Once upon a time a child got a test consisting of multiple-choice questions as homework. A multiple-choice question consists of four choices: A, B, C and D. Each choice has a description, and the child should find out the only one that is correct.
Fortunately the child knows how to solve such complicated test. The child will follow the algorithm:
- If there is some choice whose description at least twice shorter than all other descriptions, or at least twice longer than all other descriptions, then the child thinks the choice is great.
- If there is exactly one great choice then the child chooses it. Otherwise the child chooses C (the child think it is the luckiest choice).
You are given a multiple-choice questions, can you predict child's choose?
The first line starts with "A." (without quotes), then followed the description of choice A. The next three lines contains the descriptions of the other choices in the same format. They are given in order: B, C, D. Please note, that the description goes after prefix "X.", so the prefix mustn't be counted in description's length.
Each description is non-empty and consists of at most 100 characters. Each character can be either uppercase English letter or lowercase English letter, or "_".
Print a single line with the child's choice: "A", "B", "C" or "D" (without quotes).
A.VFleaKing_is_the_author_of_this_problem
B.Picks_is_the_author_of_this_problem
C.Picking_is_the_author_of_this_problem
D.Ftiasch_is_cute
D
A.ab
B.abcde
C.ab
D.abc
C
A.c
B.cc
C.c
D.c
B
In the first sample, the first choice has length 39, the second one has length 35, the third one has length 37, and the last one has length 15. The choice D (length 15) is twice shorter than all other choices', so it is great choice. There is no other great choices so the child will choose D.
In the second sample, no choice is great, so the child will choose the luckiest choice C.
In the third sample, the choice B (length 2) is twice longer than all other choices', so it is great choice. There is no other great choices so the child will choose B.
题意:四个字符串除去前面的两个字符,长度大于等于其余的两倍,长度小于等于其余的1/2;
如果唯一输出那个选项,否则输出C;
思路:模拟;
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long #define pi (4*atan(1.0)) const int N=5e5+10,M=4e6+10,inf=1e9+10; int a[10]; char ch[110]; int da,xiao; int check() { int ans=0; for(int i=1;i<=4;i++) { int flag1=0,flag2=0; for(int t=1;t<=4;t++) { if(i==t)continue; if(a[i]>=2*a[t]) flag1++; if(2*a[i]<=a[t]) flag2++; } if(flag1==3) ans++,da=i; if(flag2==3) ans++,xiao=i; } return ans; } int main() { int x,y,z,i,t; for(i=1;i<=4;i++) { scanf("%s",&ch); a[i]=strlen(ch)-2; } if(check()==1) { if(da) printf("%c ",'A'+da-1); else printf("%c ",xiao-1+'A'); } else printf("C "); return 0; }
At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite set of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers something about his set S:
- its elements were distinct integers from 1 to limit;
- the value of
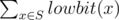 was equal to sum; here lowbit(x) equals 2k where k is the position of the first one in the binary representation of x. For example, lowbit(100102) = 102, lowbit(100012) = 12, lowbit(100002) = 100002 (binary representation).
was equal to sum; here lowbit(x) equals 2k where k is the position of the first one in the binary representation of x. For example, lowbit(100102) = 102, lowbit(100012) = 12, lowbit(100002) = 100002 (binary representation).
Can you help Picks and find any set S, that satisfies all the above conditions?
The first line contains two integers: sum, limit (1 ≤ sum, limit ≤ 105).
In the first line print an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105), denoting the size of S. Then print the elements of set S in any order. If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
If it's impossible to find a suitable set, print -1.
5 5
2
4 5
4 3
3
2 3 1
5 1
-1
In sample test 1: lowbit(4) = 4, lowbit(5) = 1, 4 + 1 = 5.
In sample test 2: lowbit(1) = 1, lowbit(2) = 2, lowbit(3) = 1, 1 + 2 + 1 = 4.
题意:用lowbit(i) 1<=i<=limit;选出一些数的和得到sum;
思路:lowbit函数得到的肯定是2的次方;从大往小减,得到答案,详见代码;
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long #define pi (4*atan(1.0)) const int N=5e5+10,M=4e6+10,inf=1e9+10; int a[50]={1,2,4,8,16,32,64,128,256,512,1024,2048,4096,8192,16384,32768,65536,131072,262144,524288}; vector<int>v[50]; int flag[50]; int ans[50]; int lowbit(int x) { return x&-x; } int main() { int x,y,z,i,t,len=0,base=1,sum=0; scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); for(int i=1;i<=y;i++) v[lower_bound(a,a+20,lowbit(i))-a].push_back(i); for(i=524288;i>=1;i/=2) { if(x<i)continue; int pos=lower_bound(a,a+20,i)-a; int si=v[pos].size(); ans[pos]=min(si,x/i); sum+=ans[pos]; x-=ans[pos]*i; } if(x) printf("-1 "); else { printf("%d ",sum); for(i=0;i<20;i++) if(ans[i]) { for(t=0;t<ans[i];t++) printf("%d ",v[i][t]); } } return 0; }
On Children's Day, the child got a toy from Delayyy as a present. However, the child is so naughty that he can't wait to destroy the toy.
The toy consists of n parts and m ropes. Each rope links two parts, but every pair of parts is linked by at most one rope. To split the toy, the child must remove all its parts. The child can remove a single part at a time, and each remove consume an energy. Let's define an energy value of part i as vi. The child spend vf1 + vf2 + ... + vfk energy for removing part i where f1, f2, ..., fk are the parts that are directly connected to the i-th and haven't been removed.
Help the child to find out, what is the minimum total energy he should spend to remove all n parts.
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000; 0 ≤ m ≤ 2000). The second line contains n integers: v1, v2, ..., vn(0 ≤ vi ≤ 105). Then followed m lines, each line contains two integers xi and yi, representing a rope from part xi to part yi(1 ≤ xi, yi ≤ n; xi ≠ yi).
Consider all the parts are numbered from 1 to n.
Output the minimum total energy the child should spend to remove all n parts of the toy.
4 3
10 20 30 40
1 4
1 2
2 3
40
4 4
100 100 100 100
1 2
2 3
2 4
3 4
400
7 10
40 10 20 10 20 80 40
1 5
4 7
4 5
5 2
5 7
6 4
1 6
1 3
4 3
1 4
160
One of the optimal sequence of actions in the first sample is:
- First, remove part 3, cost of the action is 20.
- Then, remove part 2, cost of the action is 10.
- Next, remove part 4, cost of the action is 10.
- At last, remove part 1, cost of the action is 0.
So the total energy the child paid is 20 + 10 + 10 + 0 = 40, which is the minimum.
In the second sample, the child will spend 400 no matter in what order he will remove the parts.
题意:给你一个图,n个点,m条边,每次拆一个点的消耗为与其直接相连的点的权值和吗,求最小的消耗;
思路:贪心,去每条边两点权值最小值即可;
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long //#define mod 1000000007 #define pi (4*atan(1.0)) const int N=1e5+10,M=1e6+10,inf=1e9+10; int a[N]; int main() { int x,y,z,i,t; while(~scanf("%d%d",&x,&y)) { for(i=1;i<=x;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]); ll ans=0; for(i=1;i<=y;i++) { int u,v; scanf("%d%d",&u,&v); ans+=min(a[u],a[v]); } printf("%lld ",ans); } return 0; }