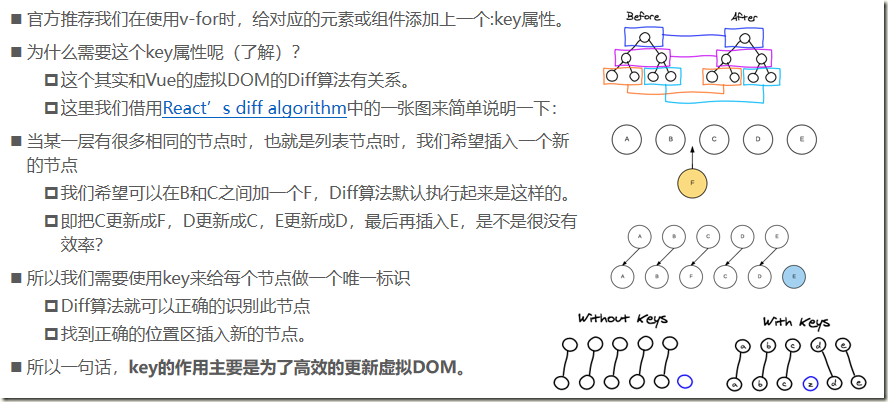
一、插值操作
1.1、Mustache语法
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h2>{{message}}</h2> <h2>{{message}}, lawrence</h2> <!--mustache语法中,不仅仅可以直接写变量,也可以写简单的表达式--> <h2>{{firstName + lastName}}</h2> <h2>{{firstName + ' ' + lastName}}</h2> <h2>{{firstName}} {{lastName}}</h2> <h2>{{counter * 2}}</h2> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { message: 'Hello Vuejs', firstName: 'Kobe', lastName: 'bryant', counter: 100 } }) </script> </body> </html>
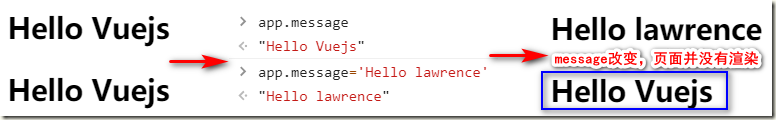
1.2、v-once指令
在某些情况下,我们可能不希望界面随意的跟随改变,可以使用v-once指令。
- 该指令后面不需要跟任何表达式(比如之前的v-for后面是由跟表达式的)
- 该指令表示元素和组件只渲染一次,不会随着数据的改变而改变
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h2>{{message}}</h2> <h2 v-once>{{message}}</h2> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { message: 'Hello Vuejs' } }) </script> </body> </html>
1.3、v-html指令
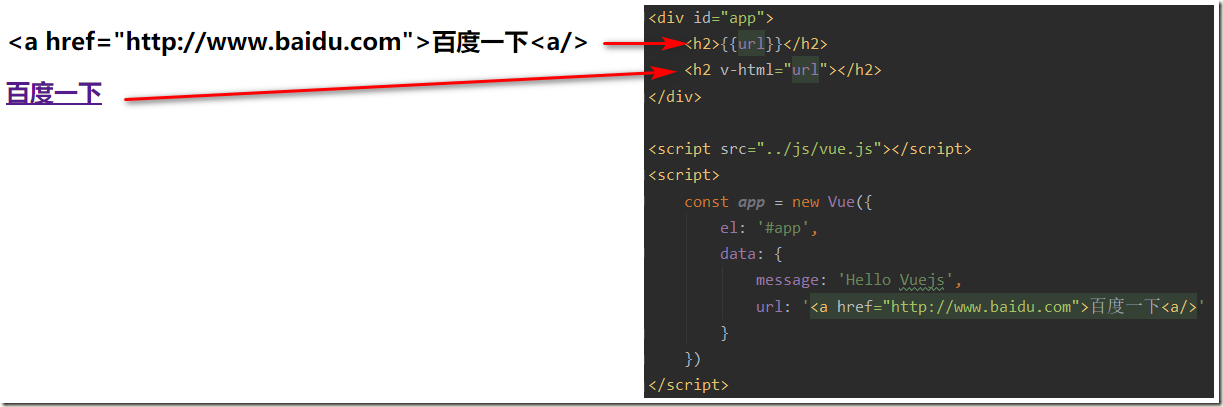
某些情况下,我们从服务器请求到的数据本身就是一个HTML代码:
- 如果我们直接通过{{}}来输出,会将HTML代码也一起输出。
- 但是我们可能希望的是按照HTML格式进行解析,并且显示对应的内容。
如果我们希望解析出HTML展示:
- 可以使用v-html指令
- 该指令后面往往会跟上一个string类型
- 会将string的html解析出来并且进行渲染
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h2>{{url}}</h2> <h2 v-html="url"></h2> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { message: 'Hello Vuejs', url: '<a href="http://www.baidu.com">百度一下<a/>' } }) </script> </body> </html>
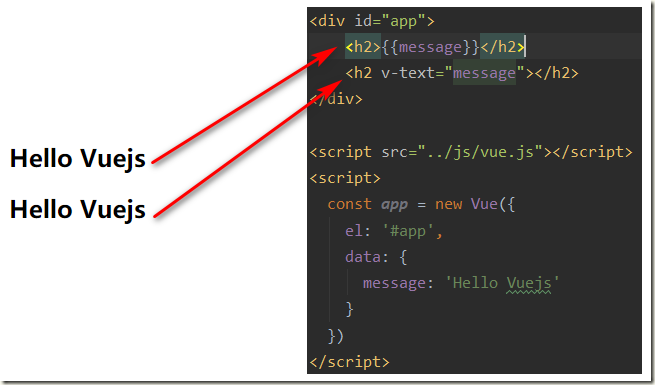
1.4、v-text指令
v-text作用和Mustache比较相似:都是用于将数据显示在界面中
v-text通常情况下,接受一个string类型
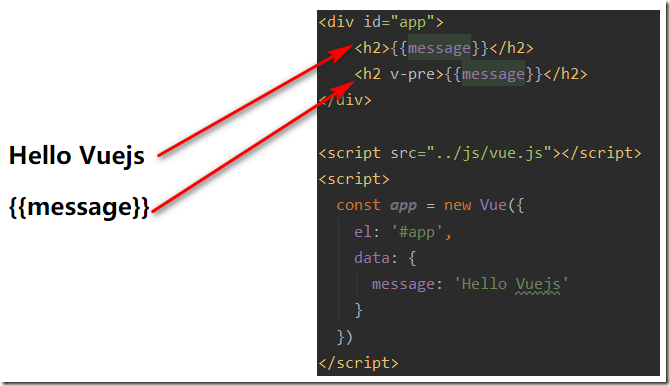
1.5、v-pre指令
v-pre用于跳过这个元素和它子元素的编译过程,用于显示原本的Mustache语法。
