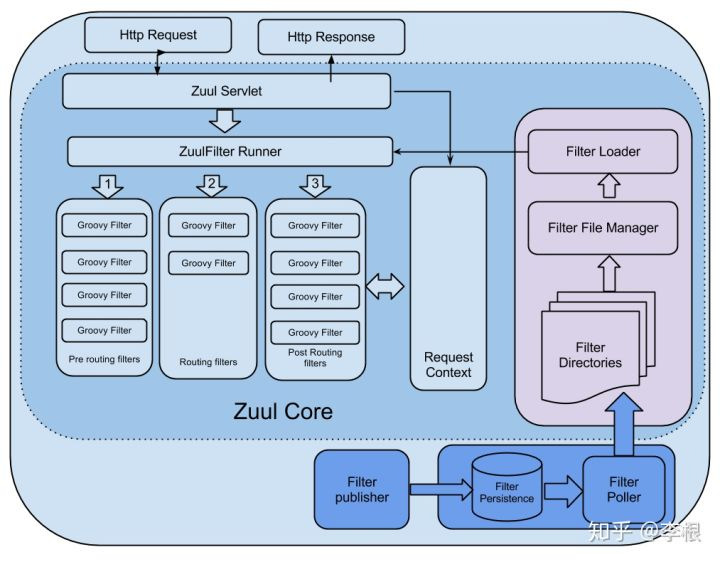
先上一张流程图:
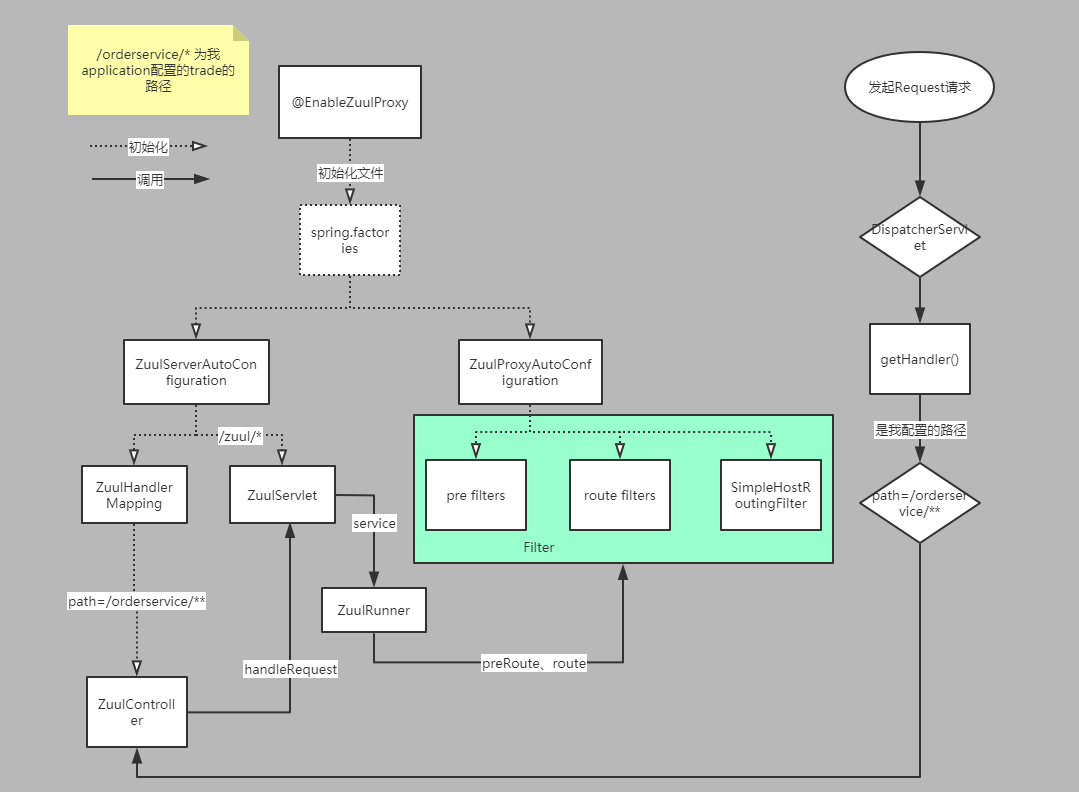
我们Zuul的使用如下:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableZuulProxy
public class ZuulApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ZuulApplication.class);
}
}
application.properties配置:
zuul.routes.study-trade.service-id=study-trade
zuul.routes.study-trade.path=/orderservice/**
-
