链表

链表(线性数据结构)是一种真正的动态数组结构(最简单的),更深入的理解引用(指针),更深入的理解递归,可以辅助组成其他数据结构。
数据存储在“节点”(Node)中,节点可以理解为火车车厢,节节相连。

优点:真正的动态,不需要处理固定容量的问题。不想静态数组一样需要扩容。
缺点:丧失了随机访问的能力。不能像数组那样通过索引可以拿出指定的元素。必须通过链表一点一点的找到。
数组和链表的对比
- 数组
- 数组最好用于索引有语意的情况。scores[2]
- 最大的优点:支持快速查询
- 链表
- 链表不适合用于索引有语意的情况。
- 最大的优点:动态
基本实现
public class LinkedList<E> {
private class Node{
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e, Node next){
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e){
this(e, null);
}
public Node(){
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return e.toString();
}
}
}
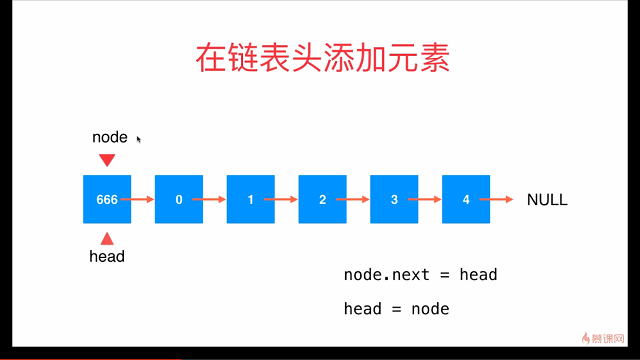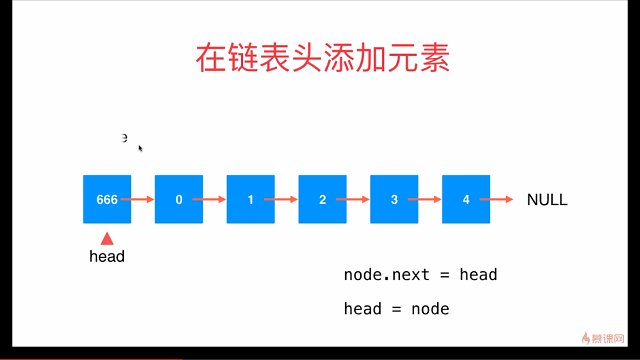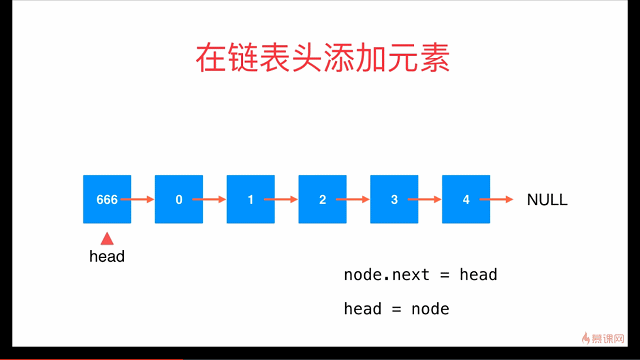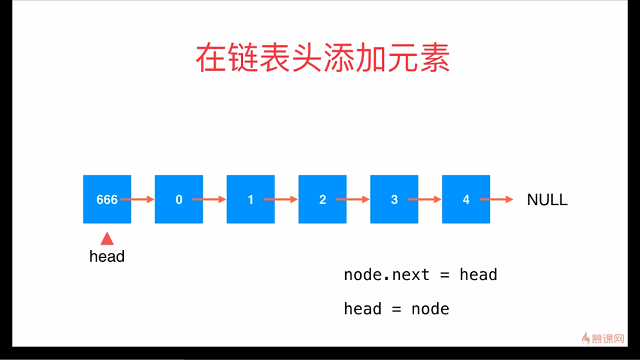
在链表头添加元素

public class LinkedList<E> {
private class Node{
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e, Node next){
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e){
this(e, null);
}
public Node(){
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return e.toString();
}
}
private Node head;
private int size;
public LinkedList(){
head = null;
size = 0;
}
// 获取链表中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在链表头添加新的元素e
public void addFirst(E e){
// Node node = new Node(e);
// node.next = head;
// head = node;
head = new Node(e, head);
size ++;
}
// 在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新的元素e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
if(index == 0)
addFirst(e);
else{
Node prev = head;
for(int i = 0 ; i < index - 1 ; i ++)
prev = prev.next;
// Node node = new Node(e);
// node.next = prev.next;
// prev.next = node;
prev.next = new Node(e, prev.next);
size ++;
}
}
// 在链表末尾添加新的元素e
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
}
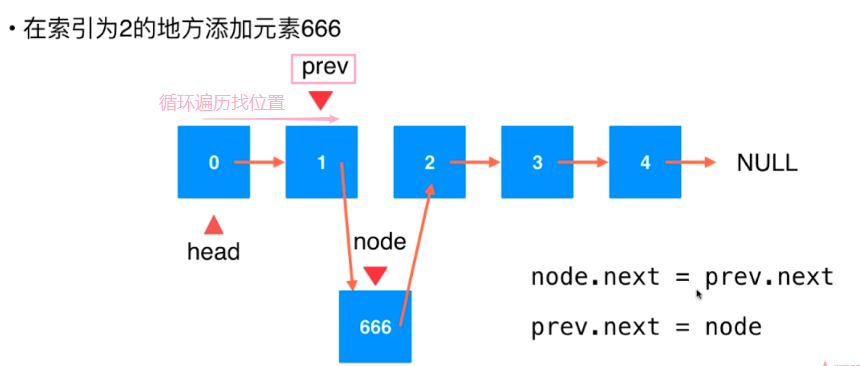
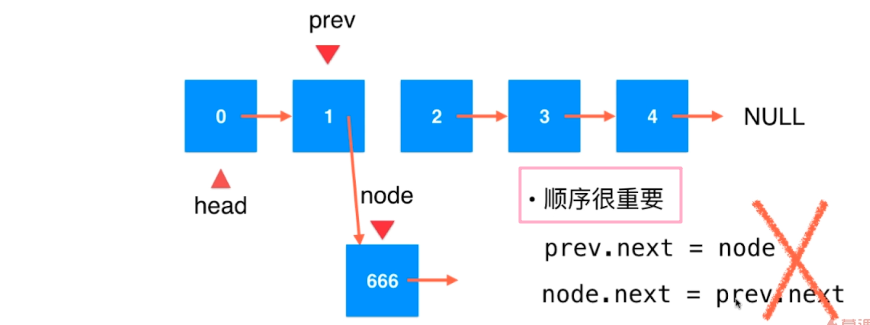
在链表中间添加元素
关键:找到要添加的节点的前一个节点
链表的“索引”
public class LinkedList<E> {
private class Node{
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e, Node next){
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e){
this(e, null);
}
public Node(){
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return e.toString();
}
}
private Node head;
private int size;
public LinkedList(){
head = null;
size = 0;
}
// 获取链表中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在链表头添加新的元素e
public void addFirst(E e){
// Node node = new Node(e);
// node.next = head;
// head = node;
head = new Node(e, head);
size ++;
}
// 在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新的元素e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
if(index == 0)
addFirst(e);
else{
Node prev = head;
for(int i = 0 ; i < index - 1 ; i ++)
prev = prev.next;
// Node node = new Node(e);
// node.next = prev.next;
// prev.next = node;