比如下面的代码:
- 第一个h2元素中的内容会被编译解析出来对应的内容
- 第二个h2元素中会直接显示{{message}}
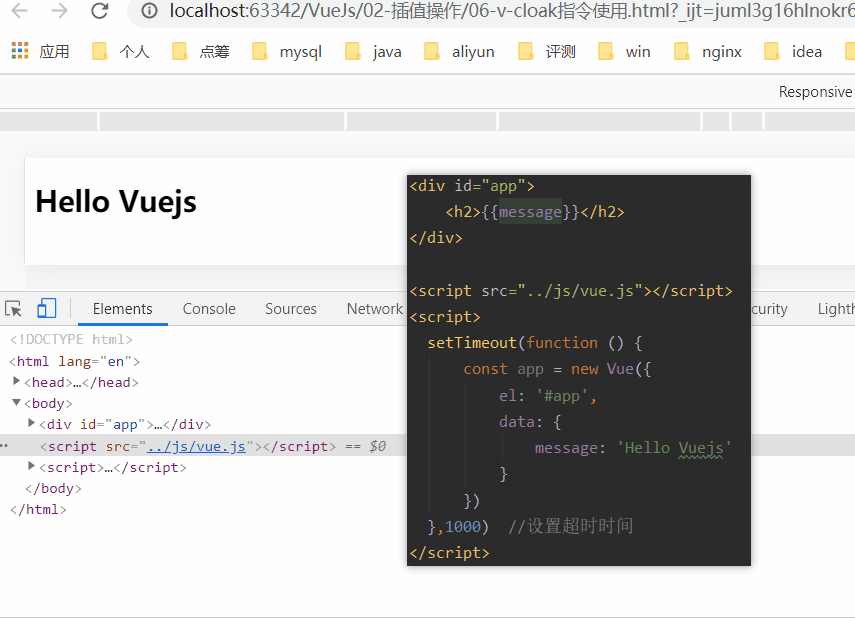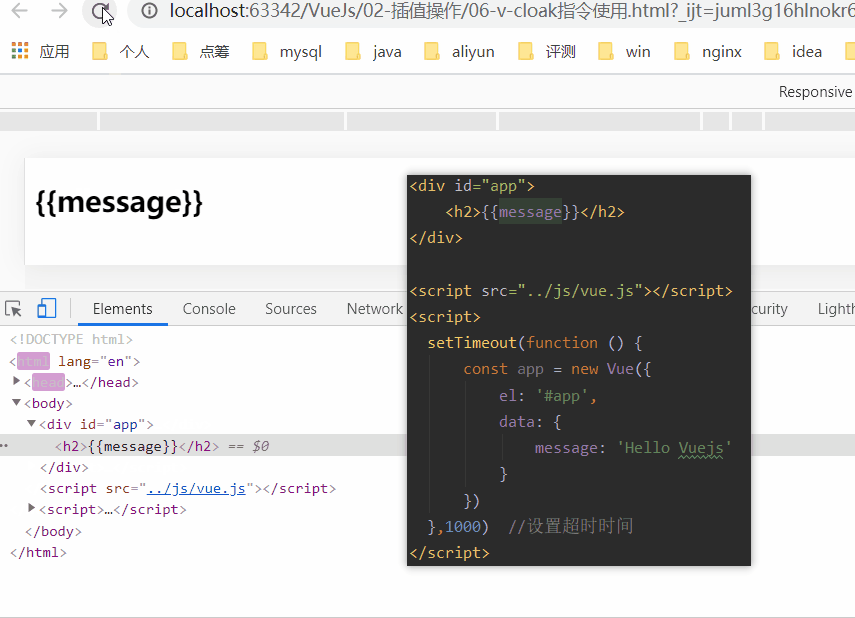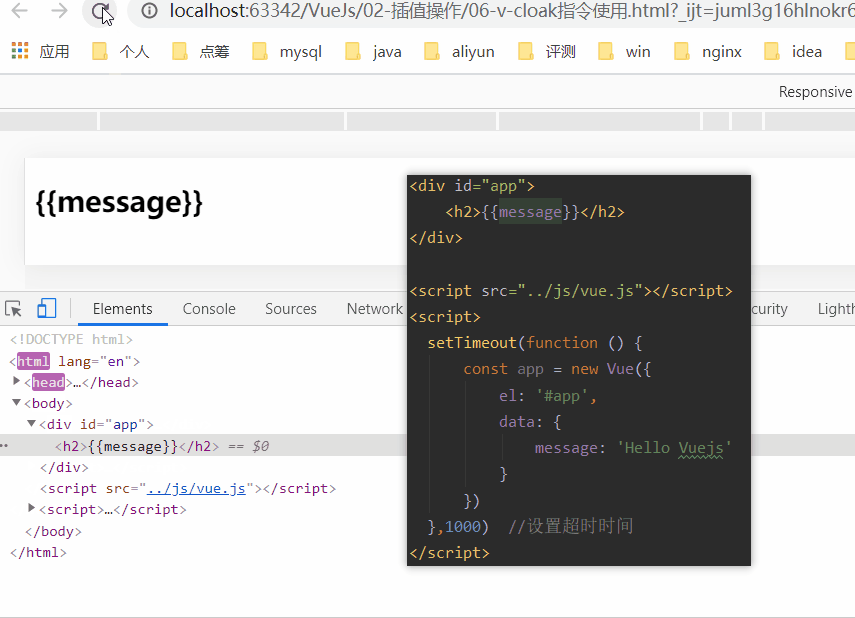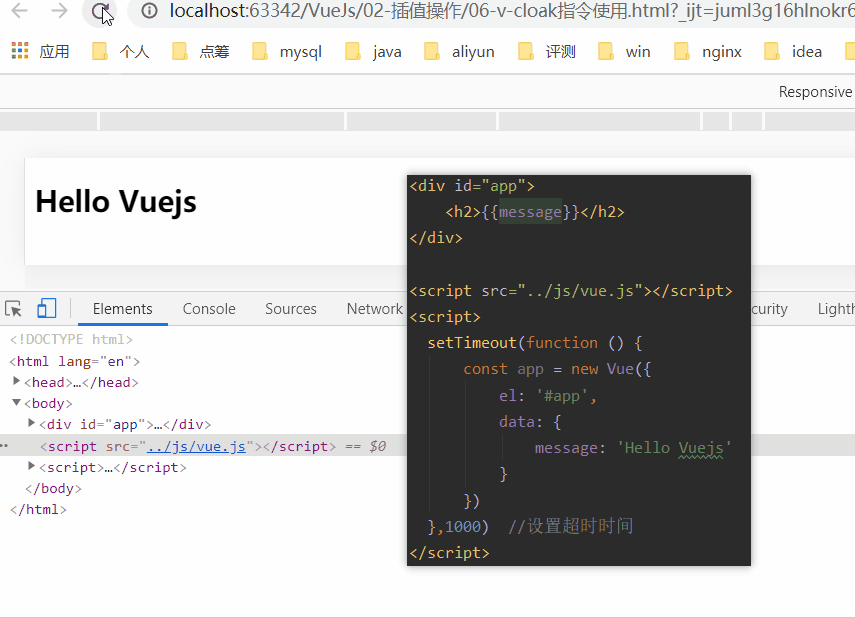
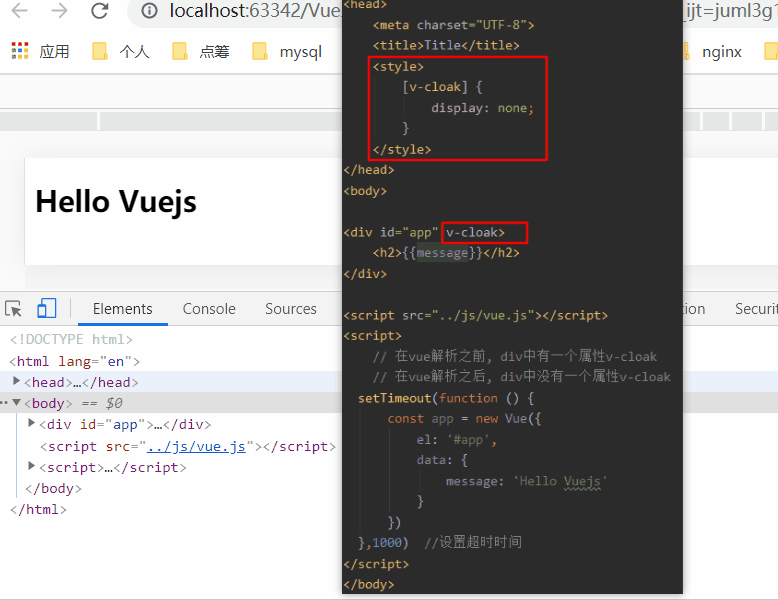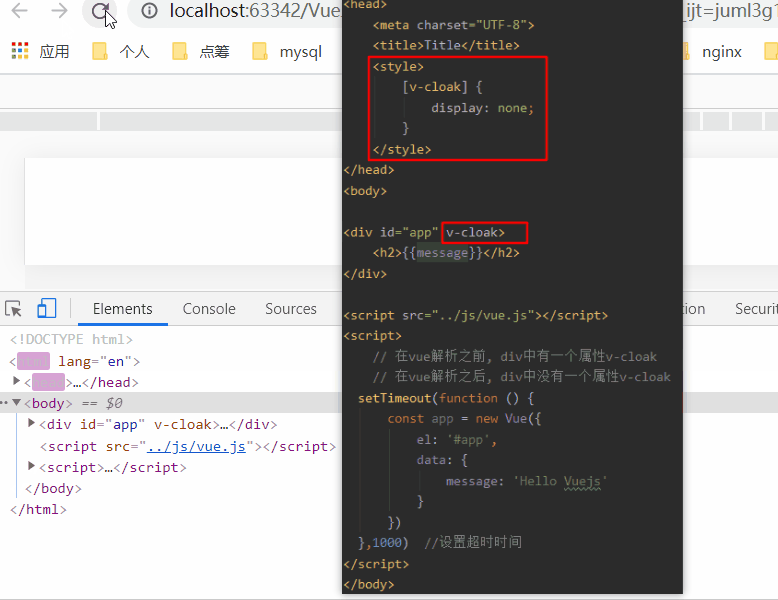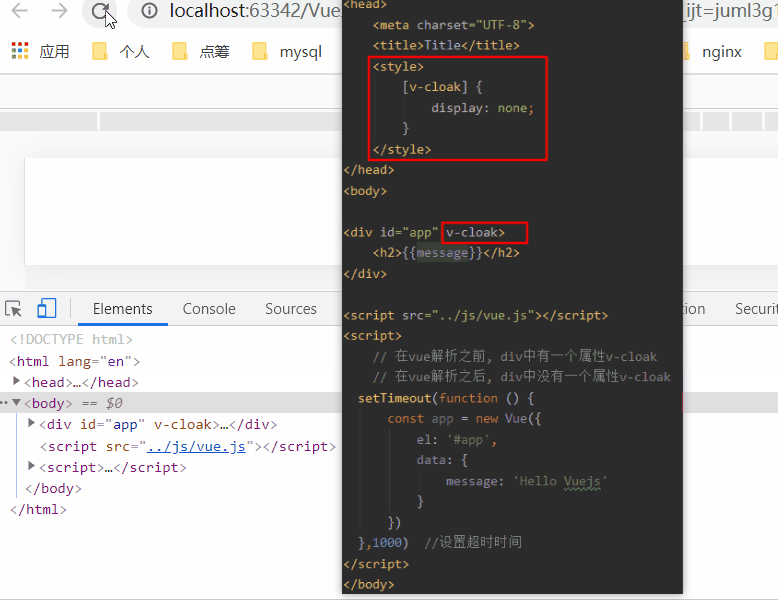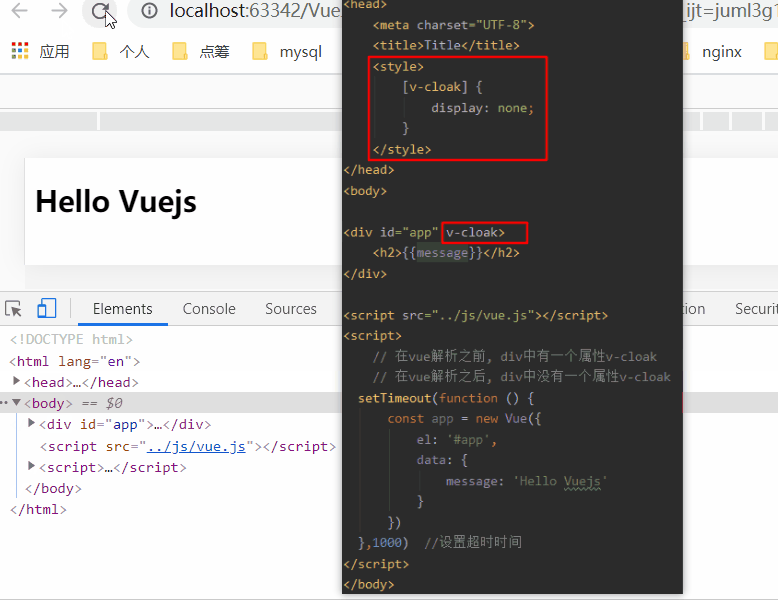
1.6、v-cloak指令
在某些情况下,我们浏览器可能会直接显然出未编译的Mustache标签。
cloak: 斗篷
当没有使用v-cloak时:
当在标签上使用v-cloak时:
二、动态绑定属性
2.1、v-bind基础
v-bind用于绑定一个或多个属性值,或者向另一个组件传递props值,除了内容需要动态来决定外,某些属性我们也希望动态来绑定:
- 比如动态绑定a元素的href属性
- 比如动态绑定img元素的src属性
- 动态绑定一些类、样式
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <!-- 错误的做法: 这里不可以使用mustache语法--> <!--<img src="{{imgURL}}" alt="">--> <!-- 正确的做法: 使用v-bind指令 --> <img v-bind:src="imgURL" alt=""> <a v-bind:href="aHref">百度一下</a> <!--<h2>{{}}</h2>--> <!--语法糖的写法--> <img :src="imgURL" alt=""> <a :href="aHref">百度一下</a> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { message: '你好啊', imgURL: 'https://cn.vuejs.org/images/logo.png', aHref: 'http://www.baidu.com' } }) </script> </body> </html>
2.2、v-bind绑定class(对象语法)
对象语法的含义是:class后面跟的是一个对象
用法一:直接通过{}绑定一个类
<h2 :class="{'active': isActive}">Hello World</h2>
用法二:也可以通过判断,传入多个值
<h2 :class="{'active': isActive, 'line': isLine}">Hello World</h2>
用法三:和普通的类同时存在,并不冲突
注:如果isActive和isLine都为true,那么会有title/active/line三个类
<h2 class="title" :class="{'active': isActive, 'line': isLine}">Hello World</h2>
用法四:如果过于复杂,可以放在一个methods或者computed中
注:classes是一个计算属性
<h2 class="title" :class="classes">Hello World</h2>