从我们的开启Zuul注解@EnableZuulProxy开始看起,这个比较简单,就是引入了ZuulProxyMarkerConfiguration.Marker这个Bean。
-
再找到Zuul这个包下面的spring.factories这个文件,里面有两个类,我们看一下
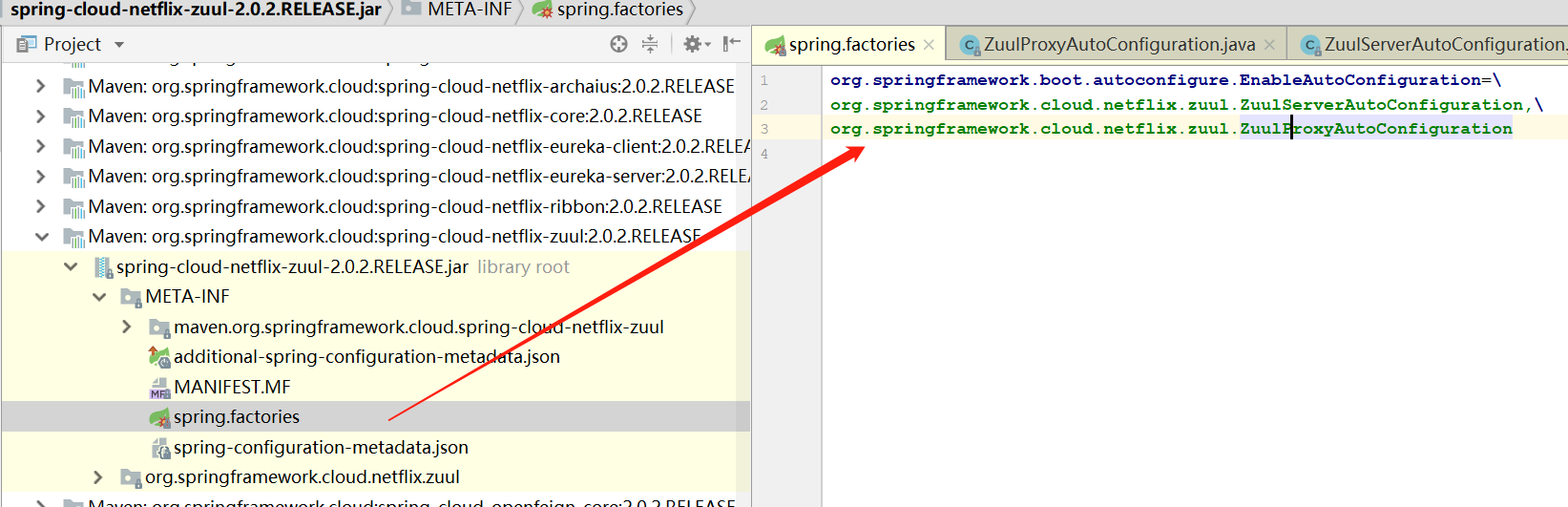
-
有一个是ZuulServerAutoConfiguration类,它里面初始化了ZuulHandlerMapping,ZuulController,ZuulServlet。还有一个zuulProperties变量,它会将我们application.yml文件里配置的路由映射规则读进来
-
而另一个类ZuulProxyAutoConfiguration,他重要的一点是会初始化RibbonRoutingFilter,PreDecorationFilter,SimpleHostRoutingFilter
-
以上就是应用初始化相关的准备
-
当我们请求过来时会怎么样呢?