prev.next = new Node(e, prev.next);
size ++;
}
}
// 在链表末尾添加新的元素e
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
}
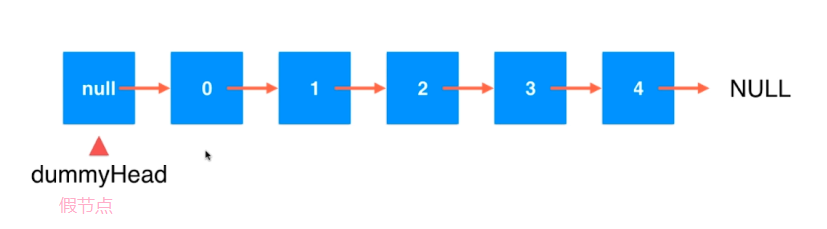
为链表设立虚拟头节点
类似于循环队列当中有意识浪费一个空间,用来规范统一插入元素
public class LinkedList<E> {
private class Node{
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e, Node next){
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e){
this(e, null);
}
public Node(){
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return e.toString();
}
}
private Node dummyHead;
private int size;
public LinkedList(){
dummyHead = new Node();
size = 0;
}
// 获取链表中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新的元素e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
Node prev = dummyHead;
for(int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++)
prev = prev.next;
prev.next = new Node(e, prev.next);
size ++;
}
// 在链表头添加新的元素e
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0, e);
}
// 在链表末尾添加新的元素e
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
}
链表元素的查询和修改
public class LinkedList<E> {
private class Node{
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e, Node next){
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e){
this(e, null);
}
public Node(){
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return e.toString();
}
}
private Node dummyHead;
private int size;
public LinkedList(){
dummyHead = new Node();
size = 0;
}
// 获取链表中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新的元素e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
Node prev = dummyHead;
for(int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++)
prev = prev.next;
prev.next = new Node(e, prev.next);
size ++;
}
// 在链表头添加新的元素e
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0, e);
}
// 在链表末尾添加新的元素e
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
// 获得链表的第index(0-based)个位置的元素
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public E get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Illegal index.");
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
for(int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++)
cur = cur.next;
return cur.e;
}
// 获得链表的第一个元素
public E getFirst(){
return get(0);
}
// 获得链表的最后一个元素
public E getLast(){
return get(size - 1);
}
// 修改链表的第index(0-based)个位置的元素为e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public void set(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Illegal index.");
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
for(int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++)
cur = cur.next;
cur.e = e;
}
// 查找链表中是否有元素e
public boolean contains(E e){
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.e.equals(e))
return true;
