一、结果缓存
结果缓存,用于加速热门数据的访问速度,Dubbo提供声明式缓存,以减少用户加缓存的工作量。
lru 基于最近最少使用原则删除多余缓存,保持最热的数据被缓存,实现如下:
<dubbo:reference id="userService" group="*" interface="com.patty.dubbo.api.service.UserService" timeout="10000" retries="3" mock="true" check="false"> <dubbo:method name="findAllUsers" merger="myMerger" cache="lru"> </dubbo:method> </dubbo:reference>
cache="lru"表示采用lru缓存策略,运行后,可在与数据库交互的代码块上打个断点,会发现,首次请求时会穿透数据库,再次请求,则直接走dubbo缓存拿数据了。当然,实际应用中,最后还是继承redis到dubbo,实现缓存策略。
集成Redis(服务提供方):
1) pom.xml中加入redis依赖
<!-- Redis --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency>
2)配置jedis
/** * Jedis数据源配置 * * @return JedisPoolConfig */ @Bean public JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig() { JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig(); jedisPoolConfig.setMaxIdle(maxIdle); jedisPoolConfig.setMinIdle(minIdle); jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(maxWait); return jedisPoolConfig; } /** * Jedis数据连接工场 * * @return JedisConnectionFactory */ @Bean public JedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory(JedisPoolConfig poolConfig) { JedisConnectionFactory factory = new JedisConnectionFactory(); factory.setHostName(host); factory.setPort(port); factory.setTimeout(timeout); if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(password)) { factory.setPassword(password); } factory.setDatabase(database); factory.setPoolConfig(poolConfig); return factory; }
3)实现redis操作逻辑
@Component public class RedisBaseService { private Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RedisBaseService.class); @Autowired private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate; /** * 获取Set集合数据 * param key * return Set<String> */ public Set<String> getSets(String key) { return redisTemplate.opsForSet().members(key); } /** * 移除Set集合中的value * param k * param v */ public Long removeSetValue(String key, String value) { if (key == null && value == null) { return 0L; } return redisTemplate.opsForSet().remove(key, value); } /** * 保存到Set集合中 * param k * param v */ public Long setSet(String k, String v) { if (k == null && v == null) { return 0L; } return redisTemplate.opsForSet().add(k, v); } /** * 存储Map格式 * param key * param hashKey * param hashValue */ public void setMap(String key, String hashKey, Object hashValue) { redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, hashKey, hashValue); } /** * 根据key获取map对象 * param key */ public Map<Object, Object> getMap(String key) { return redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(key); } /** * 存储带有过期时间的key-value * param key * param value * param timeOut 过期时间 * param unit 时间单位 */ public void setTime(String key, String value, Long timeOut, TimeUnit unit) { if (value == null) { LOGGER.info("redis存储的value的值为空"); throw new IllegalArgumentException("redis存储的value的值为空"); } if (timeOut > 0) { redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value, timeOut, unit); } else { redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value); } } /** * 存储key-value * param key * return Object */ public void set(String key, String value) { if (value == null) { LOGGER.info("redis存储的value的值为空"); throw new IllegalArgumentException("redis存储的value的值为空"); } redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value); } /** * 根据key获取value * param key * return Object */ public String get(String key) { return redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); } /** * 判断key是否存在 * param key * return Boolean */ public Boolean exists(String key) { return redisTemplate.hasKey(key); } /** * 删除key对应的value * param key */ public void removeValue(String key) { if (exists(key)) redisTemplate.delete(key); } /** * 模式匹配批量删除key * param keyPattern */ public void removePattern(String keyPattern) { Set<String> keys = redisTemplate.keys(keyPattern); if (keys.size() > 0) redisTemplate.delete(keys); } }
4) 在业务逻辑中,加入缓存设置
/** * 根据id查询指定用户 * * @param id * @return */ public UserVo findUserById(String id) { if (redisBaseService.exists(id)) { Map<Object, Object> userMap = redisBaseService.getMap(id); return new UserVo( id, (String) userMap.get("name"), Integer.valueOf(userMap.get("age") + ""), (String) userMap.get("phoneNo")); } else { User user = userDao.findUserById(id); redisBaseService.setMap(id, "name", user.getName()); redisBaseService.setMap(id, "age", user.getAge() + ""); redisBaseService.setMap(id, "phoneNo", user.getPhoneNo()); return this.UserToUserVo(user); } }
5)具体代码参见:https://github.com/pattywgm/dubbo-demo.git
二、上下文信息
上下文中存放的是当前调用过程中所需的环境信息。RpcContext是一个ThreadLocal的临时状态记录器,当接收到RPC请求,或发起RPC请求时,RpcContext的状态都会变化。比如:A调B,B再调C,则B机器上,在B调C之前,RpcContext记录的是A调B的信息,在B调C之后,RpcContext记录的是B调C的信息。
服务提供方:
public class XxxServiceImpl implements XxxService { public void xxx() { // 服务方法实现 boolean isProviderSide = RpcContext.getContext().isProviderSide(); // 本端是否为提供端,这里会返回true String clientIP = RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost(); // 获取调用方IP地址 String application = RpcContext.getContext().getUrl().getParameter("application"); // 获取当前服务配置信息,所有配置信息都将转换为URL的参数 // ... yyyService.yyy(); // 注意:每发起RPC调用,上下文状态会变化 boolean isProviderSide = RpcContext.getContext().isProviderSide(); // 此时本端变成消费端,这里会返回false // ... } }
服务消费方:
xxxService.xxx(); // 远程调用 boolean isConsumerSide = RpcContext.getContext().isConsumerSide(); // 本端是否为消费端,这里会返回true String serverIP = RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost(); // 获取最后一次调用的提供方IP地址 String application = RpcContext.getContext().getUrl().getParameter("application"); // 获取当前服务配置信息,所有配置信息都将转换为URL的参数 // ... yyyService.yyy(); // 注意:每发起RPC调用,上下文状态会变化 // ...
