
1.spring框架
为了入门,可以参照一下链接:
https://blog.csdn.net/u010013573/article/details/86547687
要看spring源码之前先思考spring和servlet是怎么挂钩的?,在servlet规范中,servlet容器例如:tomcat,每个容器可以有很多个应用,每个应用都有对应的servletContext,这个在项目启动的时候,回去读取web.xml加载listener、filter、servlet的信息,
初始化servletContext的时候,会生成ServletContextEvent,方法中会有servletContext的引用
public class ServletContextEvent extends EventObject {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public ServletContextEvent(ServletContext source) {
super(source);
}
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
return (ServletContext)super.getSource();
}
}
然后这个ServletContextEvent会传到ServletContextListener中 (web.xml中的加载顺序:context-param -> listener -> filter -> servlet)
public interface ServletContextListener extends EventListener {
default void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
//我们spring就是在这个初始化方法做一些数据库连接、bean容器等组件,此时filter和servlet还没有初始化,所以初始化的时候,就可以用到spring的组件了
}
default void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
}
}
看看Spring实现了ServletContextListener 的ContextLoaderListener (属于listener顺序)
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
public ContextLoaderListener() {
}
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}
2.springMVC
看springMVC源码核心的是看 DispatcherServlet,我参照别人看了源码,相对比较简单
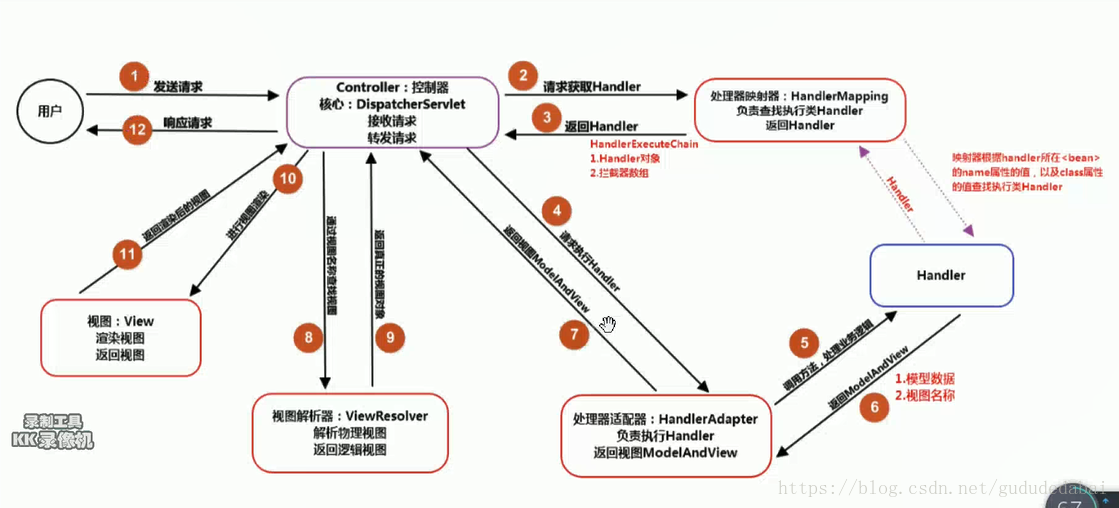
https://blog.csdn.net/gududedabai/article/details/83352106
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet ..
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware
最终还是实现Servlet,我们从servlet的service入口方法看起,在子类FrameworkServlet中
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());
if (httpMethod != HttpMethod.PATCH && httpMethod != null) {
super.service(request, response);
} else {
this.processRequest(request, response);//只要不是HttpMethod.PATCH方式就会调用
} }
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
...
this.doService(request, response);
...
}
doService方法会在DispatcherServlet中实现,这里已经进入SpringMVC了,之前都是servlet规范,所以SpringMVC也是要遵循Servlet规范的
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
...
this.doDispatch(request, response);核心在这里,
...
}
//最核心的代码在这里
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Object dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = this.checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = processedRequest != request;
mappedHandler = this.getHandler(processedRequest);//获取handler
if (mappedHandler == null) {
this.noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
HandlerAdapter ha = this.getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());//获取适配器,例如注解的、xml,一共有三种,在springMVC包里面的DispatcherServlet.properties有配置
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if ((new ServletWebRequest(request, response)).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());//执行handler,返回视图
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
this.applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
} catch (Exception var20) {
dispatchException = var20;
} catch (Throwable var21) {
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", var21);
}
this.processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, (Exception)dispatchException);
} catch (Exception var22) {
this.triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, var22);
} catch (Throwable var23) {
this.triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", var23));
}
} finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
} else if (multipartRequestParsed) {
this.cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
参照: https://www.cnblogs.com/diandianquanquan/p/10965047.html
3.springBoot
参照: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_34128501/article/details/92424885
参照: https://blog.csdn.net/hongtaolong/article/details/104886913 这个有点用处,让你知道启动的时候调用到tomcat的流程
4.springcCoud
5.Mybatis
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/cheng_1017/article/details/112600890
6.Dubbo