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
// Node cur = dummyHead.next;
// while(cur != null){
// res.append(cur + "->");
// cur = cur.next;
// }
for(Node cur = dummyHead.next ; cur != null ; cur = cur.next)
res.append(cur + "->");
res.append("NULL");
return res.toString();
}
}
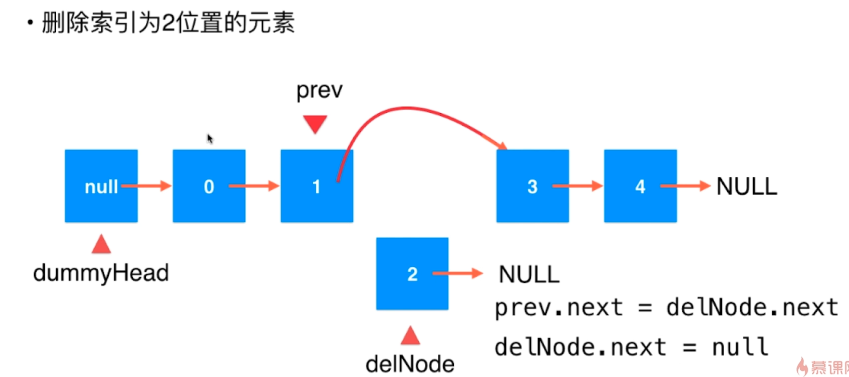
链表元素的删除
指针的指向改变,没有被指向的节点被回收
public class LinkedList<E> {
private class Node{
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e, Node next){
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e){
this(e, null);
}
public Node(){
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return e.toString();
}
}
private Node dummyHead;
private int size;
public LinkedList(){
dummyHead = new Node();
size = 0;
}
// 获取链表中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新的元素e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
Node prev = dummyHead;
for(int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++)
prev = prev.next;
prev.next = new Node(e, prev.next);
size ++;
}
// 在链表头添加新的元素e
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0, e);
}
// 在链表末尾添加新的元素e
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
// 获得链表的第index(0-based)个位置的元素
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public E get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Illegal index.");
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
for(int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++)
cur = cur.next;
return cur.e;
}
// 获得链表的第一个元素
public E getFirst(){
return get(0);
}
// 获得链表的最后一个元素
public E getLast(){
return get(size - 1);
}
// 修改链表的第index(0-based)个位置的元素为e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public void set(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Illegal index.");
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
for(int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++)
cur = cur.next;
cur.e = e;
}
// 查找链表中是否有元素e
public boolean contains(E e){
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.e.equals(e))
return true;
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
// 从链表中删除index(0-based)位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public E remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
Node prev = dummyHead;
for(int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++)
prev = prev.next;
Node retNode = prev.next;
prev.next = retNode.next;
retNode.next = null;
size --;
return retNode.e;
}
// 从链表中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
// 从链表中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
// 从链表中删除元素e
public void removeElement(E e){
Node prev = dummyHead;
while(prev.next != null){
if(prev.next.e.equals(e))
break;
prev = prev.next;
}
if(prev.next != null){
