翻转单链表
题目描述

思路
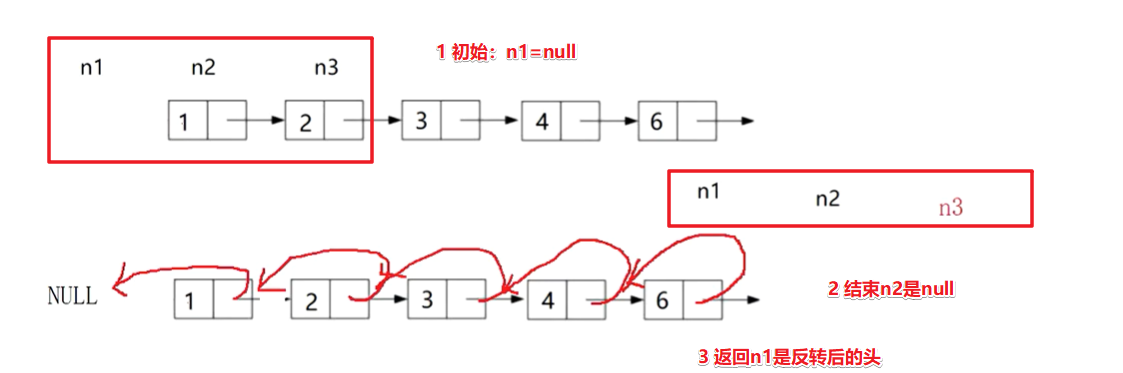
三个指针,分别n1,n2,n3;三个指针不断往后移动。
Java代码
方法1:三个指针标记循环往后走
//方法3:三个指针循环后移
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null) {return null;}
ListNode n0 = null;
ListNode n1 = head;
ListNode n2 = n1.next;
while(n1!=null){
//翻转
n1.next = n0;
//三个指针移动
n0 = n1;
n1 = n2;
//在结尾的地方,这里存在为空的情况,需判断
if(n2!=null){
n2 = n2.next;
}
}
return n0;//最终结束是返回n1
}
输出最优:
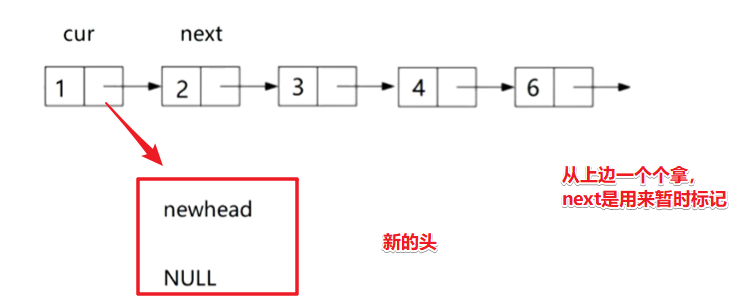
方法2:头插法
思路:
Java代码:
//方法4:头插法
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode newHead = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
//保存下一个
ListNode next = cur.next;
//摘一个下来
cur.next = newHead;
newHead = cur;
//然后取下一个
cur = next;
}
//退出while就是取完了
return newHead;
}
效率:
方法3:借助栈
//方法1:借助栈完成反转
public ListNode reverseList1(ListNode head) {
//借助栈
Deque<ListNode> stack = new LinkedList();
ListNode newHead=null; //返回的逆转栈
//安全验证
if(head==null) return null;
if(head.next==null) return head;
//一个个入栈
while(head!=null){
stack.push(head);
head = head.next;
}
head = stack.pop();
ListNode cur = head;
//出栈
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
ListNode node = stack.pop();
/* //探究:验证节点指向的测试代码
System.out.println("node:"+node+"--->>node.Next:"+node.next);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}*/
//我们虽然正向存入了栈中,但是每个节点的next的指向还没变,在这里要消除
node.next=null; //这一步关键(//消除正向原本的指向关系)
cur.next = node;
cur = node;
}
return head;
}
方法4:简单递归
//方法2:简单递归
public ListNode reverseList2(ListNode head) {
if(head==null) {return null;}
if (head.next==null) {return head;}
//1 前向遍历得到最后的那个节点,并标记
ListNode rev = head;
while (rev.next!=null){
rev = rev.next; //即rev标记了最后的节点
}
//2 我们再次前向遍历,改变指针指向顺序
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur.next!=null){
cur.next.next=cur;
cur.next=null;
//节点后移
cur=cur.next;
}
//返回最后的那个节点做头节点
return rev;
}