我使用orderservice前缀来访问study-trade服务:http://localhost:8000/orderservice/trade/testTrade/3
7. 请求发送过来走到ZuulHandlerMapping,并调用到registerHandlers方法,routes就是我application.yml里配置的映射关系
private void registerHandlers() {
Collection<Route> routes = this.routeLocator.getRoutes();
if (routes.isEmpty()) {
this.logger.warn("No routes found from RouteLocator");
}
else {
for (Route route : routes) {
//注册到
registerHandler(route.getFullPath(), this.zuul);
}
}
}
- 在走到DispatcherServlet里的doDispatch方法,然后使用ZuulController取处理请求
//mappedHandler.getHandler()就是ZuulController
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
- ZuulController接收到请求,会使用ZuulServlet来处理请求,他的service方法如下:
public void service(javax.servlet.ServletRequest servletRequest, javax.servlet.ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
init((HttpServletRequest) servletRequest, (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse);
// Marks this request as having passed through the "Zuul engine", as opposed to servlets
// explicitly bound in web.xml, for which requests will not have the same data attached
RequestContext context = RequestContext.getCurrentContext();
context.setZuulEngineRan();
try {
preRoute();
} catch (ZuulException e) {
error(e);
postRoute();
return;
}
try {
route();
} catch (ZuulException e) {
error(e);
postRoute();
return;
}
try {
postRoute();
} catch (ZuulException e) {
error(e);
return;
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
error(new ZuulException(e, 500, "UNHANDLED_EXCEPTION_" + e.getClass().getName()));
} finally {
RequestContext.getCurrentContext().unset();
}
}
可以看出他里面调用了preRoute,postRoute,route。我们自己定义的Filter也是通过这里的代码得以执行的。
10. 点开ZuulServlet的preRoute等这几个方法时,看到他其实又是使用ZuulRunner来处理的
void preRoute() throws ZuulException {
zuulRunner.preRoute();
}
void init(HttpServletRequest servletRequest, HttpServletResponse servletResponse) {
zuulRunner.init(servletRequest, servletResponse);
}
- 以preRoute()方法为例,它里面又是使用了FilterProcessor.getInstance()来处理方法,看 FilterProcessor.getInstance()样子,感觉是一个单例,点进去看了下,确实是使用了饿汉模式的单例。
public void preRoute() throws ZuulException {
FilterProcessor.getInstance().preRoute();
}
- 接下来一起探究下FilterProcessor类吧
public void preRoute() throws ZuulException {
try {
runFilters("pre");
} catch (ZuulException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new ZuulException(e, 500, "UNCAUGHT_EXCEPTION_IN_PRE_FILTER_" + e.getClass().getName());
}
}
public Object runFilters(String sType) throws Throwable {
if (RequestContext.getCurrentContext().debugRouting()) {
Debug.addRoutingDebug("Invoking {" + sType + "} type filters");
}
boolean bResult = false;
//找到相应sType的ZuulFilter集合,然后执行run方法
List<ZuulFilter> list = FilterLoader.getInstance().getFiltersByType(sType);
if (list != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
ZuulFilter zuulFilter = list.get(i);
Object result = processZuulFilter(zuulFilter);
if (result != null && result instanceof Boolean) {
bResult |= ((Boolean) result);
}
}
}
return bResult;
}
相当于是FilterProcessor从filterloader中获取zuulfilter。而zuulfilter是被filterFileManager所加载,并支持groovy热加载,采用了轮询的方式热加载。有了这些filter之后,zuulservelet首先执行的Pre类型的过滤器,再执行route类型的过滤器,最后执行的是post类型的过滤器,如果在执行这些过滤器有错误的时候则会执行error类型的过滤器。执行完这些过滤器,最终将请求的结果返回给客户端。 RequestContext就是会一直跟着整个请求周期的上下文对象,filters之间有什么信息需要传递就set一些值进去就行了。
- 那么是怎么调用其他服务的呢?其中有一个RibbonRoutingFilter,就实现了调用其他服务的方法,具体内容不表
- 附上一张更全的架构设计图