Node delNode = prev.next;
prev.next = delNode.next;
delNode.next = null;
size --;
}
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
while(cur != null){
res.append(cur + "->");
cur = cur.next;
}
res.append("NULL");
return res.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i ++){
linkedList.addFirst(i);
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
linkedList.add(2, 666);
System.out.println(linkedList);
linkedList.remove(2);
System.out.println(linkedList);
linkedList.removeFirst();
System.out.println(linkedList);
linkedList.removeLast();
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
}
链表的时间复杂度分析
添加操作 O(n)

删除操作 O(n)

修改操作 O(n)
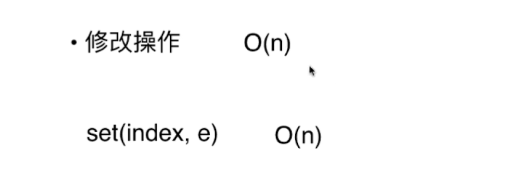
查找操作 O(n)

总结:
使用链表实现栈
public class LinkedListStack<E> implements Stack<E> {
private LinkedList<E> list;
public LinkedListStack(){
list = new LinkedList<>();
}
@Override
public int getSize(){
return list.getSize();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty(){
return list.isEmpty();
}
@Override
public void push(E e){
list.addFirst(e);
}
@Override
public E pop(){
return list.removeFirst();
}
@Override
public E peek(){
return list.getFirst();
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append("Stack: top ");
res.append(list);
return res.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedListStack<Integer> stack = new LinkedListStack<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i ++){
stack.push(i);
System.out.println(stack);
}
stack.pop();
System.out.println(stack);
}
}
链表栈和数组栈性能比较
import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
// 测试使用stack运行opCount个push和pop操作所需要的时间,单位:秒
private static double testStack(Stack<Integer> stack, int opCount){
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
Random random = new Random();
for(int i = 0 ; i < opCount ; i ++)
stack.push(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
for(int i = 0 ; i < opCount ; i ++)
stack.pop();
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
return (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int opCount = 100000;
ArrayStack<Integer> arrayStack = new ArrayStack<>();
double time1 = testStack(arrayStack, opCount);
System.out.println("ArrayStack, time: " + time1 + " s");
LinkedListStack<Integer> linkedListStack = new LinkedListStack<>();
double time2 = testStack(linkedListStack, opCount);
System.out.println("LinkedListStack, time: " + time2 + " s");
// 其实这个时间比较很复杂,因为LinkedListStack中包含更多的new操作
}
}
运行结果
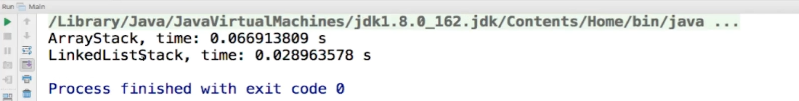
总结:
new 对象过程比较耗时,因为要在内存中找到可以开辟空间的地方。但是数组当中添加和移除元素并重新维护整个数组比较耗时。
数据量越大,反而链表栈的时间会长
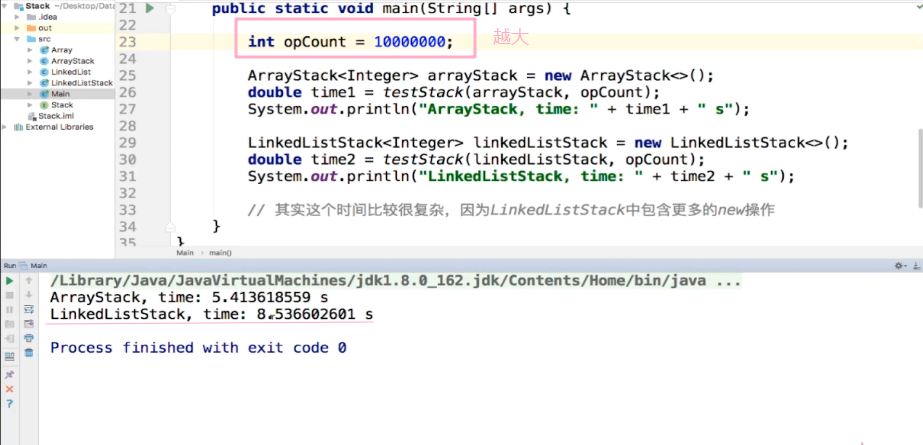
数组栈和链表栈同一复杂度,差异不是很大。巨大差异,才影响性能。
使用链表实现队列
从尾节点删除元素不是很容易
改进:从head端删除元素,从tail端插入元素
