我的LeetCode:https://leetcode-cn.com/u/ituring/
我的LeetCode刷题源码[GitHub]:https://github.com/izhoujie/Algorithmcii
LeetCode 138. 复制带随机指针的链表
题目
给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
要求返回这个链表的 深拷贝。
我们用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
- val:一个表示 Node.val 的整数。
- random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从 0 到 n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为 null 。
示例 1:

输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
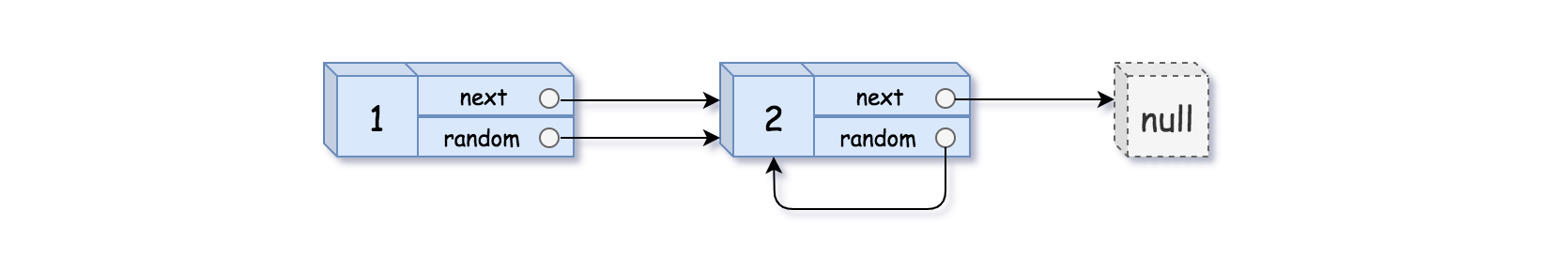
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
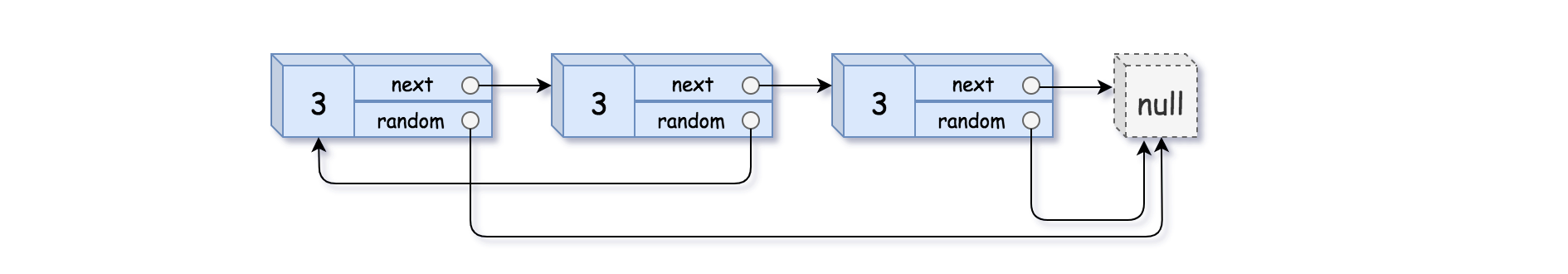
输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
示例 4:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
解释:给定的链表为空(空指针),因此返回 null。
提示:
- -10000 <= Node.val <= 10000
Node.random 为空(null)或指向链表中的节点。
节点数目不超过 1000 。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解题思路
思路1-使用HashMap
思路解析:HashMap保存新建节点与原节点的对应关系;
然后再补充新节点random节点的数据;
需要使用额外的HashMap空间;
算法复杂度:
- 时间复杂度: $ {color{Magenta}{Omicronleft(n ight)}} $
- 空间复杂度: $ {color{Magenta}{Omicronleft(n ight)}} $
思路2-直接在原节点后复制新节点/增殖,然后剥离出新节点;
思路解析:
- 利用next和next.next的指向调整复制并把新节点连接到原节点的后面,紧邻复制;
- 然后复制原节点的random到新节点,复制完成后剥离出新链表;
这里未用到额外的空间;
算法复杂度: - 时间复杂度: $ {color{Magenta}{Omicronleft(n ight)}} $
- 空间复杂度: $ {color{Magenta}{Omicronleft(1 ight)}} $
算法源码示例
package leetcode;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* @author ZhouJie
* @date 2020年5月12日 下午2:25:54
* @Description: 138. 复制带随机指针的链表
*
*/
public class LeetCode_0138 {
}
//Definition for a Node.
class Node_0138 {
int val;
Node_0138 next;
Node_0138 random;
public Node_0138(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
class Solution_0138 {
/**
* @author: ZhouJie
* @date: 2020年3月14日 下午5:42:59
* @param: @param head
* @param: @return
* @return: Node_0138
* @Description: 1-map哈希表;
*
*/
public Node_0138 copyRandomList_1(Node_0138 head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
HashMap<Node_0138, Node_0138> map = new HashMap<Node_0138, Node_0138>();
for (Node_0138 node = head; node != null; node = node.next) {
map.put(node, new Node_0138(node.val));
}
for (Node_0138 node = head; node != null; node = node.next) {
map.get(node).next = map.get(node.next);
map.get(node).random = map.get(node.random);
}
return map.get(head);
}
/**
* @author: ZhouJie
* @date: 2020年3月14日 下午5:47:17
* @param: @param head
* @param: @return
* @return: Node_0138
* @Description: 2-原地复制,在节点后复制一个节点,然后再剥离链表;
*
*/
public Node_0138 copyRandomList_2(Node_0138 head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
// 在原节点后复制节点 1->2->3 => 1->1`->2->2`->3->3`
for (Node_0138 node = head, copy = null; node != null; node = node.next.next) {
copy = new Node_0138(node.val);
copy.next = node.next;
node.next = copy;
}
// 把复制后的random节点链接上
for (Node_0138 node = head; node != null; node = node.next.next) {
if (node.random != null) {
node.next.random = node.random.next;
}
}
// 原节点head的下一个几点就是新链表的头结点
Node_0138 newHead = head.next;
// 剥离节点,一个一个间隔剥离节点
for (Node_0138 node = head, temp = null; node != null && node.next != null;) {
temp = node.next;
node.next = temp.next;
node = temp;
}
return newHead;
}
}