标题中的substring方法指的是字符串的substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)方法,这个方法在jdk6,7是有差异的。
substring有什么用?
substring返回的是字符串索引位置beginIndex开始,endIndex-1结束的字符串。
来看这个例子:
String x = "abcdef";
x = x.substring(1,3);
System.out.println(x);输出:
bc下面看看在JDK之间,它们的实现原理有什么不一样,及值得注意的地方。
JDK 6
String背后是由char数组构成的,在JDK6中,String包含三个字段:char value[], int offset, int count,意思很简单。
substring被调用时,它会创建一个新的字符串,但字符串的值还指向堆中同样的字符数组。它们的区别只是数量和下标引用不一样,如图所示。
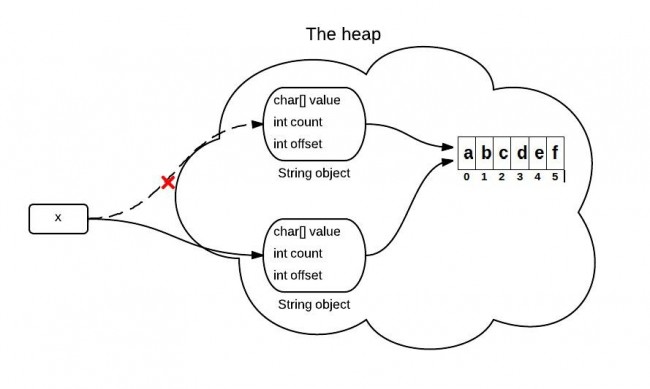
JDK6中的部分源码可以说明这个问题。
//JDK 6
String(int offset, int count, char value[]) {
this.value = value;
this.offset = offset;
this.count = count;
}
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
//check boundary
return new String(offset + beginIndex, endIndex - beginIndex, value);
}会有什么问题?
如果一个很长的字符串,但是每次使用substring(),你只需要很小的一部分。这将会导致性能问题,因为只需要一小部分,却引用了整个字符数组内容。对于JDK 6,解决方案是使用以下内容:
x = x.substring(x, y) + ""JDK 7,8
JDK6这种问题在JDK7+中已经改善了,JDK7+中实际是重新创建了一个字符数组,如图。
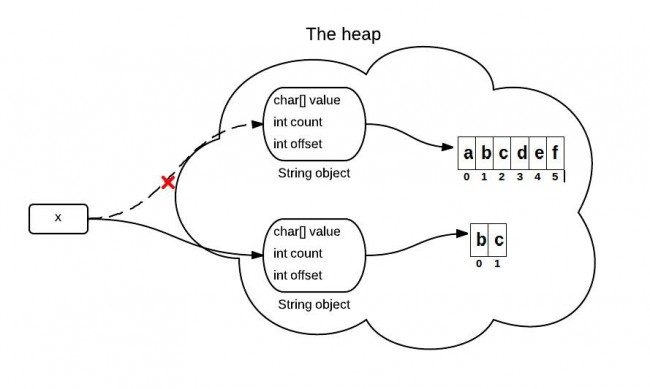
JDK7中的部分源码,JDK8类似。
//JDK 7
public String(char value[], int offset, int count) {
//check boundary
this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset + count);
}
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
//check boundary
int subLen = endIndex - beginIndex;
return new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
}对于JDK的这种差异,我们知道就好,现在应该都是JDK7及8了吧,其实对于小字符串的这种操作性能也是可以忽略不计的。
推荐阅读
分享Java干货,高并发编程,热门技术教程,微服务及分布式技术,架构设计,区块链技术,人工智能,大数据,Java面试题,以及前沿热门资讯等。