一、IO流类图结构
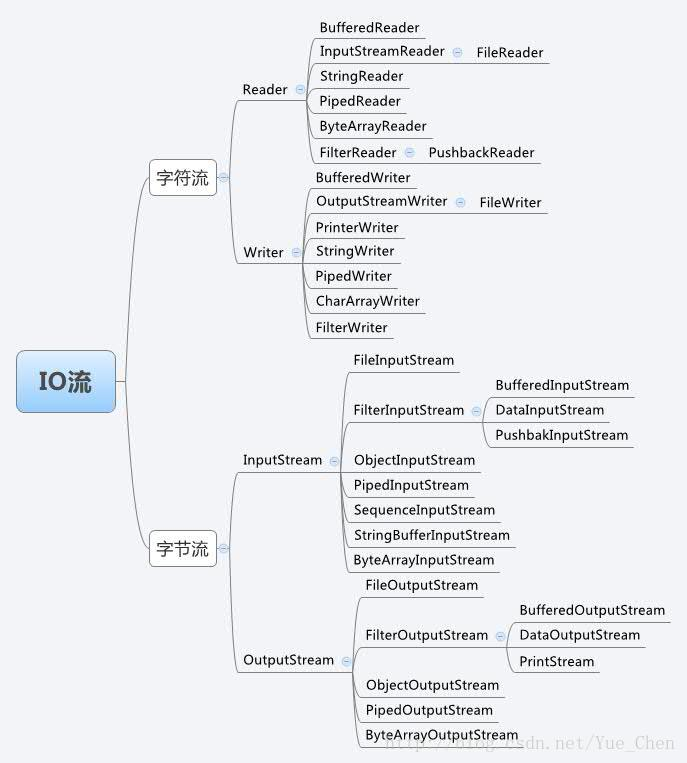
二、字节流
1、输入字节流 InputStream
OutputStream是所有的输出字节流的父类,它是一个抽象类。ByteArrayInputStream、StringBufferInputStream、FileInputStream是三种基本的介质流,它们分别从Byte 数组、StringBuffer、和本地文件中读取数据。PipedInputStream是从与其它线程共用的管道中读取数据ObjectInputStream和所有FilterInputStream的子类都是装饰流(装饰器模式的主角)
2、输出字节流 OutputStream
OutputStream是所有的输出字节流的父类,它是一个抽象类。ByteArrayOutputStream、FileOutputStream是两种基本的介质流,它们分别向Byte 数组、和本地文件中写入数据。PipedOutputStream是向与其它线程共用的管道中写入数据。ObjectOutputStream和所有FilterOutputStream的子类都是装饰流。
三、常用节点流
节点流:直接与数据源相连,读入或读出。
- 父 类 :
InputStream、OutputStream、Reader、Writer - 文 件 :
FileInputStream、FileOutputStrean、FileReader、FileWriter文件进行处理的节点流 - 数 组 :
ByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream、CharArrayReader、CharArrayWriter对数组进行处理的节点流(对应的不再是文件,而是内存中的一个数组) - 字符串 :
StringReader、StringWriter对字符串进行处理的节点流 - 管 道 :
PipedInputStream、PipedOutputStream、PipedReader、PipedWriter对管道进行处理的节点
四、常用的处理流
处理流:处理流和节点流一块使用,在节点流的基础上,再套接一层,套接在节点流上的就是处理流。如BufferedReader.处理流的构造方法总是要带一个其他的流对象做参数。一个流对象经过其他流的多次包装,称为流的链接。
- 缓冲流:
BufferedInputStrean、BufferedOutputStream、BufferedReader、BufferedWriter增加缓冲功能,避免频繁读写硬盘。 - 转换流:
InputStreamReader、OutputStreamReader实现字节流和字符流之间的转换。 - 数据流:
DataInputStream、DataOutputStream等-提供将基础数据类型写入到文件中,或者读取出来。
五、字节流常用方法说明及举例
1、FileInputStream / FileOutputStream
(1)构造方法
FileInputStream public FileInputStream(File file) //通过打开一个到实际文件的连接来创建一个 FileInputStream,该文件通过文件系统中的 File 对象 file 指定。 public FileInputStream(String name) //通过打开一个到实际文件的连接来创建一个 FileInputStream,该文件通过文件系统中的路径名 name 指定。 FileOutputStream public FileOutputStream(File file) //通过打开一个到实际文件的连接来创建一个 FileInputStream,该文件通过文件系统中的 File 对象 file 指定。 public FileOutputStream(String name) //通过打开一个到实际文件的连接来创建一个 FileInputStream,该文件通过文件系统中的路径名 name 指定。
(2)常用方法
FileInputStream public abstract int read() throws IOException: //一次读取一个字节; 返回:下一个数据字节;如果已到达文件末尾,则返回 -1。 public int read(byte[] b) throws IOException: //一次读取一个字节数组 (读取实际的字节数) 指定字节数组的长度是:1024或者1024的倍数 ;返回:读入缓冲区的字节总数,如果因为已经到达文件末尾而没有更多的数据,则返回 -1。 public void close() throws IOException //关闭此文件输入流并释放与此流有关的所有系统资源。 FileInputStream public void write(int b) throws IOException: //一次写一个字节 b- 要写入的字节。 public int write(byte[] b) throws IOException: //一次写一个字节数组 public void close() throws IOException //关闭此文件输入流并释放与此流有关的所有系统资源。
(3) 举例
public class FileInputStreamDemo { public void demo() throws Exception{ FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("fis.txt") ; int by = 0 ; while((by=fis.read())!=-1) { System.out.print((char)by); } fis.close(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt") ; //FileNotFoundException // 使用流对象给文件中写入数据 fos.write("hello".getBytes()); //关闭资源 /** * 1)将文件和流对象不建立关系了 (fos对象不指向fos.txt) * 2)及时释放掉流对象所占用的内存空间 */ fos.close(); /** * 如果关闭流对象了,那么就不能对流对象进行操作了 */ } } //使用FileInputStream和FileOutputStream实现文件的复制 import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; /** * 使用文件输入流和文件输出流实现文件的复制 * @author Administrator * */ public class SummaryFISAndFOS { public static void main(String[] args){ /** * 1.先将文件中的内容读入到输入流中 * 2.将输入流中的数据通过输出流写入到目标文件中 * 3.关闭输入流和输出流 */ try { long begin=System.currentTimeMillis(); //从输入流中读取数据 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("FOSDemo.txt"); //向输出流中写入数据 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("FISAndFOSDest.txt"); //先定义一个字节缓冲区,减少I/O次数,提高读写效率 byte[] buffer=new byte[10240]; int size=0; while((size=fis.read(buffer))!=-1){ f os.write(buffer, 0, size); } fis.close(); fos.close(); long end=System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("使用文件输入流和文件输出流实现文件的复制完毕!耗时:"+(end-begin)+"毫秒"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //解决JNI问题(Java Native Interface) System.exit(0); } }
2、FilterInputStream/FilterOutputStream (装饰模式、过滤字节流) 装饰模式说明链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/xinye/p/3910149.html
