空间复杂度看新开了什么数据结构就够了
公式=几个点*每个点执行了多少次
二叉树都是n次

二分法查找:lgn
全部查找:n

n:找一个数,但是两边都要找。相当于遍历。类似于rotated sorted array的有重复 遍历版本。

nlgn:先分成两半,再全部合并。类似于merge sort.
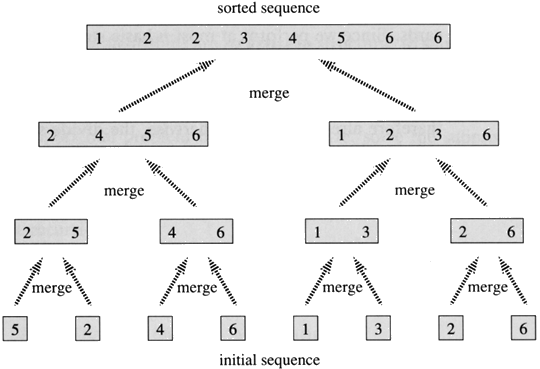
//recursive and append public static void mergeSort(int[] a, int n) { if (n < 2) { return; } int mid = n / 2; int[] l = new int[mid]; int[] r = new int[n - mid]; for (int i = 0; i < mid; i++) { l[i] = a[i]; } for (int i = mid; i < n; i++) { r[i - mid] = a[i]; } mergeSort(l, mid); mergeSort(r, n - mid); merge(a, l, r, mid, n - mid); } public static void merge( int[] a, int[] l, int[] r, int left, int right) { int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0; while (i < left && j < right) { if (l[i] < r[j]) { a[k++] = l[i++]; } else { a[k++] = r[j++]; } } while (i < left) { a[k++] = l[i++]; } while (j < right) { a[k++] = r[j++]; } }

package com.java2novice.sorting; public class MyQuickSort { private int array[]; private int length; public void sort(int[] inputArr) { if (inputArr == null || inputArr.length == 0) { return; } this.array = inputArr; length = inputArr.length; quickSort(0, length - 1); } private void quickSort(int lowerIndex, int higherIndex) { int i = lowerIndex; int j = higherIndex; // calculate pivot number, I am taking pivot as middle index number int pivot = array[lowerIndex+(higherIndex-lowerIndex)/2]; // Divide into two arrays while (i <= j) { /** * In each iteration, we will identify a number from left side which * is greater then the pivot value, and also we will identify a number * from right side which is less then the pivot value. Once the search * is done, then we exchange both numbers. */ while (array[i] < pivot) { i++; } while (array[j] > pivot) { j--; } if (i <= j) { exchangeNumbers(i, j); //move index to next position on both sides i++; j--; } } // call quickSort() method recursively if (lowerIndex < j) quickSort(lowerIndex, j); if (i < higherIndex) quickSort(i, higherIndex); } private void exchangeNumbers(int i, int j) { int temp = array[i]; array[i] = array[j]; array[j] = temp; } public static void main(String a[]){ MyQuickSort sorter = new MyQuickSort(); int[] input = {24,2,45,20,56,75,2,56,99,53,12}; sorter.sort(input); for(int i:input){ System.out.print(i); System.out.print(" "); } } }
左边一直是最右的小数做索引,右边一直是最右的大数做索引。

https://blog.csdn.net/github_30242787/article/details/50819414
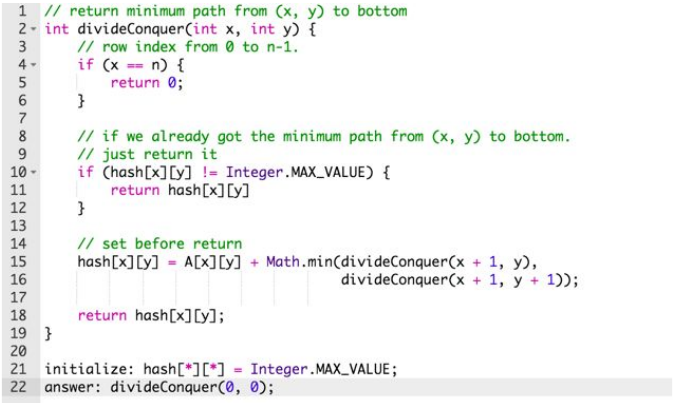
动态规划约等于分治+记忆化
优点:快的原因:因为有了记忆化,所以算过的直接用就行,就不用再算一遍了.
缺点:dc属于recursion,要少用