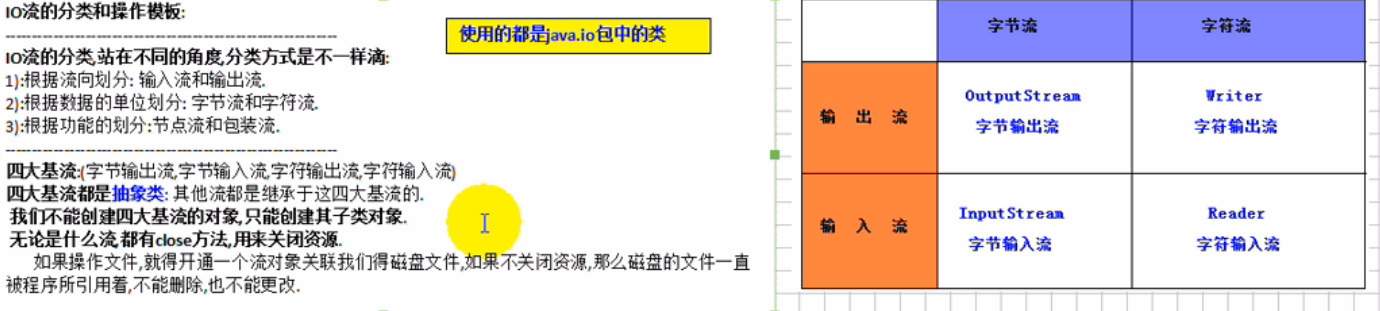
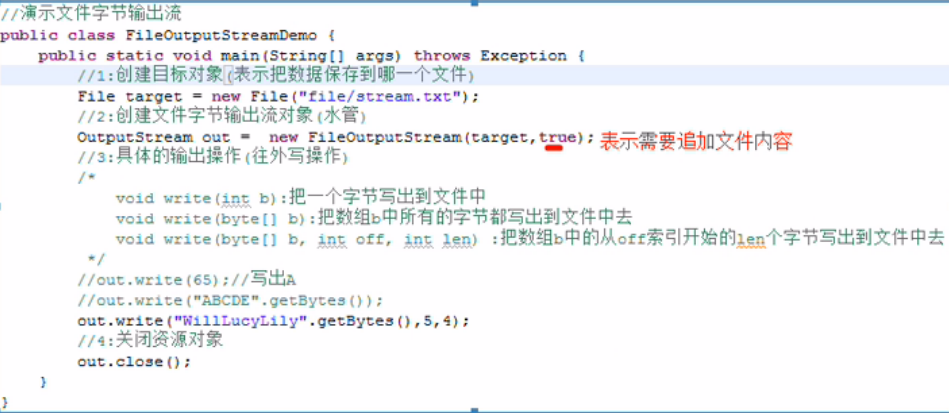


public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建源
File f =new File("file/stream.txt");
//创建文件字节输入流
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(f);
//具体读取操作
/*
* 如果读取到最后没有,就返回-1;
* int read() 读取一个字节
* int read(byte[] b) 读取多个字节并且存储到b数组中,从数组0开始存
* int read(byte[] ,int off,int len) 读取多个字节,从数组的Off开始读取位置到len读取的结束位置
*/
//in.read();获取该文件的第一个字节
byte[] b=new byte[5];//创建一个byte字节数组,用来存放数据
// int d=in.read(b);//返回的是这个文件中存储的字节长度
// String str=new String(b,0,d);//把字节数组转换成字符串,从开始位置一直读到最后位置
// System.out.println(str);
int len=-1;
while((len=in.read(b))>0){
String str =new String(b,0,len);
System.out.println(str);
}
//关闭资源文件
in.close();
}
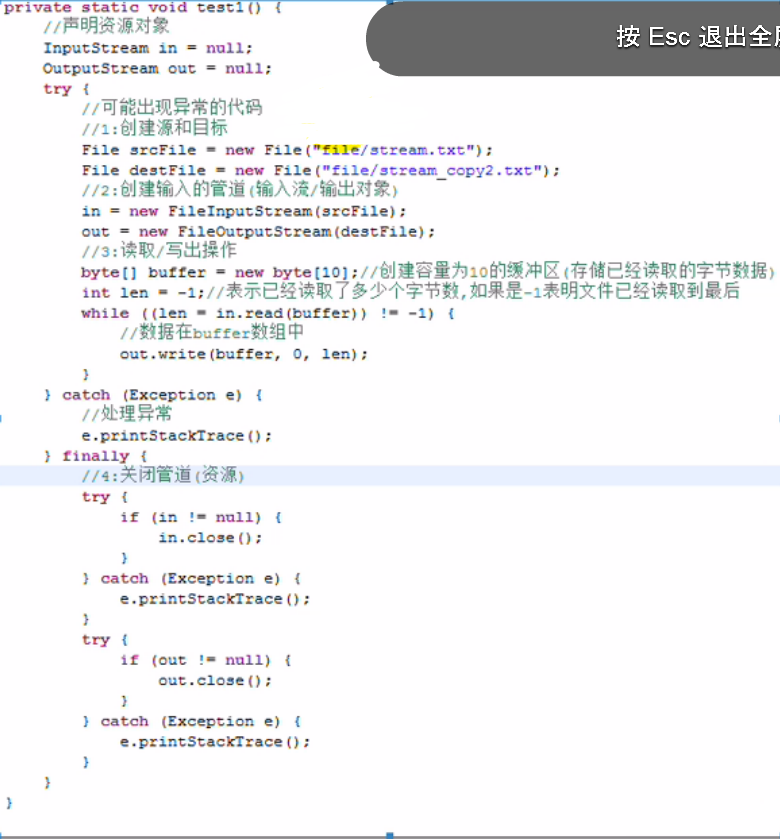
从Java 7开始的自动资源关闭
private static void text2() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
File f = new File("file/stream.txt");
File cp = new File("file/copy.txt");
try (
//打开资源代码
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(f); FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(cp, true);) {
//可能出现的异常
byte[] content = new byte[5];
int len = -1;
while ((len = in.read(content)) != -1) {
String text = new String(content, 0, len);
out.write(text.getBytes());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}