FilterInputStream 构造方法: protected FilterInputStream(InputStream in)
1)、 FilterInputStream <--------- BufferedInputStream 缓冲流
FilterOutputStream <--------- BufferedOutputStream
(1) 构造方法
BufferedInputStream public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) //指定大小缓冲流 BufferedOutputStream public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size)
(2)常用方法
BufferedInputStream public void close() throws IOException public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException public synchronized int read() throws IOException public synchronized int available() throws IOException //判断是否可以读取下个字节 BufferedOutputStream public synchronized void write(int b) throws IOException public synchronized void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException public synchronized void flush() throws IOException
(3)举例
/** * BufferedInputStream 测试程序 * * @author skywang */ public class BufferedInputStreamTest { private static final int LEN = 5; public static void main(String[] args) { testBufferedInputStream() ; } /** * BufferedInputStream的API测试函数 */ private static void testBufferedInputStream() { // 创建BufferedInputStream字节流,内容是ArrayLetters数组 try { File file = new File("bufferedinputstream.txt"); InputStream in =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file), 512); // 从字节流中读取5个字节。“abcde”,a对应0x61,b对应0x62,依次类推... for (int i=0; i<LEN; i++) { // 若能继续读取下一个字节,则读取下一个字节 if (in.available() >= 0) { // 读取“字节流的下一个字节” int tmp = in.read(); System.out.printf("%d : 0x%s ", i, Integer.toHexString(tmp)); } } // 若“该字节流”不支持标记功能,则直接退出 if (!in.markSupported()) { System.out.println("make not supported!"); return ; } // 标记“当前索引位置”,即标记第6个位置的元素--“f” // 1024对应marklimit in.mark(1024); // 跳过22个字节。 in.skip(22); // 读取5个字节 byte[] buf = new byte[LEN]; in.read(buf, 0, LEN); // 将buf转换为String字符串。 String str1 = new String(buf); System.out.printf("str1=%s ", str1); // 重置“输入流的索引”为mark()所标记的位置,即重置到“f”处。 in.reset(); // 从“重置后的字节流”中读取5个字节到buf中。即读取“fghij” in.read(buf, 0, LEN); // 将buf转换为String字符串。 String str2 = new String(buf); System.out.printf("str2=%s ", str2); in.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SecurityException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } /** * BufferedOutputStream 测试程序 * * @author skywang */ public class BufferedOutputStreamTest { private static final int LEN = 5; // 对应英文字母“abcddefghijklmnopqrsttuvwxyz” private static final byte[] ArrayLetters = { 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x65, 0x66, 0x67, 0x68, 0x69, 0x6A, 0x6B, 0x6C, 0x6D, 0x6E, 0x6F, 0x70, 0x71, 0x72, 0x73, 0x74, 0x75, 0x76, 0x77, 0x78, 0x79, 0x7A }; public static void main(String[] args) { testBufferedOutputStream() ; } /** * BufferedOutputStream的API测试函数 */ private static void testBufferedOutputStream() { // 创建“文件输出流”对应的BufferedOutputStream // 它对应缓冲区的大小是16,即缓冲区的数据>=16时,会自动将缓冲区的内容写入到输出流。 try { File file = new File("out.txt"); OutputStream out =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file), 16); // 将ArrayLetters数组的前10个字节写入到输出流中 out.write(ArrayLetters, 0, 10); // 将“换行符 ”写入到输出流中 out.write(' '); // TODO! //out.flush(); readUserInput() ; out.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SecurityException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 读取用户输入 */ private static void readUserInput() { System.out.println("please input a text:"); Scanner reader=new Scanner(System.in); // 等待一个输入 String str = reader.next(); System.out.printf("the input is : %s ", str); } }
2)FilterInputStream <--------- PrintStream 输出打印流
1、构造方法
