Java 中的 this
this 这个关键字,相当于普通话里的“我”
小明说 “我吃了” 这个时候,“我” 代表小明
小红说 “我吃了” 这个时候,“我” 代表小红
"我"代表当前人物
步骤 1 : this代表当前对象
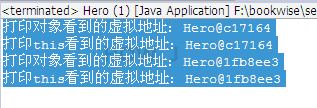
public class Hero {
String name; //姓名
float hp; //血量
float armor; //护甲
int moveSpeed; //移动速度
//打印内存中的虚拟地址
public void showAddressInMemory(){
System.out.println("打印this看到的虚拟地址:"+this);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hero garen = new Hero();
garen.name = "盖伦";
//直接打印对象,会显示该对象在内存中的虚拟地址
//格式:Hero@c17164 c17164即虚拟地址,每次执行,得到的地址不一定一样
System.out.println("打印对象看到的虚拟地址:"+garen);
//调用showAddressInMemory,打印该对象的this,显示相同的虚拟地址
garen.showAddressInMemory();
Hero teemo = new Hero();
teemo.name = "提莫";
System.out.println("打印对象看到的虚拟地址:"+teemo);
teemo.showAddressInMemory();
}
}
步骤 2 : 通过this访问属性
通过this关键字访问对象的属性
public class Hero {
String name; //姓名
float hp; //血量
float armor; //护甲
int moveSpeed; //移动速度
//参数名和属性名一样
//在方法体中,只能访问到参数name
public void setName1(String name){
name = name;
}
//为了避免setName1中的问题,参数名不得不使用其他变量名
public void setName2(String heroName){
name = heroName;
}
//通过this访问属性
public void setName3(String name){
//name代表的是参数name
//this.name代表的是属性name
this.name = name;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hero h =new Hero();
h.setName1("teemo");
System.out.println(h.name);
h.setName2("garen");
System.out.println(h.name);
h.setName3("死歌");
System.out.println(h.name);
}
}
步骤 3 : 通过this调用其他的构造方法
如果要在一个构造方法中,调用另一个构造方法,可以使用this()
public class Hero {
String name; //姓名
float hp; //血量
float armor; //护甲
int moveSpeed; //移动速度
//带一个参数的构造方法
public Hero(String name){
System.out.println("一个参数的构造方法");
this.name = name;
}
//带两个参数的构造方法
public Hero(String name,float hp){
this(name);
System.out.println("两个参数的构造方法");
this.hp = hp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hero teemo = new Hero("提莫",383);
System.out.println(teemo.name);
}
}
练习: 构造方法(this)
(设计一个构造方法,参数分别是
String name
float hp
float armor
int moveSpeed
不仅如此,在这个构造方法中,调用这个构造方法
public Hero(String name,float hp))
答案:
public class Hero {
String name; // 姓名
float hp; // 血量
float armor; // 护甲
int moveSpeed; // 移动速度
// 带一个参数的构造方法
public Hero(String name) {
System.out.println("一个参数的构造方法");
this.name = name;
}
// 带两个参数的构造方法
public Hero(String name, float hp) {
this(name);
System.out.println("两个参数的构造方法");
this.hp = hp;
}
// 带有四个参数的构造方法
public Hero(String name, float hp, float armor, int moveSpeed) {
this(name,hp);
this.armor = armor;
this.moveSpeed = moveSpeed;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hero teemo = new Hero("提莫", 383);
System.out.println(teemo.name);
Hero db = new Hero("死哥",400,27,360);
System.out.println(db.moveSpeed);
}
}