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .active { color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h2 class="active">{{message}}</h2> <h2 :class="active">{{message}}</h2> <!--<h2 v-bind:class="{key1: value1, key2: value2}">{{message}}</h2>--> <!--<h2 v-bind:class="{类名1: true, 类名2: boolean}">{{message}}</h2>--> <h2 class="title" v-bind:class="{active: isActive,line: isLine}">{{message}}</h2> <h2 class="title" v-bind:class="getClasses()">{{message}}</h2> <button @click="btnClick">点击</button> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { message: 'Hello Vuejs', isActive: true, isLine: true }, methods: { btnClick:function () { this.isActive = !this.isActive }, getClasses: function () { return {active: this.isActive,line: this.isLine} } } }) </script> </body> </html>
2.3、v-bind动态绑定class(数组语法)
数组语法的含义是:class后面跟的是一个数组
用法一:直接通过{}绑定一个类
<h2 :class="['active']">Hello World</h2>
用法二:也可以传入多个值
<h2 :class=“[‘active’, 'line']">Hello World</h2>
用法三:和普通的类同时存在,并不冲突
注:会有title/active/line三个类
<h2 class="title" :class=“[‘active’, 'line']">Hello World</h2>
用法四:如果过于复杂,可以放在一个methods或者computed中
注:classes是一个计算属性
<h2 class="title" :class="classes">Hello World</h2>
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h2 class="title" :class="[active, line]">{{message}}</h2> <h2 class="title" :class="getClasses()">{{message}}</h2> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { message: '你好啊', active: 'aaaaaa', line: 'bbbbbbb' }, methods: { getClasses: function () { return [this.active, this.line] } } }) </script> </body> </html>
