Beans
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Submission(s): 1819 Accepted Submission(s): 921
Problem Description
Bean-eating is an interesting game, everyone owns an M*N matrix, which is filled with different qualities beans. Meantime, there is only one bean in any 1*1 grid. Now you want to eat the beans and collect the qualities, but everyone must obey by the following rules: if you eat the bean at the coordinate(x, y), you can’t eat the beans anyway at the coordinates listed (if exiting): (x, y-1), (x, y+1), and the both rows whose abscissas are x-1 and x+1.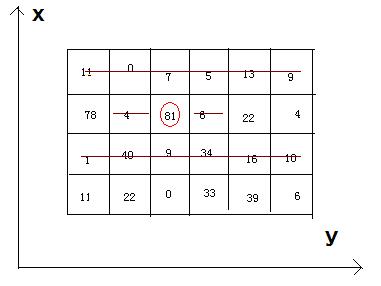

Input
There are a few cases. In each case, there are two integer M (row number) and N (column number). The next M lines each contain N integers, representing the qualities of the beans. We can make sure that the quality of bean isn't beyond 1000, and 1<=M*N<=200000.
Output
For each case, you just output the MAX qualities you can eat and then get.
Sample Input
4 6
11 0 7 5 13 9
78 4 81 6 22 4
1 40 9 34 16 10
11 22 0 33 39 6
Sample Output
242
Source
Recommend
gaojie
把二维按行列分解然后dp。
dp[i][0] 表示不取第i个能到的最大值
所以dp[i][0] = Max(dp[i-1][0],dp[i-1][1]);
dp[i][1] 表示取第i个能到的最大值
所以dp[i][1] = dp[i-1][0]+value[i];
row[i]记录下每一行的最优情况,然后再按照上面的方法进行dp
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> using namespace std; const int N=200010; int m,n; int dp[N][2],val[N],row[N]; int main(){ //freopen("input.txt","r",stdin); while(~scanf("%d%d",&m,&n)){ memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp)); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){ scanf("%d",&val[j]); dp[j][0]=max(dp[j-1][0],dp[j-1][1]); dp[j][1]=dp[j-1][0]+val[j]; } row[i]=max(dp[n][0],dp[n][1]); } for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ dp[i][0]=max(dp[i-1][0],dp[i-1][1]); dp[i][1]=dp[i-1][0]+row[i]; } printf("%d\n",max(dp[m][0],dp[m][1])); } return 0; }
挺有意思的题。 吃了一个豆豆后,上下2行的豆豆都不能吃。这个很关键,突破口就在这。那我们只要考虑一行最多能吃多少,然后得到每行最多能吃多少。这样得到的m个数排成一行,就很之前求一行的一样了,就是如果前面一个吃了,后面的就不能再吃,也就是不能相邻。这道题和树形DP那道 不能和有直接关系的上级一起出席聚会的题很像。 所以对于一行还说,状态表示dp[i][j],j要么取0,要么取1,表示第i个数取了没。
状态转移就是dp[i][0]=max(dp[i-1][0],dp[i-1][1]) dp[i][1]=dp[i-1][0]+val[i]
这道题只给出了M*N,不可能用2个数定一个位置。所以就用了dp[i][j],1<=i<=M*N j=0,1
得到每行的最大值后(max(dp[i][0],dp[i][1]),i=n*k),再对这些最大值dp,方法一样,状态的第一个参数也是MAX,因为N可能为1.
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> const int maxn=200010; int dp_row[maxn][2]; int dp_col[maxn][2]; int max(int a,int b){ return a>b?a:b; } int main(){ //freopen("input.txt","r",stdin); int m,n; while(scanf("%d%d",&m,&n)!=EOF){ memset(dp_row,0,sizeof(dp_row)); memset(dp_col,0,sizeof(dp_col)); int tmp; for(int i=1;i<=m*n;i++){ scanf("%d",&tmp); if(i%n==1){ dp_row[i][0]=0; dp_row[i][1]=tmp; }else{ dp_row[i][0]=max(dp_row[i-1][0],dp_row[i-1][1]); dp_row[i][1]=dp_row[i-1][0]+tmp; } } for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ dp_col[i][0]=max(dp_col[i-1][0],dp_col[i-1][1]); dp_col[i][1]=dp_col[i-1][0]+max(dp_row[i*n][0],dp_row[i*n][1]); } printf("%d\n",max(dp_col[m][0],dp_col[m][1])); } return 0; }