Labyrinth
Time limit: 1.0 second
Memory limit: 64 MB
Memory limit: 64 MB
Administration
of the labyrinth has decided to start a new season with new wallpapers.
For this purpose they need a program to calculate the surface area of
the walls inside the labyrinth. This job is just for you!
The labyrinth is represented by a matrix N×N (3 ≤ N
≤ 33, you see, ‘3’ is a magic digit!). Some matrix cells contain a dot
character (‘.’) that denotes an empty square. Other cells contain a
diesis character (‘#’) that denotes a square filled by monolith block of
stone wall. All squares are of the same size 3×3 meters.
The
walls are constructed around the labyrinth (except for the upper left
and lower right corners, which are used as entrances) and on the cells
with a diesis character. No other walls are constructed. There always
will be a dot character at the upper left and lower right corner cells
of the input matrix.
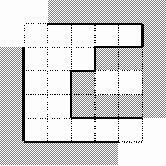
Your
task is to calculate the area of visible part of the walls inside the
labyrinth. In other words, the area of the walls' surface visible to a
visitor of the labyrinth. Note that there's no holes to look or to move
through between any two adjacent blocks of the wall. The blocks are
considered to be adjacent if they touch each other in any corner. See
picture for an example: visible walls inside the labyrinth are drawn
with bold lines. The height of all the walls is 3 meters.
Input
The first line of the input contains the single number N. The next N lines contain N
characters each. Each line describes one row of the labyrinth matrix.
In each line only dot and diesis characters will be used and each line
will be terminated with a new line character. There will be no spaces in
the input.
Output
Your program should print to the output a single integer — the exact value of the area of the wallpaper needed.
Sample
| input | output |
|---|---|
5 ..... ...## ..#.. ..### ..... |
198 |
Problem Author: Vladimir Pinaev
【分析】简单BFS,先从起点出发,遇到#边ans就++;存在不连通情况,所以要从终点再找一遍,最后减去两个角的四条边。

#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <time.h> #include <string> #include <map> #include <stack> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <queue> #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define mod 10000 typedef long long ll; using namespace std; const int N=35; const int M=100005; int n,m,k,ans=0,t,cnt; int vis[N][N]; int d[4][2]={0,1,1,0,-1,0,0,-1}; char w[N][N]; struct man{ int x,y; }; void bfs(int x,int y) { queue<man>q; vis[x][y]=1; man s;s.x=x;s.y=y; q.push(s); while(!q.empty()){ man t=q.front();q.pop(); for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int xx=t.x+d[i][0]; int yy=t.y+d[i][1]; if(xx<0||xx>=n||yy<0||yy>=n)ans++; else if(w[xx][yy]=='#')ans++; else if(!vis[xx][yy]){ man k;k.x=xx;k.y=yy; q.push(k); vis[xx][yy]=1; } } } } int main() { scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ scanf("%s",w[i]); } bfs(0,0); if(!vis[n-1][n-1])bfs(n-1,n-1); printf("%d ",(ans-4)*9); return 0; }
