主要利用状态之间的转换吧,可以把各个状态之间的转换成矩阵,利用矩阵乘法来找出有多少条路径。题解转自:
http://blog.csdn.net/morgan_xww/article/details/7834801
•题意:有m种DNA序列是有疾病的,问有多少种长度为n的DNA序列不包含任何一种有疾病的DNA序列。(仅含A,T,C,G四个字符)
•样例m=4,n=3,{“AA”,”AT”,”AC”,”AG”}
•答案为36,表示有36种长度为3的序列可以不包含疾病
这个和矩阵有什么关系呢???
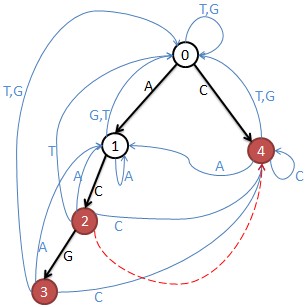
•上图是例子{“ACG”,”C”},构建trie图后如图所示,从每个结点出发都有4条边(A,T,C,G)
•从状态0出发走一步有4种走法:
–走A到状态1(安全);
–走C到状态4(危险);
–走T到状态0(安全);
–走G到状态0(安全);
•所以当n=1时,答案就是3
•当n=2时,就是从状态0出发走2步,就形成一个长度为2的字符串,只要路径上没有经过危险结点,有几种走法,那么答案就是几种。依此类推走n步就形成长度为n的字符串。
•建立trie图的邻接矩阵M:
2 1 0 0 1
2 1 1 0 0
1 1 0 1 1
2 1 0 0 1
2 1 0 0 1
M[i,j]表示从结点i到j只走一步有几种走法。
那么M的n次幂就表示从结点i到j走n步有几种走法。
注意:危险结点要去掉,也就是去掉危险结点的行和列。结点3和4是单词结尾所以危险,结点2的fail指针指向4,当匹配”AC”时也就匹配了”C”,所以2也是危险的。
矩阵变成M:
2 1
2 1
计算M[][]的n次幂,然后 Σ(M[0,i]) mod 100000 就是答案。
由于n很大,可以使用二分来计算矩阵的幂
自己写的代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <climits>
#include <string.h>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#define LL __int64
using namespace std;
const int dictsize=4;
const int QN=1000;
const int root=0;
const LL MOD=100000;
int ID[130];
int head,tail;
int que[QN];
struct Node {
int fail,next[dictsize];
bool tag;
void initial(){
fail=-1,tag=false;
for(int i=0;i<dictsize;i++) next[i]=-1;
}
}trie[150];
int tot,n,l;
char str[15];
struct Matrix{
LL mat[105][105];
};
Matrix a,per;
Matrix operator *(Matrix a,Matrix b){
Matrix c;
for(int i=0;i<=tot;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=tot;j++){
c.mat[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<=tot;k++)
c.mat[i][j]=(c.mat[i][j]+a.mat[i][k]*b.mat[k][j])%MOD;
}
}
return c;
}
void Insert_trie(){
int p=0,i=0;
while(str[i]){
if(trie[p].next[ID[str[i]]]==-1) trie[p].next[ID[str[i]]]=++tot;
p=trie[p].next[ID[str[i]]];
i++;
}
trie[p].tag=true;
}
void build_ac(){
que[tail++]=root;
int i,tmp,p;
while(head!=tail){
tmp=que[head++];
p=-1;
for(int i=0;i<dictsize;i++){
if(trie[tmp].next[i]!=-1){
if(tmp==root) trie[trie[tmp].next[i]].fail=root;
else{
p=trie[tmp].fail;
while(p!=-1){
if(trie[p].next[i]!=-1){
trie[trie[tmp].next[i]].fail=trie[p].next[i];
break;
}
p=trie[p].fail;
}
if(p==-1){
trie[trie[tmp].next[i]].fail=root;
}
}
if(trie[trie[trie[tmp].next[i]].fail].tag){
trie[trie[tmp].next[i]].tag=true;
}
que[tail++]=trie[tmp].next[i];
}
else{ //trie[tmp].next[i]==-1
if(tmp==root) trie[tmp].next[i]=root;
else{
p=trie[tmp].fail;
while(p!=-1){
if(trie[p].next[i]!=-1){
trie[tmp].next[i]=trie[p].next[i];
break;
}
p=trie[p].fail;
}
if(p==-1){
trie[tmp].next[i]=root;
}
}
}
}
}
}
void build_map(){
memset(a.mat,0,sizeof(a.mat));
for(int i=0;i<=tot;i++){
for(int j=0;j<dictsize;j++){
if(!trie[i].tag&&!trie[trie[i].next[j]].tag)
a.mat[i][trie[i].next[j]]++;
}
}
}
Matrix multi(int k){
Matrix ans,p=a;
memset(ans.mat,0,sizeof(ans.mat));
for(int i=0;i<=tot;i++)
ans.mat[i][i]=1;
while(k){
if(k&1) ans=ans*p;
k>>=1;
p=p*p;
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
ID['A']=0,ID['G']=1,ID['C']=2,ID['T']=3;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&l)!=EOF){
tot=head=tail=0;
for(int i=0;i<110;i++)
trie[i].initial();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%s",str);
Insert_trie();
}
build_ac();
build_map();
Matrix ans=multi(l);
LL print=0;
for(int i=0;i<=tot;i++)
print=(print+ans.mat[0][i])%MOD;
printf("%I64d
",print);
}
return 0;
}