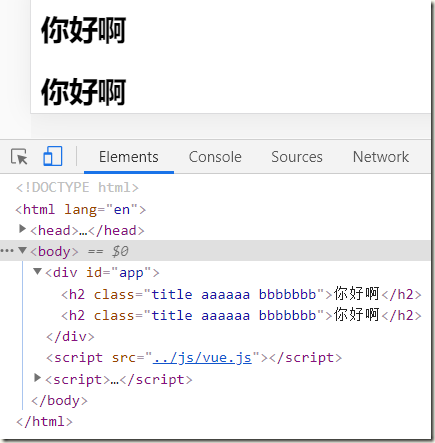
2.4、v-bind动态绑定style(对象语法)
:style="{color: currentColor, fontSize: fontSize + 'px'}"
style后面跟的是一个对象类型
对象的key是CSS属性名称
对象的value是具体赋的值,值可以来自于data中的属性
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .title { font-size: 50px; color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <!--<h2 :style="{key(属性名): value(属性值)}">{{message}}</h2>--> <!--'50px'必须加上单引号, 否则是当做一个变量去解析--> <!--<h2 :style="{fontSize: '50px'}">{{message}}</h2>--> <!--finalSize当成一个变量使用--> <!--<h2 :style="{fontSize: finalSize}">{{message}}</h2>--> <h2 :style="{fontSize: finalSize + 'px', backgroundColor: finalColor}">{{message}}</h2> <h2 :style="getStyles()">{{message}}</h2> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { message: '你好啊', finalSize: 100, finalColor: 'red', }, methods: { getStyles: function () { return {fontSize: this.finalSize + 'px', backgroundColor: this.finalColor} } } }) </script> </body> </html>
2.5、v-bind动态绑定style(数组语法)
<div v-bind:style="[baseStyles, overridingStyles]"></div>
style后面跟的是一个数组类型
多个值以,分割即可
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h2 :style="[baseStyle, baseStyle1]">{{message}}</h2> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { message: '你好啊', baseStyle: {backgroundColor: 'red'}, baseStyle1: {fontSize: '100px'}, } }) </script> </body> </html>
2.6、v-for与v-bind结合
<div id="app"> <ul> <!--<li v-for="m in movies">{{m}}</li>--> <li v-for="(m, index) in movies">{{index}}-{{m}}</li> </ul> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { movies: ['海王', '海尔兄弟', '火影忍者', '进击的巨人'] } }) </script>