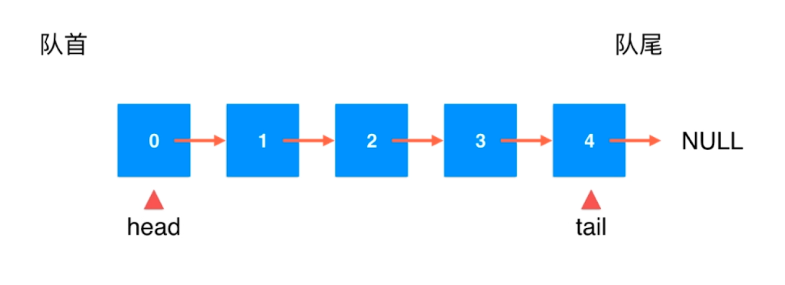
由于没有dummyHead,要注意链表为空的情况(可以自己实现)
public class LinkedListQueue<E> implements Queue<E> {
private class Node{
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e, Node next){
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e){
this(e, null);
}
public Node(){
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return e.toString();
}
}
private Node head, tail;
private int size;
public LinkedListQueue(){
head = null;
tail = null;
size = 0;
}
@Override
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
@Override
public void enqueue(E e){
if(tail == null){
tail = new Node(e);
head = tail;
}
else{
tail.next = new Node(e);
tail = tail.next;
}
size ++;
}
@Override
public E dequeue(){
if(isEmpty())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot dequeue from an empty queue.");
Node retNode = head;
head = head.next;
retNode.next = null;
if(head == null)
tail = null;
size --;
return retNode.e;
}
@Override
public E getFront(){
if(isEmpty())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Queue is empty.");
return head.e;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append("Queue: front ");
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
res.append(cur + "->");
cur = cur.next;
}
res.append("NULL tail");
return res.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
LinkedListQueue<Integer> queue = new LinkedListQueue<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++){
queue.enqueue(i);
System.out.println(queue);
if(i % 3 == 2){
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
}
}
数组队列和循环队列和链表队列的比较
import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
// 测试使用q运行opCount个enqueueu和dequeue操作所需要的时间,单位:秒
private static double testQueue(Queue<Integer> q, int opCount){
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
Random random = new Random();
for(int i = 0 ; i < opCount ; i ++)
q.enqueue(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
for(int i = 0 ; i < opCount ; i ++)
q.dequeue();
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
return (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int opCount = 100000;
ArrayQueue<Integer> arrayQueue = new ArrayQueue<>();
double time1 = testQueue(arrayQueue, opCount);
System.out.println("ArrayQueue, time: " + time1 + " s");
LoopQueue<Integer> loopQueue = new LoopQueue<>();
double time2 = testQueue(loopQueue, opCount);
System.out.println("LoopQueue, time: " + time2 + " s");
LinkedListQueue<Integer> linkedListQueue = new LinkedListQueue<>();
double time3 = testQueue(linkedListQueue, opCount);
System.out.println("LinkedListQueue, time: " + time3 + " s");
}
}
运行结果:
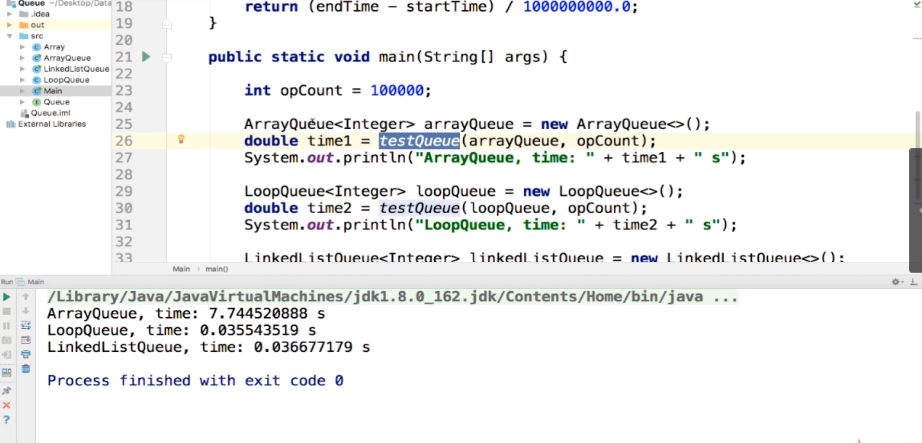
总结:
循环队列和链表队列的复杂度差异不大,数组队列差异巨大。