Web 项目一般给特定人群使用,有些是局域网用户量不足1K的内部系统,也有些广域网用户上万的中型项目,当然还有用户上亿的大型项目。
这些大大小小的 Web 项目都会有用户登录的存在,登录后有特定的权限,访问特定的资源。
未登录的用户无法访问系统资源,这块功能通常都是有 Filter 来进行限制。
在 Filter 中进行自由服务的配置,可以使用户在不登陆的情况下也能对特定资源进行访问。
用户认证和授权可以采用开源的第三方框架,比如 Shiro,Spring Security.......
小型项目中继承 javax.servlet.Filter 接口简单实现也是可行的方案。
最近项目中遇到一些服务需要用户在未登录的情况下,在其他移动设备上面进行操作。
怎样保证暴露在外的服务坚不可摧呢?
本篇借自己一次相似需求的实现,来分享在实践中遇到的问题和解决思路,仅当作抛砖引玉之用,文中如有什么不妥,还望看客老爷拍砖。
1. 具体业务流程
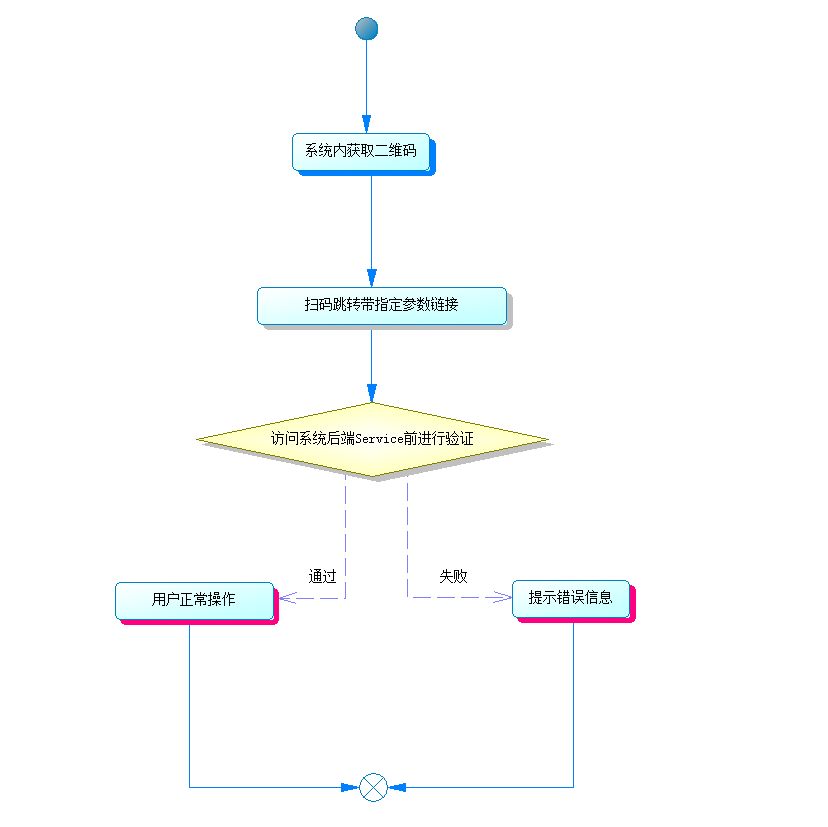
因为服务是在系统外用户未登录的情况下,在其他移动设备上面进行操作。
笔者这里的"坚不可摧"主要是指在访问后端 Service 前进行的两次保证。
1.保证服务的安全性,只提供给正确的人,并且传递参数不能被其他人轻易获取。
2.保证服务的即时性,每次生成的访问链接,只能在有限的时间段内提供服务,避免其他人截获该连接,在任何时间对该用户的资源进行操作。
2. 访问服务安全性保障初实践
访问链接的安全性保障,首当其中会想到链接后的参数加密。
加密的方式有很多,首先得排除不可逆加密(MD5、SHA、HMAC......),毕竟解密后,需要使用参数来做为操作的一些依据。
好的,再来考虑双向加密,因为是同一系统加解密,个人认为没有必要使用非对称加密算法。
最后将目光锁定在了对称加密,使用公共密钥进行加解密(BASE64 确实是有点 low,直接抹杀掉)。
常用的对称加密(DES、IDEA、RC2、RC4、SKIPJACK、RC5、AES..)中,根据项目要求或者自己喜好选用合适的算法。
至于加密算法的实现,我这里没有找第三方开源项目,使用的是 JDK JCE 框架包。
如果你对 JCE 中算法实现感兴趣,可以去读读源码。
具体业务对称加解密工具类实现:

import org.apache.commons.lang.time.DateFormatUtils; import javax.crypto.Cipher; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import java.security.Key; import java.security.Security; import java.util.Date; public class EncryptionDecryption { private static String strDefaultKey = "helloDecrypt"; private Cipher encryptCipher = null; private Cipher decryptCipher = null; public static String byteArr2HexStr(byte[] arrB) throws Exception { int iLen = arrB.length; StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(iLen * 2); for (int i = 0; i < iLen; i++) { int intTmp = arrB[i]; while (intTmp < 0) { intTmp = intTmp + 256; } if (intTmp < 16) { sb.append("0"); } sb.append(Integer.toString(intTmp, 16)); } return sb.toString(); } public static