三、计算属性
3.1、计算属性基本使用
计算属性是写在实例的computed选项中的
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h2>{{firstName + ' ' + lastName}}</h2> <h2>{{firstName}} {{lastName}}</h2> <h2>{{getFullName()}}</h2> <h2>{{fullName}}</h2> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { firstName: 'lebron', lastName: 'James' }, //计算属性 computed: { fullName: function () { return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName; } }, methods: { getFullName: function () { return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName; } } }) </script> </body> </html>
3.2、计算属性复杂操作
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h2>总价格: {{totalPrice}}</h2> <h2>总价格: {{getTotalPrice()}}</h2> <h2>总价格: {{totalPrice2}}</h2> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { books: [ {id: 110, name: 'Unix编程艺术', price: 119}, {id: 111, name: '代码大全', price: 105}, {id: 112, name: '深入理解计算机原理', price: 98}, {id: 113, name: '现代操作系统', price: 87}, ] }, methods: { getTotalPrice: function () { let result = 0 for (let i=0; i < this.books.length; i++) { result += this.books[i].price } return result } }, computed: { totalPrice: function () { let result = 0 //遍历方式一 for (let i=0; i < this.books.length; i++) { result += this.books[i].price } //遍历方式二 // for (let i in this.books) { // result += this.books[i].price // } //遍历方式三 // for (let book of this.books) { // result += book.price // } return result }, //高阶函数 totalPrice2: function () { return this.books.reduce((total,b) => { return total + b.price },0) } } }) </script> </body> </html>
