请求响应流程图

response
response是用来向客户端响应的对象!
需要回忆一下http响应内容:
l 首行:状态码
l 响应头:
- 1头1值,1头多值;
l 响应体(正文):html
response响应状态码:
l setStatus(int sc):一般用来发送非错误的状态码。
l sendError(int sc):一般用来发送错误的状态码
l sendError(int sc, String msg):同上,但可以带错误信息
response发送响应头:
l setHeader(String header, String value):设置响应头;
l addHeader(String header, String value):添加响应头;适合一头多值。
l setIntHeader(String header, int value):专门为int类型值由准备的!
l addIntHeader(String header, int value)
l setDateHeader(String header, long value):专门为时间毫秒值类型准备的!
l addDateHeader(String header, long value)
response发送响应体:
l PrintWriter getWriter():用来向客户端发送文本数据(html就是文本数据);
l ServletOutputStream getOutputStream():用来向客户端发送字节数据(图片、mp3等);
l 同一个response对象,不能即使用getOut()和getOutputStream();
响应编码问题:
l response.setCharaceterEncoding(“utf-8”):让tomcat把数据转换成utf-8再发;
l response.setHeader(“Content-Type”, “text/html;chartset=utf-8”):
- 让tomcat把数据转换成utf-8再发;
- 添加Content-Type头,即通知浏览器我们发送的是什么编码的字符!
l 设置ContentType响应头的便捷方法:response.setContentType(“text/html;charset=utf-8”)等同与response.setHeader(“Content-Type”, “text/html;charset=utf-8”);
所以,在发送response之前,调用response.setContentType(“text/html;charset=utf-8”);
l 重定向的便捷方法:
- 原始的重定向:
设置状态码为302:response.setStatus(302);
设置Location头:response.setHeader(“Location”, “url”);
- 便捷方法:
response.sendRedirect(“url”);
1.response概述
response是Servlet.service方法的一个参数,类型为javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse。在客户端发出每个请求时,服务器都会创建一个response对象,并传入给Servlet.service()方法。response对象是用来对客户端进行响应的,这说明在service()方法中使用response对象可以完成对客户端的响应工作。
response对象的功能分为以下四种:
l 设置响应头信息;
l 发送状态码;
l 设置响应正文;
l 重定向;
2 response响应正文
response是响应对象,向客户端输出响应正文(响应体)可以使用response的响应流,repsonse一共提供了两个响应流对象:
l PrintWriter out = response.getWriter():获取字符流;
l ServletOutputStream out = response.getOutputStream():获取字节流;
当然,如果响应正文内容为字符,那么使用response.getWriter(),如果响应内容是字节,例如下载时,那么可以使用response.getOutputStream()。
注意,在一个请求中,不能同时使用这两个流!也就是说,要么你使用repsonse.getWriter(),要么使用response.getOutputStream(),但不能同时使用这两个流。不然会抛出IllegalStateException异常。
2.1 字符响应流
l 字符编码
在使用response.getWriter()时需要注意默认字符编码为ISO-8859-1,如果希望设置字符流的字符编码为utf-8,可以使用response.setCharaceterEncoding(“utf-8”)来设置。这样可以保证输出给客户端的字符都是使用UTF-8编码的!
但客户端浏览器并不知道响应数据是什么编码的!如果希望通知客户端使用UTF-8来解读响应数据,那么还是使用response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8")方法比较好,因为这个方法不只会调用response.setCharaceterEncoding(“utf-8”),还会设置content-type响应头,客户端浏览器会使用content-type头来解读响应数据。
l 缓冲区
response.getWriter()是PrintWriter类型,所以它有缓冲区,缓冲区的默认大小为8KB。也就是说,在响应数据没有输出8KB之前,数据都是存放在缓冲区中,而不会立刻发送到客户端。当Servlet执行结束后,服务器才会去刷新流,使缓冲区中的数据发送到客户端。
如果希望响应数据马上发送给客户端:
- 向流中写入大于8KB的数据;
- 调用response.flushBuffer()方法来手动刷新缓冲区;
3 设置响应头信息
可以使用response对象的setHeader()方法来设置响应头!使用该方法设置的响应头最终会发送给客户端浏览器!
l response.setHeader(“content-type”, “text/html;charset=utf-8”):设置content-type响应头,该头的作用是告诉浏览器响应内容为html类型,编码为utf-8。而且同时会设置response的字符流编码为utf-8,即response.setCharaceterEncoding(“utf-8”);
l response.setHeader("Refresh","5; URL=http://www.itcast.cn"):5秒后自动跳转到传智主页。
4 设置状态码及其他方法
l response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"):等同与调用response.setHeader(“content-type”, “text/html;charset=utf-8”);
l response.setCharacterEncoding(“utf-8”):设置字符响应流的字符编码为utf-8;
l response.setStatus(200):设置状态码;
l response.sendError(404, “您要查找的资源不存在”):当发送错误状态码时,Tomcat会跳转到固定的错误页面去,但可以显示错误信息。
5 重定向
5.1 什么是重定向
当你访问http://www.sun.com时,你会发现浏览器地址栏中的URL会变成http://www.oracle.com/us/sun/index.htm,这就是重定向了。
重定向是服务器通知浏览器去访问另一个地址,即再发出另一个请求。
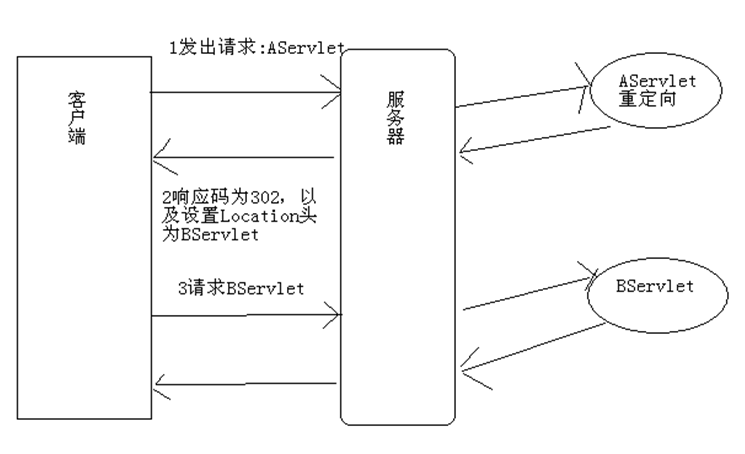
5.2 完成重定向
响应码为200表示响应成功,而响应码为302表示重定向。所以完成重定向的第一步就是设置响应码为302。
因为重定向是通知浏览器再第二个请求,所以浏览器需要知道第二个请求的URL,所以完成重定向的第二步是设置Location头,指定第二个请求的URL地址。
public class AServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.setStatus(302);//设置响应码为302,表示重定向 response.setHeader("Location", "http://www.itcast.cn");//设置新请求的URL } }
上面代码的作用是:当访问AServlet后,会通知浏览器重定向到传智主页。客户端浏览器解析到响应码为302后,就知道服务器让它重定向,所以它会马上获取响应头Location,然发出第二个请求。
5.3 便捷的重定向方式
public class AServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.sendRedirect("http://www.itcast.cn"); } }
response.sendRedirect()方法会设置响应头为302,以设置Location响应头。
如果要重定向的URL是在同一个服务器内,那么可以使用相对路径,例如:
public class AServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.sendRedirect("/hello/BServlet"); } }
重定向的URL地址为:http://localhost:8080/hello/BServlet。
5.4 重定向小结
l 重定向是两次请求;
l 重定向的URL可以是其他应用,不局限于当前应用;
l 重定向的响应头为302,并且必须要有Location响应头;
l 重定向就不要再使用response.getWriter()或response.getOutputStream()输出数据,不然可能会出现异常;
request
回忆http请求格式:
l 首行:请求方式、请求路径、请求协议及版本;
l 请求头:
l 请求正文:post请求参数。username=qdmmy6&password=123
request功能:
l 获取请求参数
- 无论是GET还是POST都能获取:String getParameter(String 参数的名称)
l 获取请求路径相关的方法:http://127.0.0.1:8080/day10_2/AServlet?name=liSi&pass=123
- 获取协议;
- 获取主机名;
- 获取端口号;
- 获取Servlet路径
- 获取参数字符串
l 获取请求头!
l 域功能:request是域对象!
l 转发和包含!
l request的获取请求方式和客户端IP
- String getMethod():获取请求方式;
- String getRemoteAddr():获取客户端的IP地址。
l request获取请求参数:
- String getParameter(String paramName):通过参数名获取参数值(适用与单值参数)
- String[] getParameterValues(String paramName):通过参数名获取参数值(适用与多值参数)
- Enumeration getParameterNames():获取所有参数的名称
- Map<String,String[]> getParameterMap():获取所有参数,其中key为参数名,值为参数值。
l request请求参数编码问题
- 第一:浏览器发过来的是什么编码的数据:
地址栏:GBK;
页面:由当前页面的编码决定!
- 第二:tomcat把浏览器的请求参数当成什么编码的数据。
tomcat默认认为数据是iso的
GET:解了重编!new String(username.getBytes(“ISO-8859-1”), “UTF-8”);
POST:在调用getParamter()之前,先调用request.setCharacterEncoding(“utf-8”);(其实POST也可以解了重编!)
URL编码:
l 作用:为了让浏览器安全的传递参数(GET)给服务器
- GET请求中参数可以包含中文,但早期很多浏览器都不支持!
- 请求中如果路径中包含了中文,死定了!
l URL编码后,中文在客户端传递给服务器时,就不会出错!
- 编码:String URLEncoder.encode(String s, String charset);
- 解码:String URLDecoder.decode(String s, String charset);
- 我们需要在页面中对链接做处理:把中文参数使用URL编码;
- 服务器:会自动识别URL编码后的数据,然后自动解码!
使用js做URL编码:
<script type="text/javascript">
var s = window.encodeURI("张三");
alert(s);
</script>
request获取请求头:
l String getHeader(String header):通过头名称获取头值。
request域对象:范围(一个请求链!)
l Servlet中有三大域:request、session、application(ServletContext)
l 其中某个Servlet:可以调用setAttribute(String name, Object value)来保存数据;
l 另一个Servlet:可以调用Object value = getAttribute(String name)来获取数据。
request与请求转发和请求包含
l 请求转发和请求包含:RequestDispatcher的forward()、include()
l 相同点:
- 都是一个请求
- 都可以使用request域来传递数据
l 不同点:
- 转发:留头不留体,头是响应头,体是响应体。
- 包含:留头又留体
注意事项:
l 包含就不能转发、转发就不要包含!
l 如果转发或包含了,那么就不能再重定向!
1 request概述
request是Servlet.service()方法的一个参数,类型为javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest。在客户端发出每个请求时,服务器都会创建一个request对象,并把请求数据封装到request中,然后在调用Servlet.service()方法时传递给service()方法,这说明在service()方法中可以通过request对象来获取请求数据。

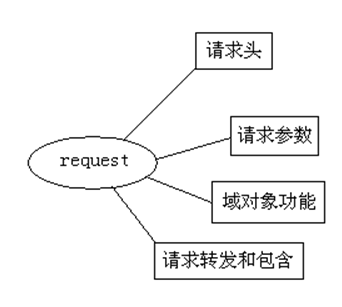
request的功能可以分为以下几种:
l 封装了请求头数据;
l 封装了请求正文数据,如果是GET请求,那么就没有正文;
l request是一个域对象,可以把它当成Map来添加获取数据;
l request提供了请求转发和请求包含功能。
2 request域方法
request是域对象!在JavaWeb中一共四个域对象,其中ServletContext就是域对象,它在整个应用中只创建一个ServletContext对象。request其中一个,request可以在一个请求中共享数据。
一个请求会创建一个request对象,如果在一个请求中经历了多个Servlet,那么多个Servlet就可以使用request来共享数据。现在我们还不知道如何在一个请求中经历之个Servlet,后面在学习请求转发和请求包含后就知道了。
下面是request的域方法:
l void setAttribute(String name, Object value):用来存储一个对象,也可以称之为存储一个域属性,例如:servletContext.setAttribute(“xxx”, “XXX”),在request中保存了一个域属性,域属性名称为xxx,域属性的值为XXX。请注意,如果多次调用该方法,并且使用相同的name,那么会覆盖上一次的值,这一特性与Map相同;
l Object getAttribute(String name):用来获取request中的数据,当前在获取之前需要先去存储才行,例如:String value = (String)request.getAttribute(“xxx”);,获取名为xxx的域属性;
l void removeAttribute(String name):用来移除request中的域属性,如果参数name指定的域属性不存在,那么本方法什么都不做;
l Enumeration getAttributeNames():获取所有域属性的名称;
3 request获取请求头数据
request与请求头相关的方法有:
l String getHeader(String name):获取指定名称的请求头;
l Enumeration getHeaderNames():获取所有请求头名称;
l int getIntHeader(String name):获取值为int类型的请求头。
4 request获取请求相关的其它方法
request中还提供了与请求相关的其他方法,有些方法是为了我们更加便捷的方法请求头数据而设计,有些是与请求URL相关的方法。
l int getContentLength():获取请求体的字节数,GET请求没有请求体,没有请求体返回-1;
l String getContentType():获取请求类型,如果请求是GET,那么这个方法返回null;如果是POST请求,那么默认为application/x-www-form-urlencoded,表示请求体内容使用了URL编码;
l String getMethod():返回请求方法,例如:GET
l Locale getLocale():返回当前客户端浏览器的Locale。java.util.Locale表示国家和言语,这个东西在国际化中很有用;
l String getCharacterEncoding():获取请求编码,如果没有setCharacterEncoding(),那么返回null,表示使用ISO-8859-1编码;
l void setCharacterEncoding(String code):设置请求编码,只对请求体有效!注意,对于GET而言,没有请求体!!!所以此方法只能对POST请求中的参数有效!
l String getContextPath():返回上下文路径,例如:/hello
l String getQueryString():返回请求URL中的参数,例如:name=zhangSan
l String getRequestURI():返回请求URI路径,例如:/hello/oneServlet
l StringBuffer getRequestURL():返回请求URL路径,例如:http://localhost/hello/oneServlet,即返回除了参数以外的路径信息;
l String getServletPath():返回Servlet路径,例如:/oneServlet
l String getRemoteAddr():返回当前客户端的IP地址;
l String getRemoteHost():返回当前客户端的主机名,但这个方法的实现还是获取IP地址;
l String getScheme():返回请求协议,例如:http;
l String getServerName():返回主机名,例如:localhost
l int getServerPort():返回服务器端口号,例如:8080
System.out.println("request.getContentLength(): " + request.getContentLength());
System.out.println("request.getContentType(): " + request.getContentType());
System.out.println("request.getContextPath(): " + request.getContextPath());
System.out.println("request.getMethod(): " + request.getMethod());
System.out.println("request.getLocale(): " + request.getLocale());
System.out.println("request.getQueryString(): " + request.getQueryString());
System.out.println("request.getRequestURI(): " + request.getRequestURI());
System.out.println("request.getRequestURL(): " + request.getRequestURL());
System.out.println("request.getServletPath(): " + request.getServletPath());
System.out.println("request.getRemoteAddr(): " + request.getRemoteAddr());
System.out.println("request.getRemoteHost(): " + request.getRemoteHost());
System.out.println("request.getRemotePort(): " + request.getRemotePort());
System.out.println("request.getScheme(): " + request.getScheme());
System.out.println("request.getServerName(): " + request.getServerName());
System.out.println("request.getServerPort(): " + request.getServerPort());
4.1 案例:request.getRemoteAddr():封IP
可以使用request.getRemoteAddr()方法获取客户端的IP地址,然后判断IP是否为禁用IP。
String ip = request.getRemoteAddr();
System.out.println(ip);
if(ip.equals("127.0.0.1")) {
response. getWriter().print("您的IP已被禁止!");
} else {
response.getWriter().print("Hello!");
}
5 request获取请求参数
最为常见的客户端传递参数方式有两种:
l 浏览器地址栏直接输入:一定是GET请求;
l 超链接:一定是GET请求;
l 表单:可以是GET,也可以是POST,这取决与<form>的method属性值;
GET请求和POST请求的区别:
l GET请求:
- 请求参数会在浏览器的地址栏中显示,所以不安全;
- 请求参数长度限制长度在1K之内;
- GET请求没有请求体,无法通过request.setCharacterEncoding()来设置参数的编码;
l POST请求:
- 请求参数不会显示浏览器的地址栏,相对安全;
- 请求参数长度没有限制;
<a href="/hello/ParamServlet?p1=v1&p2=v2">超链接</a> <hr/> <form action="/hello/ParamServlet" method="post[崔6] "> 参数1:<input type="text" name="p1"/><br/> 参数2:<input type="text" name="p2"/><br/> <input type="submit" value="提交"/> </form>
下面是使用request获取请求参数的API:
l String getParameter(String name):通过指定名称获取参数值;
|
public void doGet[崔7] (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { String v1 = request.getParameter("p1"); String v2 = request.getParameter("p2"); System.out.println("p1=" + v1); System.out.println("p2=" + v2); }
public void doPost[崔8] (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { String v1 = request.getParameter("p1"); String v2 = request.getParameter("p2"); System.out.println("p1=" + v1); System.out.println("p2=" + v2); } |
l String[] getParameterValues(String name):当多个参数名称相同时,可以使用方法来获取;
|
<a href="/hello/ParamServlet?name=zhangSan&name=liSi[崔9] ">超链接</a> |
|
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { String[] names = request.getParameterValues("name");[崔10] System.out.println(Arrays.toString(names));[崔11] } |
l Enumeration getParameterNames():获取所有参数的名字;
|
<form action="/hello/ParamServlet" method="post"> 参数1:<input type="text" name="p1"/><br/> 参数2:<input type="text" name="p2"/><br/> <input type="submit" value="提交"/> </form> |
|
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { Enumeration names = request.getParameterNames()[崔12] ; while(names.hasMoreElements()) { System.out.println(names.nextElement()); } } |
l Map getParameterMap():获取所有参数封装到Map中,其中key为参数名,value为参数值,因为一个参数名称可能有多个值,所以参数值是String[],而不是String。
|
<a href="/day05_1/ParamServlet?p1=v1&p1=vv1&p2=v2&p2=vv2">超链接</a> |
|
Map<String,String[]> paramMap = request.getParameterMap(); for(String name : paramMap.keySet()) { String[] values = paramMap.get(name); System.out.println(name + ": " + Arrays.toString(values)); } |
|
p2: [v2, vv2] p1: [v1, vv1] |
6 请求转发和请求包含
无论是请求转发还是请求包含,都表示由多个Servlet共同来处理一个请求。例如Servlet1来处理请求,然后Servlet1又转发给Servlet2来继续处理这个请求。
6.1 请求转发
在AServlet中,把请求转发到BServlet:
|
public class AServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("AServlet"); RequestDispatcher rd = request.getRequestDispatcher("/BServlet");[崔13] rd.forward(request, response)[崔14] ; } } |
|
public class BServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("BServlet"); } } |
|
Aservlet BServlet |
6.2 请求包含
在AServlet中,把请求包含到BServlet:
|
public class AServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("AServlet"); RequestDispatcher rd = request.getRequestDispatcher("/BServlet"); rd.include[崔15] (request, response); } } |
|
public class BServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("BServlet"); } } |
|
Aservlet BServlet |
6.3 请求转发与请求包含比较
l 如果在AServlet中请求转发到BServlet,那么在AServlet中就不允许再输出响应体,即不能再使用response.getWriter()和response.getOutputStream()向客户端输出,这一工作应该由BServlet来完成;如果是使用请求包含,那么没有这个限制;
l 请求转发虽然不能输出响应体,但还是可以设置响应头的,例如:response.setContentType(”text/html;charset=utf-8”);
l 请求包含大多是应用在JSP页面中,完成多页面的合并;
l 请求请求大多是应用在Servlet中,转发目标大多是JSP页面;
6.4 请求转发与重定向比较
l 请求转发是一个请求,而重定向是两个请求;
l 请求转发后浏览器地址栏不会有变化,而重定向会有变化,因为重定向是两个请求;
l 请求转发的目标只能是本应用中的资源,重定向的目标可以是其他应用;
l 请求转发对AServlet和BServlet的请求方法是相同的,即要么都是GET,要么都是POST,因为请求转发是一个请求;
l 重定向的第二个请求一定是GET;
路径
客户端路径:表单、超链接、重定向。
l 以“/”开头,是相对http://localhsot:8080
l 不以“/”开头,是相对当前页面所在路径,例如当前页面:http://localhsot:8080/day10_2/index.jsp,链接的href=”AServlet”,那么指向中的url为http://localhsot:8080/day10_2/AServlet
l 客户端路径不要使用相对,而是使用绝对!即使用“/”开头,后面给项目名!
服务器端路径:转发和包含
l 只需要给出Servlet路径即可,无需项目名,但也要使用“/”开头!
l ServletContext获取资源路径:以“/”开头,相对当前项目目录,例如:servletcontext.getRealPath(“/a.jpg”),它返回的是真实路径。F:/tomcat/webapps/day10_2/a.jpg
l Class和ClassLoader用来获取classpath下的资源!例如:classLoader.getResourceAsStream(“a.jpg”),即classes下的a.jpg;
l 例如:clazz.getResourceAsStream(“a.jpg”),即classes下cn/itcast/web/servlet/a.jpg
1 与路径相关的操作
l 超链接:客户端路径!
l 表单:客户端路径!
l 转发
l 包含
l 重定向
l <url-pattern>
l ServletContext获取资源
l Class获取资源
l ClassLoader获取资源
2 客户端路径
超链接、表单、重定向都是客户端路径,客户端路径可以分为三种方式:
l 绝对路径;
l 以“/”开头的相对路径;
l 不以“/”开头的相对路径;
例如:http://localhost:8080/hello1/pages/a.html中的超链接和表单如下:
|
绝对路径:<a href="http://localhost:8080/hello2/index.html">链接1</a> 客户端路径:<a href="/hello3/pages/index.html">链接2</a> 相对路径:<a href="index.html">链接3</a> <hr/> 绝对路径: <form action="http://localhost:8080/hello2/index.html"> <input type="submit" value="表单1"/> </form> 客户端路径: <form action="/hello2/index.html"> <input type="submit" value="表单2"/> </form> 相对路径: <form action="index.html"> <input type="submit" value="表单3"/> </form> |
l 链接1和表单1:没什么可说的,它使用绝对路径;
l 链接2和表单2:以“/”开头,相对主机,与当前a.html的主机相同,即最终访问的页面为http://localhost:8080/hello2/index.html;
l 链接3和表单3:不以“/”开头,相对当前页面的路径,即a.html所有路径,即最终访问的路径为:http://localhost:8080/hello1/pages/index.html;
重定向1:
|
public class AServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.sendRedirect("/hello/index.html"); } } |
假设访问AServlet的路径为:http://localhost:8080/hello/servlet/AServlet
因为路径以“/”开头,所以相对当前主机,即http://localhost:8080/hello/index.html。
重定向2:
|
public class AServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.sendRedirect("index.html"); } } |
假设访问AServlet的路径为:http://localhost:8080/hello/servlet/AServlet
因为路径不以“/”开头,所以相对当前路径,即http://localhost:8080/hello/servlet/index.html
2.1 建议使用“/”
强烈建议使用“/”开头的路径,这说明在页面中的超链接和表单都要以“/”开头,后面是当前应用的名称,再是访问路径:
<form action="/hello/servlet/AServlet">
</form>
<a href="/hello/b.html">链接</a>
其中/hello是当前应用名称,这也说明如果将来修改了应用名称,那么页面中的所有路径也要修改,这一点确实是个问题。这一问题的处理方案会在学习了JSP之后讲解!
在Servlet中的重定向也建议使用“/”开头。同理,也要给出应用的名称!例如:
|
response.sendRedirect("/hello/BServlet"); |
其中/hello是当前应用名,如果将来修改了应用名称,那么也要修改所有重定向的路径,这一问题的处理方案是使用request.getContextPath()来获取应用名称。
|
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/BServlet"); |
3 服务器端路径
服务器端路径必须是相对路径,不能是绝对路径。但相对路径有两种形式:
l 以“/”开头;
l 不以“/”开头;
其中请求转发、请求包含都是服务器端路径,服务器端路径与客户端路径的区别是:
l 客户端路径以“/”开头:相对当前主机;
l 服务器端路径以“/”开头:相对当前应用;
转发1:
|
public class AServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { request.getRequestDispatcher("/BServlet").forward(request, response); } } |
假设访问AServlet的路径为:http://localhost:8080/hello/servlet/AServlet
因为路径以“/”开头,所以相对当前应用,即http://localhost:8080/hello/BServlet。
转发2:
|
public class AServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { request.getRequestDispatcher("BServlet").forward(request, response); } } |
假设访问AServlet的路径为:http://localhost:8080/hello/servlet/AServlet
因为路径不以“/”开头,所以相对当前应用,即http://localhost:8080/hello/servlet/BServlet。
4 <url-pattern>路径
<url-pattern>必须使用“/”开头,并且相对的是当前应用。
5 ServletContext获取资源
必须是相对路径,可以“/”开头,也可以不使用“/”开头,但无论是否使用“/”开头都是相对当前应用路径。
例如在AServlet中获取资源,AServlet的路径路径为:http://localhost:8080/hello/servlet/AServlet:
|
public class AServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { String path1 = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("a.txt"); String path2 = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/a.txt"); System.out.println(path1); System.out.println(path2); } } |
path1和path2是相同的结果:http://localhost:8080/hello/a.txt
6 Class获取资源
Class获取资源也必须是相对路径,可以“/”开头,也可以不使用“/”开头。
|
package cn.itcast;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class Demo { public void fun1() { InputStream in = Demo.class.getResourceAsStream("/a.txt"); }
public void fun2() { InputStream in = Demo.class.getResourceAsStream("a.txt"); } } |
其中fun1()方法获取资源时以“/”开头,那么相对的是当前类路径,即/hello/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt文件;
其中fun2()方法获取资源时没有以“/”开头,那么相对当前Demo.class所在路径,因为Demo类在cn.itcast包下,所以资源路径为:/hello/WEB-INF/classes/cn/itcast/a.txt。
7 ClassLoader获取资源
ClassLoader获取资源也必须是相对路径,可以“/”开头,也可以不使用“/”开头。但无论是否以“/”开头,资源都是相对当前类路径。
|
public class Demo { public void fun1() { InputStream in = Demo.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("/a.txt"); }
public void fun2() { InputStream in = Demo.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("a.txt"); } } |
fun1()和fun2()方法的资源都是相对类路径,即classes目录,即/hello/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt
编码
1 请求编码
1.1 直接在地址栏中给出中文
请求数据是由客户端浏览器发送服务器的,请求数据的编码是由浏览器决定的。例如在浏览器地址栏中给出:http://localhost:8080/hello/AServlet?name=传智,那么其中“传智”是什么编码的呢?不同浏览器使用不同的编码,所以这是不确定的!
l IE:使用GB2312;
l FireFox:使用GB2312;
l Chrome:使用UTF-8;
通常没有哪个应用要求用户在浏览器地址栏中输入请求数据的,所以大家只需了解一下即可。
1.2 在页面中发出请求
通常向服务器发送请求数据都需要先请求一个页面,然后用户在页面中输入数据。页面中有超链接和表单,通过超链接和表单就可以向服务器发送数据了。
因为页面是服务器发送到客户端浏览器的,所以这个页面本身的编码由服务器决定。而用户在页面中输入的数据也是由页面本身的编码决定的。
index.html
|
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>index.html</title> <meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">[崔16] </head>
<body> <form action="/hello/servlet/AServlet"> 名称:<input type="text" name="name"/> <input type="submit" value="提交"/> </form> <a href="/hello/servlet/AServlet?name=传智">链接</a> </body> </html> |
当用户在index.html页面中输入数据时,都是UTF-8列表的。因为这个页面本身就是UTF-8编码的!
页面的编译就是页面中输入数据的编码。
1.3 GET请求解读编码
当客户端通过GET请求发送数据给服务器时,使用request.getParameter()获取的数据是被服务器误认为ISO-8859-1编码的,也就是说客户端发送过来的数据无论是UTF-8还是GBK,服务器都认为是ISO-8859-1,这就说明我们需要在使用request.getParameter()获取数据后,再转发成正确的编码。
例如客户端以UTF-8发送的数据,使用如下转码方式:
String name = request.getParameter(“name”);
name = new String(name.getBytes(“iso-8859-1”), “utf-8”);
1.4 POST请求解读编码
当客户端通过POST请求发送数据给服务器时,可以在使用request.getParameter()获取请求参数之前先通过request.setCharacterEncoding()来指定编码,然后再使用reuqest.getParameter()方法来获取请求参数,那么就是用指定的编码来读取了。
也就是说,如果是POST请求,服务器可以指定编码!但如果没有指定编码,那么默认还是使用ISO-8859-1来解读。
request.setCharacterEncoding(“utf-8”);
String name = request.getParameter(“name”);
2 响应编码
响应:服务器发送给客户端数据!响应是由response对象来完成,如果响应的数据不是字符数据,那么就无需去考虑编码问题。当然,如果响应的数据是字符数据,那么就一定要考虑编码的问题了。
response.getWriter().print(“传智”);
上面代码因为没有设置repsonse.getWriter()字符流的编码,所以服务器使用默认的编码(ISO-8859-1)来处理,因为ISO-8859-1不支持中文,所以一定会出现编码的。
所以在使用response.getWriter()发送数据之前,一定要设置response.getWriter()的编码,这需要使用response.setCharacterEncoding()方法:
response.setCharacterEncoding(“utf-8”);
response.getWriter().print(“传智”);
上面代码因为在使用response.getWriter()输出之前已经设置了编码,所以输出的数据为utf-8编码。但是,因为没有告诉浏览器使用什么编码来读取响应数据,所以很可能浏览器会出现错误的解读,那么还是会出现乱码的。当然,通常浏览器都支持来设置当前页面的编码,如果用户在看到编码时,去设置浏览器的编码,如果设置的正确那么乱码就会消失。但是我们不能让用户总去自己设置编码,而且应该直接通知浏览器,服务器发送过来的数据是什么编码,这样浏览器就直接使用服务器告诉他的编码来解读!这需要使用content-type响应头。
response.setContentType(“text/html;charset=utf-8”);
response.getWriter().print(“传智”);
上面代码使用setContentType()方法设置了响应头content-type编码为utf-8,这不只是在响应中添加了响应头,还等于调用了一次response.setCharacterEncoding(“utf-8”),也就是说,通过我们只需要调用一次response.setContentType(“text/html;charset=utf-8”)即可,而无需再去调用response.setCharacterEncoding(“utf-8”)了。
在静态页面中,使用<meta>来设置content-type响应头,例如:
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
3 URL编码
通过页面传输数据给服务器时,如果包含了一些特殊字符是无法发送的。这时就需要先把要发送的数据转换成URL编码格式,再发送给服务器。
其实需要我们自己动手给数据转换成URL编码的只有GET超链接,因为表单发送数据会默认使用URL编码,也就是说,不用我们自己来编码。
例如:“传智”这两个字通过URL编码后得到的是:“%E4%BC%A0%E6%99%BA”。URL编码是先需要把“传智”转换成字节,例如我们现在使用UTF-8把“传智”转换成字符,得到的结果是:“[-28, -68, -96, -26, -103, -70]”,然后再把所有负数加上256,得到[228, 188, 160, 230, 153, 186],再把每个int值转换成16进制,得到[E4, BC, A0, E6, 99, BA],最后再每个16进制的整数前面加上“%”。
通过URL编码,把“传智”转换成了“%E4%BC%A0%E6%99%BA”,然后发送给服务器!服务器会自动识别出数据是使用URL编码过的,然后会自动把数据转换回来。
当然,在页面中我们不需要自己去通过上面的过程把“传智”转换成“%E4%BC%A0%E6%99%BA”,而是使用Javascript来完成即可。当后面我们学习了JSP后,就不用再使用Javascript了。
|
<script type="text/javascript"> function _go() { location = "/day05_2/AServlet?name=" + encodeURIComponent("传智+播客"); } </script> |
|
<a href="javascript:_go();">链接</a> |
因为URL默认只支持ISO-8859-1,这说明在URL中出现中文和一些特殊字符可能无法发送到服务器。所以我们需要对包含中文或特殊字符的URL进行URL编码。
服务器会自动识别数据是否使用了URL编码,如果使用了服务器会自动把数据解码,无需我们自己动手解码。