byte[] hexStr2ByteArr(String strIn) throws Exception { byte[] arrB = strIn.getBytes(); int iLen = arrB.length; byte[] arrOut = new byte[iLen / 2]; for (int i = 0; i < iLen; i = i + 2) { String strTmp = new String(arrB, i, 2); arrOut[i / 2] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(strTmp, 16); } return arrOut; } public EncryptionDecryption() throws Exception { this(strDefaultKey); } public EncryptionDecryption(String strKey) throws Exception { Security.addProvider(new com.sun.crypto.provider.SunJCE()); Key key = getKey(strKey.getBytes()); encryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES"); encryptCipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key); decryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES"); decryptCipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key); } //加密方法 public byte[] encrypt(byte[] arrB) throws Exception { return encryptCipher.doFinal(arrB); } public String encrypt(String strIn) throws Exception { return byteArr2HexStr(encrypt(strIn.getBytes())); } public byte[] decrypt(byte[] arrB) throws Exception { return decryptCipher.doFinal(arrB); } //解密方法 public String decrypt(String strIn) throws Exception { try { return new String(decrypt(hexStr2ByteArr(strIn))); } catch (Exception e) { return ""; } } private Key getKey(byte[] arrBTmp) throws Exception { byte[] arrB = new byte[8]; for (int i = 0; i < arrBTmp.length && i < arrB.length; i++) { arrB[i] = arrBTmp[i]; } return new javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec(arrB, "DES"); } /** *Description:将业务需要的参数,加密为字符串 */ public static String encrypt(String parm1, String pam2) { String resStr = null; try { EncryptionDecryption des = new EncryptionDecryption("定义的公钥"); if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(parm1) && StringUtil.isNotEmpty(pam2)) { resStr = des.encrypt(parm1 + "," + pam2 + "," + DateFormatUtils.format(new Date(),"yyyyMMddHHmm")); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return resStr; } }