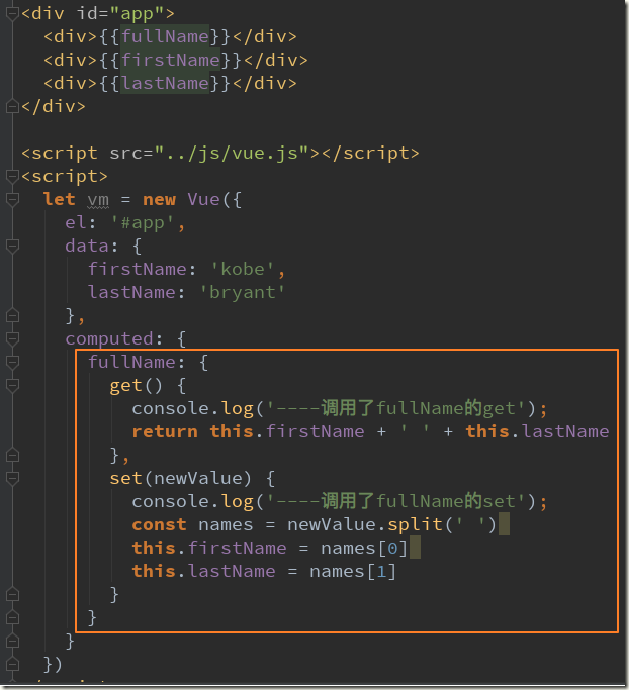
3.3、计算属性的setter和getter
3.4、计算属性的缓存
计算属性会进行缓存,如果多次使用时,计算属性只会调用一次
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <!--1.直接拼接: 语法过于繁琐--> <h2>{{firstName}} {{lastName}}</h2> <!--2.通过定义methods,调用4次--> <h2>{{getFullName()}}</h2> <h2>{{getFullName()}}</h2> <h2>{{getFullName()}}</h2> <h2>{{getFullName()}}</h2> <!--3.通过computed,调用4次--> <h2>{{fullName}}</h2> <h2>{{fullName}}</h2> <h2>{{fullName}}</h2> <h2>{{fullName}}</h2> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { firstName: 'Kobe', lastName: 'Bryant' }, methods: { getFullName: function () { console.log('getFullName'); return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName } }, computed: { fullName: function () { console.log('fullName'); return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName } } }) </script> </body> </html>
四、事件监听
4.1、v-on基本使用
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h2>{{counter}}</h2> <button v-on:click="counter++">+</button> <button v-on:click="counter--">-</button> <button v-on:click="increment">+</button> <button v-on:click="decrement">-</button> <button @click="increment">+</button> <button @click="decrement">-</button> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { counter: 0 }, methods: { increment() { this.counter++ }, decrement() { this.counter-- } } }) </script> </body> </html>
4.2、v-on参数
当通过methods中定义方法,以供@click调用时,需要注意参数问题:
- 情况一:如果该方法不需要额外参数,那么方法后的()可以不添加。但是注意:如果方法本身中有一个参数,那么会默认将原生事件event参数传递进去
