Train Problem I
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 11117 Accepted Submission(s): 4042
Problem Description
As the new term comes, the Ignatius Train Station is very busy nowadays. A lot of student want to get back to school by train(because the trains in the Ignatius Train Station is the fastest all over the world ^v^). But here comes a problem, there is only one railway where all the trains stop. So all the trains come in from one side and get out from the other side. For this problem, if train A gets into the railway first, and then train B gets into the railway before train A leaves, train A can't leave until train B leaves. The pictures below figure out the problem. Now the problem for you is, there are at most 9 trains in the station, all the trains has an ID(numbered from 1 to n), the trains get into the railway in an order O1, your task is to determine whether the trains can get out in an order O2.
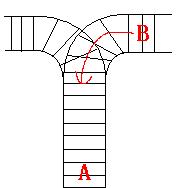
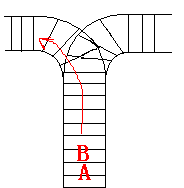
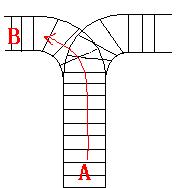



Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case consists of an integer, the number of trains, and two strings, the order of the trains come in:O1, and the order of the trains leave:O2. The input is terminated by the end of file. More details in the Sample Input.
Output
The output contains a string "No." if you can't exchange O2 to O1, or you should output a line contains "Yes.", and then output your way in exchanging the order(you should output "in" for a train getting into the railway, and "out" for a train getting out of the railway). Print a line contains "FINISH" after each test case. More details in the Sample Output.
Sample Input
3 123 321
3 123 312
Sample Output
Yes.
in
in
in
out
out
out
FINISH
No.
FINISH
For the first Sample Input, we let train 1 get in, then train 2 and train 3.
So now train 3 is at the top of the railway, so train 3 can leave first, then train 2 and train 1.
In the second Sample input, we should let train 3 leave first, so we have to let train 1 get in, then train 2 and train 3.
Now we can let train 3 leave.
But after that we can't let train 1 leave before train 2, because train 2 is at the top of the railway at the moment.
So we output "No.".
Hint
HintAuthor
Ignatius.L
1 // Project name : Defalut 2 // File name : main.cpp 3 // Author : iCoding 4 // Date & Time : 5 // Email : honi.linux@gmail.com 6 7 #include <iostream> 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #include <string> 10 #include <cmath> 11 #include <algorithm> 12 #include <fstream> 13 using namespace std; 14 15 #define MAX_TRAIN_COUNT 15 16 17 bool iFlagNoProblem; 18 19 class Stack 20 { 21 public: 22 char* a; 23 int iTop; 24 Stack(); 25 void pop(); 26 void push(int iNum); 27 char getTop(); 28 }; 29 30 31 Stack::Stack() 32 { 33 a = new char[MAX_TRAIN_COUNT]; 34 iTop = -1; 35 iFlagNoProblem = true; 36 } 37 38 void Stack::pop() 39 { 40 if (iFlagNoProblem) 41 { 42 if (iTop == -1) 43 { 44 iFlagNoProblem = false; 45 return; 46 } 47 else 48 { 49 iTop--; 50 return ; 51 } 52 } 53 else 54 { 55 return ; 56 } 57 } 58 59 char Stack::getTop() 60 { 61 if (iTop >= 0) 62 { 63 return a[iTop]; 64 } 65 else 66 { 67 return '@'; 68 } 69 } 70 71 void Stack::push(int iNum) 72 { 73 if (iFlagNoProblem) 74 { 75 iTop++; 76 a[iTop] = iNum; 77 } 78 else 79 { 80 81 } 82 } 83 84 85 int n; 86 char iStrIn[MAX_TRAIN_COUNT]; 87 char iStrOut[MAX_TRAIN_COUNT]; 88 89 string iOperatorArr[MAX_TRAIN_COUNT * 2]; 90 int iOperatorTop; 91 92 int iIndexStrIn; 93 int iIndexStrOut; 94 95 int main() 96 { 97 //freopen("in.dat", "r", stdin); 98 99 while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) 100 { 101 scanf("%s%s", iStrIn, iStrOut); 102 103 Stack iStack; 104 iOperatorTop = -1; 105 iIndexStrOut = 0; 106 for (iIndexStrIn = 0; iIndexStrIn < n; iIndexStrIn++) 107 { 108 iOperatorTop++; 109 iOperatorArr[iOperatorTop] = "in"; 110 iStack.push(iStrIn[iIndexStrIn]); 111 while (iStack.getTop() == iStrOut[iIndexStrOut]) 112 { 113 iOperatorTop++; 114 iOperatorArr[iOperatorTop] = "out"; 115 iStack.pop(); 116 iIndexStrOut++; 117 } 118 } 119 120 if (iIndexStrOut != n) 121 { 122 iFlagNoProblem = false; 123 } 124 if (iFlagNoProblem) 125 { 126 cout << "Yes." << endl; 127 for (int i = 0; i <= iOperatorTop; i++) 128 { 129 cout << iOperatorArr[i] << endl; 130 } 131 cout << "FINISH" << endl; 132 } 133 else 134 { 135 cout << "No." << endl; 136 cout << "FINISH" << endl; 137 } 138 } 139 140 return 0; 141 } 142 143 // end 144 // iCoding@CodeLab