PrintStream(OutputStream out) PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush) //将“输出流out”作为PrintStream的输出流,自动flush,采用charsetName字符集。 PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush, String charsetName) //创建file对应的FileOutputStream,然后将该FileOutputStream作为PrintStream的输出流,不自动flush,采用默认字符集。 PrintStream(File file) //创建file对应的FileOutputStream,然后将该FileOutputStream作为PrintStream的输出流,不自动flush,采用charsetName字符集 PrintStream(File file, String charsetName //创建fileName对应的FileOutputStream,然后将该FileOutputStream作为PrintStream的输出流,不自动flush,采用默认字符集。 PrintStream(String fileName) //创建fileName对应的FileOutputStream,然后将该FileOutputStream作为PrintStream的输出流,不自动flush,采用charsetName字符集 PrintStream(String fileName, String charsetName)
2、常用方法
public void println(<T>) PrintStream append(char c) // 将“字符序列从start(包括)到end(不包括)的全部字符”追加到“PrintStream输出流中” PrintStream append(CharSequence charSequence, int start, int end) // 将“字符序列的全部字符”追加到“PrintStream输出流中” PrintStream append(CharSequence charSequence) // flush“PrintStream输出流缓冲中的数据”,并检查错误 boolean checkError() // 关闭“PrintStream输出流” synchronized void close() // flush“PrintStream输出流缓冲中的数据”。 // 例如,PrintStream装饰的是FileOutputStream,则调用flush时会将数据写入到文件中 synchronized void flush() // 根据“Locale值(区域属性)”来格式化数据 PrintStream format(Locale l, String format, Object... args) // 根据“默认的Locale值(区域属性)”来格式化数据 PrintStream format(String format, Object... args)
3、举例
/** * PrintStream 的示例程序 * * @author skywang */ public class PrintStreamTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // 下面3个函数的作用都是一样:都是将字母“abcde”写入到文件“file.txt”中。 // 任选一个执行即可! testPrintStreamConstrutor1() ; //testPrintStreamConstrutor2() ; //testPrintStreamConstrutor3() ; // 测试write(), print(), println(), printf()等接口。 testPrintStreamAPIS() ; } /** * PrintStream(OutputStream out) 的测试函数 * * 函数的作用,就是将字母“abcde”写入到文件“file.txt”中 */ private static void testPrintStreamConstrutor1() { // 0x61对应ASCII码的字母'a',0x62对应ASCII码的字母'b', ... final byte[] arr={0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x65 }; // abced try { // 创建文件“file.txt”的File对象 File file = new File("file.txt"); // 创建文件对应FileOutputStream PrintStream out = new PrintStream( new FileOutputStream(file)); // 将“字节数组arr”全部写入到输出流中 out.write(arr); // 关闭输出流 out.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * PrintStream(File file) 的测试函数 * * 函数的作用,就是将字母“abcde”写入到文件“file.txt”中 */ private static void testPrintStreamConstrutor2() { final byte[] arr={0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x65 }; try { File file = new File("file.txt"); PrintStream out = new PrintStream(file); out.write(arr); out.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * PrintStream(String fileName) 的测试函数 * * 函数的作用,就是将字母“abcde”写入到文件“file.txt”中 */ private static void testPrintStreamConstrutor3() { final byte[] arr={0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x65 }; try { PrintStream out = new PrintStream("file.txt"); out.write(arr); out.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 测试write(), print(), println(), printf()等接口。 */ private static void testPrintStreamAPIS() { // 0x61对应ASCII码的字母'a',0x62对应ASCII码的字母'b', ... final byte[] arr={0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x65 }; // abced try { // 创建文件对应FileOutputStream PrintStream out = new PrintStream("other.txt"); // 将字符串“hello PrintStream”+回车符,写入到输出流中 out.println("hello PrintStream"); // 将0x41写入到输出流中 // 0x41对应ASCII码的字母'A',也就是写入字符'A' out.write(0x41); // 将字符串"65"写入到输出流中。 // out.print(0x41); 等价于 out.write(String.valueOf(0x41)); out.print(0x41); // 将字符'B'追加到输出流中 out.append('B'); // 将"CDE is 5" + 回车 写入到输出流中 String str = "CDE"; int num = 5; out.printf("%s is %d ", str, num); out.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
3、ByteArrayInputStream / ByteArrayOutputStream (内存流)
1)构造方法
ByteArrayInputStream public ByteArrayInputStream(byte[] buf) public ByteArrayInputStream(byte[] buf, int offset, int length) ByteArrayOutputStream public ByteArrayOutputStream() public ByteArrayOutputStream(int size)