- 情况二:如果需要同时传入某个参数,同时需要event时,可以通过$event传入事件。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <!--1.事件调用的方法没有参数--> <button @click="btn1Click()">按钮1</button> <button @click="btn1Click">按钮1</button> <!--2.在事件定义时, 写方法时省略了小括号, 但是方法本身是需要一个参数的, 这个时候, Vue会默认将浏览器生产的event事件对象作为参数传入到方法--> <button @click="btn2Click(123)">按钮2</button> <!--<button @click="btn2Click()">按钮2</button>--> <!--<button @click="btn2Click">按钮2</button>--> <!--3.方法定义时, 我们需要event对象, 同时又需要其他参数--> <!-- 在调用方式, 如何手动的获取到浏览器参数的event对象: $event--> <button @click="btn3Click(abc, $event)">按钮3</button> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { message: '你好啊', abc: 123 }, methods: { btn1Click() { console.log("btn1Click"); }, btn2Click(event) { console.log('--------', event); }, btn3Click(abc, event) { console.log('++++++++', abc, event); } } }) </script> </body> </html>
4.3、v-on修饰符
在某些情况下,我们拿到event的目的可能是进行一些事件处理。
Vue提供了修饰符来帮助我们方便的处理一些事件:
- .stop - 调用 event.stopPropagation()。
- .prevent - 调用 event.preventDefault()。
- .{keyCode | keyAlias} - 只当事件是从特定键触发时才触发回调。
- .native - 监听组件根元素的原生事件。
- .once - 只触发一次回调
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <!--1. .stop修饰符的使用--> <div @click="divClick"> aaaaaaa <button @click.stop="btnClick">按钮</button> </div> <!--2. .prevent修饰符的使用--> <br> <form action="baidu"> <input type="submit" value="提交" @click.prevent="submitClick"> </form> <!--3. .监听某个键盘的键帽--> <input type="text" @keyup.enter="keyUp"> <!--4. .once修饰符的使用--> <button @click.once="btn2Click">按钮2</button> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { message: '你好啊' }, methods: { btnClick() { console.log("btnClick"); }, divClick() { console.log("divClick"); }, submitClick() { console.log('submitClick'); }, keyUp() { console.log('keyUp'); }, btn2Click() { console.log('btn2Click'); } } }) </script> </body> </html>
