the ith song lasts ai seconds.
输出描述:
For each test case, output one line "YES" (without quotes) if HH is possible to stop listen at an integral point, and "NO" (without quotes) otherwise.
示例1
输入
[复制]
3
3
2000 1000 3000
3
2000 3000 1600
2
5400 1800
输出
[复制]
NO
YES
YES
说明
In the first example it's impossible to stop at an integral point.In the second example if we choose the first and the third songs, they cost 3600 seconds in total, so HH can stop at 13:00:00In the third example if we choose the first and the second songs, they cost 7200 seconds in total, so HH can stop at 14:00:00
思路
对每个时间%3600,然后做01背包看有能否凑乎3600的整数倍即可,但是这样枚举的时间复杂度至少是(3600*n*T),所以需要用bitset优化。
第一次学bitset优化01背包,详细介绍一下:
每次考虑一个时间x,首先将所有原来的时间位置左移x位,再将x位赋值位1
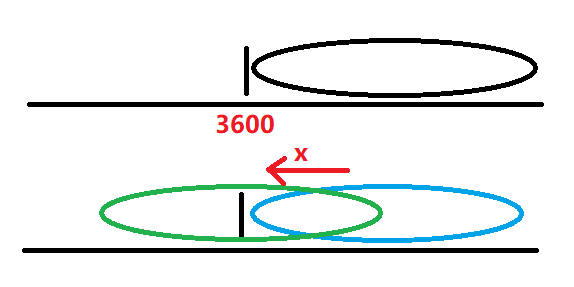
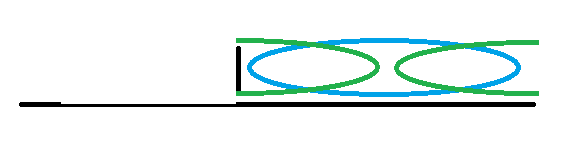
最后需要将3600前移动的部分记录下来,再将3600后的部分右移(相当于%3600)记录下来。最后的记录下来的就是:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
bitset<10010> ans,tmp;
int main(){
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
int n;
ans.reset();
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
x%=3600;
tmp = ans;
tmp<<=x;
tmp[x]=1;
ans|=tmp;
ans|=tmp>>3600;
}
if(ans[0]) cout<<"YES
";
else cout<<"NO
";
}
return 0;
}
这是看别的大佬的方法,比我的容易理解还短,但是我没想到啊
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
bitset<3600> ans,tmp;
int main(){
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
int n;
ans.reset();
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
x%=3600;
tmp.reset();tmp.set(x);
tmp|=(ans<<x)|(ans>>(3600-x));
ans|=tmp;
}
bool f=0;
if(ans.test(0)) cout<<"YES
";
else cout<<"NO
";
}
return 0;
}