2)常用方法
ByteArrayInputStream public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len) public synchronized int read() public void close() throws IOException ByteArrayOutputStream public synchronized void write(int b) public synchronized void write(byte b[], int off, int len) public synchronized byte toByteArray() public synchronized String toString() public void close() throws IOException
3)举例
/* * 1 */ public class Test { public static void readByteArray(String msg) { ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null; ByteArrayInputStream bais = null; try { baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); baos.write(msg.getBytes()); baos.flush(); bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(baos.toByteArray()); byte[] b = new byte[1024]; int len = bais.read(b); System.out.println("len:" + len); String str = new String(b, 0, len); System.out.println("str:" + str); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (baos != null) { baos.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { String msg = "hello world"; readByteArray(msg); } } /* * 2 */ import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Arrays; /** * 内存流: * ByteArrayInputStream * ByteArrayOutputSteam */ public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); try { // 将内容写入到内存 baos.write("写个啥".getBytes()); baos.flush(); // baos.toByteArray(); byte[] bs =new byte[20]; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bs)); // 将内存中的数据读取出来 ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(bs);// byte必须传递 内存中的数据转成 byte数组的格式 // 而不能直接传递一个空数组, 读取出来的数据也是空的 byte[] b = new byte[10]; int num = bais.read(b); System.err.println(Arrays.toString(b)); System.out.println(num); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }
4、ObjectOutputStream/ObjectInputStream (序列化与反序列)
1)构造方法
ObjectOutputStream public ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out) ObjectInputStream public ObjectInputStream(InputStream in)
2)举例
class User implements Serializable{//必须实现Serializable接口 String uid; String pwd; public User(String _uid,String _pwd){ this.uid = _uid; this.pwd = _pwd; } @Override public String toString() { return "账号:"+this.uid+" 密码:"+this.pwd; } } public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //假设将对象信息写入到obj.txt文件中,事先已经在硬盘中建立了一个obj.txt文件 File f = new File("F:\obj.txt"); writeObjec(f); System.out.println("OK"); } //定义方法把对象的信息写到硬盘上------>对象的序列化。 public static void writeObjec(File f) throws IOException{ FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(f);//创建文件字节输出流对象 ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(outputStream); objectOutputStream.writeObject(new User("酒香逢","123")); //最后记得关闭资源,objectOutputStream.close()内部已经将outputStream对象资源释放了,所以只需要关闭objectOutputStream即可 objectOutputStream.close(); } } public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { //假设将对象信息写入到obj.txt文件中,事先已经在硬盘中建立了一个obj.txt文件 File f = new File("F:\obj.txt"); //writeObjec(f); readObject(f); System.out.println("OK"); } //定义方法把对象的信息写到硬盘上------>对象的序列化。 public static void writeObjec(File f) throws IOException{ FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(f);//创建文件字节输出流对象 ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(outputStream); objectOutputStream.writeObject(new User("酒香逢","123")); //最后记得关闭资源,objectOutputStream.close()内部已经将outputStream对象资源释放了,所以只需要关闭objectOutputStream即可 objectOutputStream.close(); } //把文件中的对象信息读取出来-------->对象的反序列化 public static void readObject(File f) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{ FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(f);//创建文件字节输出流对象 ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(inputStream); User user = (User)objectInputStream.readObject(); System.out.println(user); } }