1、已知2个一维数组:a[]={3,4,5,6,7},b[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7};把数组a与数组b对应的元素乘积再赋值给数组b,如:b[2]=a[2]*b[2];最后输出数组b的元素。
public static void main(String[] args){ int[] a=new int[]{3,4,5,6,7}; int[] b=new int[]{1,2,3,4,5,6,7}; for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){ b[i]=a[i]*b[i]; } for(int k:b){System.out.print(k+" ");} }
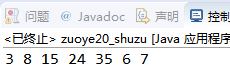
2、找出如下数组中最大的元素和最小的元素,a[][]={{3,2,6},{6,8,2,10},{5},{12,3,23}}
public static void main(String[] args){ int[][] a=new int[][]{{3,2,6},{6,8,2,10},{5},{12,3,23}}; int[] b=new int[11]; int c=0; for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){ for(int j=0;j<a[i].length;j++){ b[c]=a[i][j]; c++; } } Arrays.sort(b); for(int k:b){ System.out.print(k+" "); } System.out.println("最大的数是:"+b[b.length-1]); System.out.println("最小的数是:"+b[0]); }

第二种方法:
public static void main(String[] args){ int[][] a=new int[][]{{3,2,6},{6,8,2,10},{5},{12,3,23}}; int max=a[0][0]; int min=a[0][0]; for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){ for(int j=0;j<a[i].length;j++){ if(a[i][j]>max){ max=a[i][j]; } if(a[i][j]<min){ min=a[i][j]; } } } System.out.println("最大的数是:"+max); System.out.println("最小的数是:"+min); } }
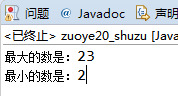
3、按要求编写Java应用程序。编写一个名为Test的主类,类中只有一个主方法;在主方法中定义一个大小为50的一维整型数组,数组名为x,数组中存放着{1,3,5,…,99}输出这个数组中的所有元素,每输出十个换一行;在主方法中定义一个大小为10*10的二维字符型数组,数组名为y,正反对角线上存的是‘*’,其余位置存的是‘#’;输出这个数组中的所有元素。
public static void main(String[] args){ int[] x = new int[50]; for(int i=0;i<50;i++){ x[i]=2*i+1; if(i==10 || i==20 || i==30 || i==40 || i==50){ System.out.println(); } System.out.print(x[i]+" "); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("10*10二维数组:"); char[][] y = new char[10][10]; for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ for(int j=0;j<10;j++){ if(i==j||j==(9-i)){ y[i][j]='#'; } else{ y[i][j]='*'; } } } for(char[] temp:y){ for(char temp2:temp){ System.out.print(temp2); } System.out.println(); } } }

4、从键盘上输入一个正整数n,请按照以下五行杨辉三角形的显示方式,输出杨辉三角形的前n行。请采用循环控制语句来实现。(三角形腰上的数为1,其他位置的数为其上一行相邻两个数之和。)
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
1 5 10 10 5 1
import java.util.Scanner; public class zuoye21_yanghuisanjiao { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("打印杨辉三角,请输入n的值:"); int n=sc.nextInt(); int[][] array = new int[n][n]; for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){ for(int j=0;j<=i;j++){ if(j==0 || j==i){ array[i][j]=1; } else if(i>=2&&j>=1) { array[i][j]=array[i-1][j-1]+array[i-1][j]; } if(array[i][j]!=0){ System.out.print(array[i][j]+" "); } } System.out.println(); } } }

二、类和对象——认识类和对象
1、编写Java应用程序。首先,定义描述学生的类——Student,包括学号(int)、姓名(String)、年龄(int)等属性;二个方法:Student(int stuNo,String name,int age)用于对对象的初始化,outPut()用于输出学生信息。其次,再定义一个主类——TestClass,在主类的main方法中创建多个Student类的对象,使用这些对象来测试Student类的功能。
Student类:
public class Student { int stuNo; String name; int age; void student(){ this.stuNo=stuNo; this.name=name; this.age=age; } void outPut(){ System.out.println("学号:"+stuNo+"姓名:"+name+"年龄:"+age); } }
TestStudent对象:
public class TestStudent { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 Student a= new Student(); a.stuNo=2013657213; a.name="张三"; a.age=24; a.outPut(); } }

2、编写一个Java应用程序,该应用程序包括2个类:Print类和主类E。Print类里有一个方法output()功能是输出100 ~ 999之间的所有水仙花数(各位数字的立方和等于这个三位数本身,如: 371 = 33 + 73 + 13。)在主类E的main方法中来测试类Print。
Print类:
public class Print { void output(){ for(int i=100;i<=999;i++){ int a=i/100; int b=(i%100)/10; int c=i%10; if(Math.pow(a,3)+Math.pow(b,3)+Math.pow(c,3)==i){ System.out.println(i); } } } }
E对象:
public class E { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 Print e=new Print(); e.output(); } }

3、编写Java应用程序。首先,定义一个Print类,它有一个方法void output(int x),如果x的值是1,在控制台打印出大写的英文字母表;如果x的值是2,在控制台打印出小写的英文字母表。其次,再定义一个主类——TestClass,在主类的main方法中创建Print类的对象,使用这个对象调用方法output ()来打印出大小写英文字母表。
Print1类:
public class Print1 { int x; void output(){ switch (x){ case 1:
System.out.println("ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"); break; case 2: System.out.println("abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"); break; } } }
Test对象:
public class TestPrint01 { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 Print1 a=new Print1(); a.x=1; a.output(); } }

4、按要求编写Java应用程序。
(1)建立一个名叫Cat的类:
属性:姓名、毛色、年龄
行为:显示姓名、喊叫
(2)编写主类:
创建一个对象猫,姓名为“妮妮”,毛色为“灰色”,年龄为2岁,在屏幕上输
出该对象的毛色和年龄,让该对象调用显示姓名和喊叫两个方法。
Cat类:
public class Cat { String name; String color; int age; void showcolor(){ System.out.println("毛色为:"+color); } void showage(){ System.out.println("年龄为:"+age); } void showname(){ System.out.println("姓名为:"+name); } void hanjiao(){ System.out.println("喵喵喵....."); } }
Catmao对象:
public class catmao { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 Cat a = new Cat(); a.age=2; a.color="灰色"; a.name="妮妮"; a.showname(); a.showcolor(); a.showage(); a.hanjiao(); } }