三、异步调用
基于NIO的非阻塞实现并行调用,客户端不需要启动多线程即可完成并行调用多个远程服务,相对多线程开销较小。
现在我们在api包中,声明两个接口:ShoppingService和EatingService,并在服务方分别实现这两个接口,如下:
public interface EatingService { public String eating(); } @Service("eatingService") public class EatingServiceImpl implements EatingService { public EatingServiceImpl() { } @Override public String eating() { try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "Eating for 5 seconds"; } }
public interface ShoppingService { public String shopping(); } @Service("shoppingService") public class ShoppingServiceImpl implements ShoppingService { public ShoppingServiceImpl(){ } @Override public String shopping() { try { Thread.sleep(6000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "Shopping for 6 seconds"; } }
其中eatingService要运行大约5S, shoppingService运行大约6S实际。
在dubbo-provider.xml中配置这两个服务,进行注册。
<dubbo:service ref="shoppingService" interface="com.patty.dubbo.api.service.ShoppingService"/> <dubbo:service ref="eatingService" interface="com.patty.dubbo.api.service.EatingService"/>
在消费方,订阅这两个服务:
1)不采用异步调用的方式
<dubbo:reference id="shoppingService" interface="com.patty.dubbo.api.service.ShoppingService" timeout="200000" async="false"></dubbo:reference> <dubbo:reference id="eatingService" interface="com.patty.dubbo.api.service.EatingService" timeout="200000" async="false"></dubbo:reference>
@RequestMapping(value = "/doSomething", method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public String doSomething() { return "Doing: " + shoppingService.shopping(); + " " + eatingService.eating();; }
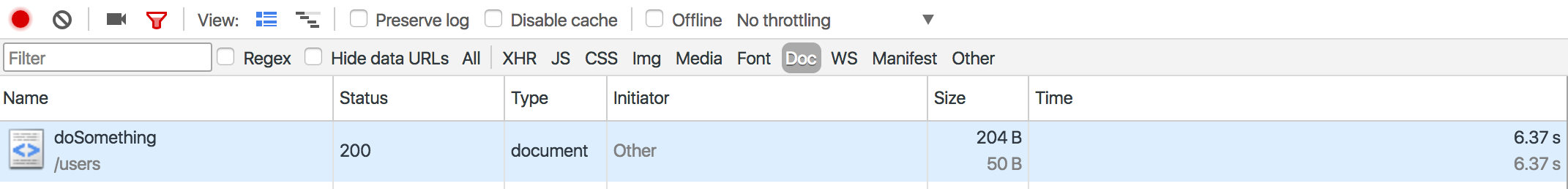
启动程序,由于未采用异步方式,整个rpc请求的返回时间大约11s左右,如图:

2)采用异步调用方式
<!-- NIO异步 --> <dubbo:reference id="shoppingService" interface="com.patty.dubbo.api.service.ShoppingService" timeout="200000" async="true"></dubbo:reference> <dubbo:reference id="eatingService" interface="com.patty.dubbo.api.service.EatingService" timeout="200000" async="true"></dubbo:reference>
@RequestMapping(value = "/doSomething", method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public String doSomething() { shoppingService.shopping(); Future<String> shoppingFuture = RpcContext.getContext().getFuture(); // 拿到调用的Future引用,当结果返回后,会被通知和设置到此Future。 eatingService.eating(); Future<String> eatingFuture = RpcContext.getContext().getFuture(); try { String doSth1 = shoppingFuture.get(); String doSth2 = eatingFuture.get(); return "Doing: " + doSth1 + " " + doSth2; } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "Doing: "; }
将async属性值设为"true", 表示采用异步调用,同时再客户端doSomething()代码块中,利用Future来承载异步返回的结果,由于是异步调用,整个调用返回的时间取决于运行时间较长的那个,本例中大概6s左右。如图: