发表时间:2019(ICLR 2019)
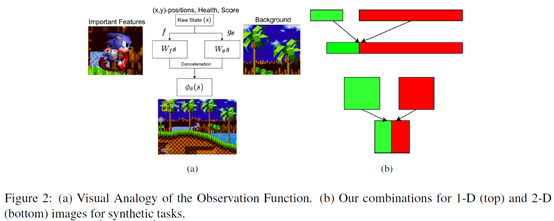
文章要点:这篇文章提到了RL里面overfitting的问题,提出了一个Observational Overfitting的问题,然后用修正观测空间的方式来检测observational overfitting,并得出结论像MLP,CNN这些Overparametrization可能会作为潜在的正则项(implicit regularization),从而缓解这个问题。具体的,Observational Overfitting就是说agent在训练的时候把一些不重要的特征和reward建立了相关性(mistakenly correlate reward with certain spurious features from the observation),比如游戏背景,游戏的计分和计时显示等等,这些特征其实和环境的dynamics没有任何关系,agent的策略也不应该和这些特征产生错误归因(false attributions),但是saliency map却显示agent把这些特征当成了决策的重要信息,导致agent在这些特征上overfitting以至于泛化性变差(the agent can use any features that are correlated with progress, even those which may not generalize across levels)。作者就提出,把观测分为两部分拼在一起作为输入,来检测observational overfitting
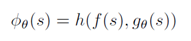
其中f映射重要的,有关系的部分,g映射不重要的,无关的部分,h就把这两部分拼起来作为最终的状态。然后就做实验来测试有没有overfitting出现。结论就是网络结构的Overparametrization可能会作为潜在的正则项(implicit regularization),从而缓解Observational Overfitting。
总结:问题是个好问题,就是这个结论感觉有点虎头蛇尾不知所云。
疑问:saliency map好像很有用,需要看看咋做的。Rademacher Complexity要看看。