3. 访问服务即时性保障初实践
如上述描述的,仅单纯的保证了链接的安全性,还不能满足当前项目要求。
还需要将每次生成的访问链接,只能在有限的时间段内提供服务,避免其他人截获该连接,在任何时间对该用户的资源进行操作。
具体序列图:
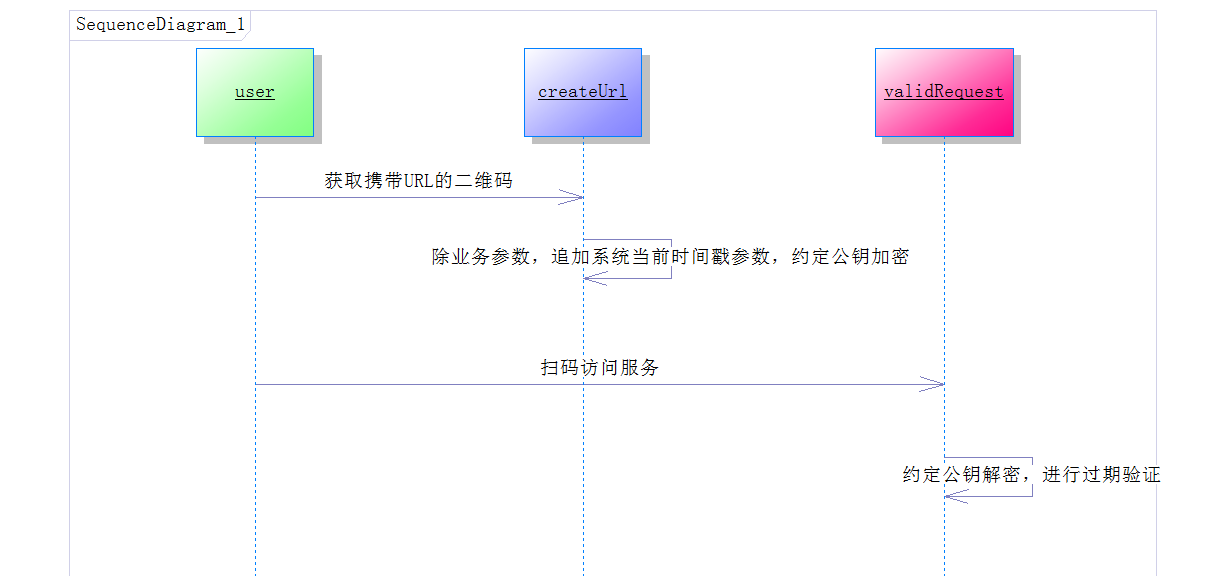
追加系统当前时间戳参数:
public static String encrypt(String parm1, String pam2) { String resStr = null; try { EncryptionDecryption des = new EncryptionDecryption("定义的公钥"); if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(parm1) && StringUtil.isNotEmpty(pam2)) { resStr = des.encrypt(parm1 + "," + pam2 + "," + DateFormatUtils.format(new Date(),"yyyyMMddHHmm")); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return resStr; }
在项目中最小粒度判断到分钟既可以,当然你也可以根据具体需求将时间戳粒度调整到秒或者毫秒级别。
约定公钥解密,进行过期验证:
private Boolean hasInvalidRequest(String param) { EncryptionDecryption encryptionDecryption = new EncryptionDecryption("定义的公钥"); String requestDate = encryptionDecryption.decrypt(param).split(",")[5]; if (requestDate.length() != 12) { return Boolean.TRUE; } Date nowDate = new Date(); int nowTime_yyyyMMdd = Integer.parseInt(DateFormatUtils.format(nowDate, "yyyyMMdd")); int requestTime_yyyyMMdd = Integer.parseInt(requestDate.substring(0, 8)); if (nowTime_yyyyMMdd > requestTime_yyyyMMdd) { return Boolean.TRUE; } int nowTime_HHmm = Integer.parseInt(DateFormatUtils.format(nowDate, "HHmm")); int requestTime_HHmm = Integer.parseInt(requestDate.substring(8)); if (nowTime_HHmm - requestTime_HHmm > Configutil.getConfig("valid_request_time")) { return Boolean.TRUE; } return Boolean.FALSE; }
判断长度,判断年月日,判断分秒,这里转为 Int 没有用Float 对比的原因,其一是不好驾驭,其二是代码不简洁。
有效的时间间隔,放到配置文件当中,因为这里是需求变动的敏感点,统一配置,代码不动,方便管理。