五、条件判断
5.1、v-if、v-else-if、v-else
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h2 v-if="score>=90">优秀</h2> <h2 v-else-if="score>=80">良好</h2> <h2 v-else-if="score>=60">及格</h2> <h2 v-else>不及格</h2> <h1>{{result}}</h1> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { score: 56 }, computed: { result() { let showMessage = ''; if (this.score >= 90) { showMessage = '优秀' } else if (this.score >= 80) { showMessage = '良好' } else if (this.score >=60) { showMessage = '及格' } else { showMessage = '不及格' } return showMessage } } }) </script> </body> </html>
5.2、条件渲染案例
用户再登录时,可以切换使用用户账号登录还是邮箱地址登录
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <span v-if="isUser"> <label for="username">用户账户</label> <input type="text" id="username" placeholder="用户账户"> </span> <span v-else> <label for="email">用户邮箱</label> <input type="text" id="email" placeholder="用户邮箱"> </span> <button @click="isUser = !isUser">切换类型</button> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { isUser: true } }) </script> </body> </html>
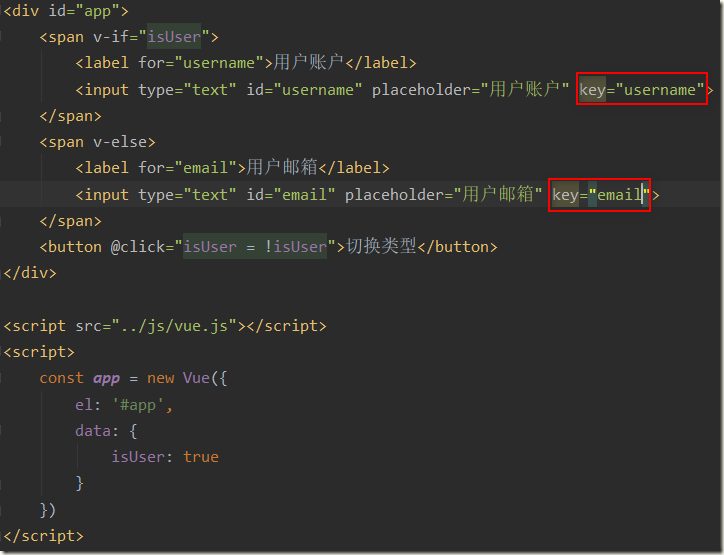
小问题:我们在有输入内容的情况下,切换了类型,我们会发现文字依然显示之前的输入的内容
解决:如果我们不希望Vue出现类似重复利用的问题,可以给对应的input添加key,并且我们需要保证key的不同
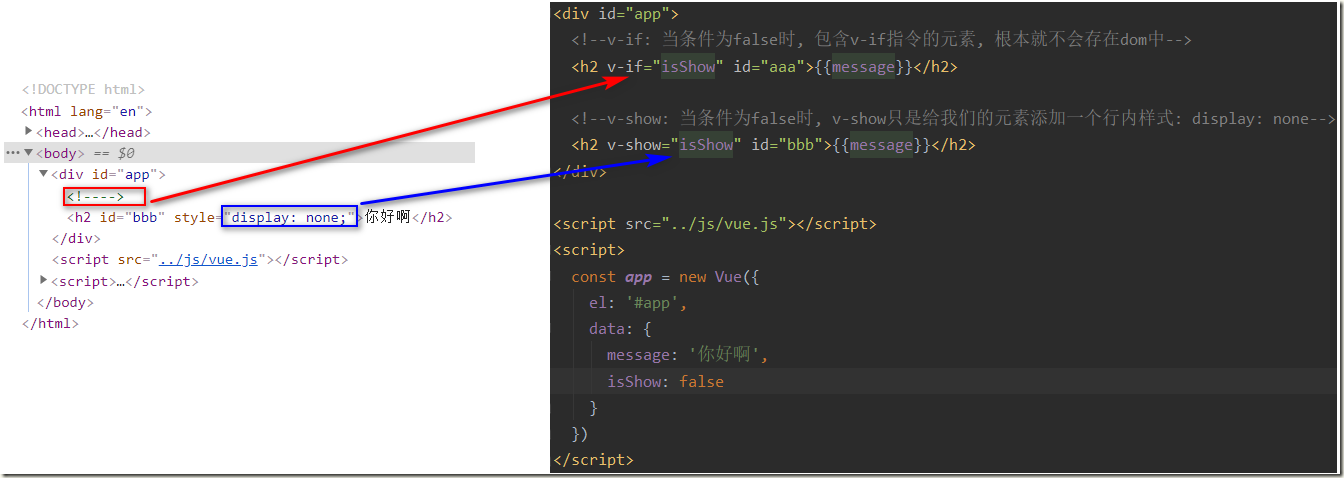
5.3、v-show指令
v-show的用法和v-if非常相似,也用于决定一个元素是否渲染
- v-if当条件为false时,压根不会有对应的元素在DOM中。
- v-show当条件为false时,仅仅是将元素的display属性设置为none而已
六、循环遍历
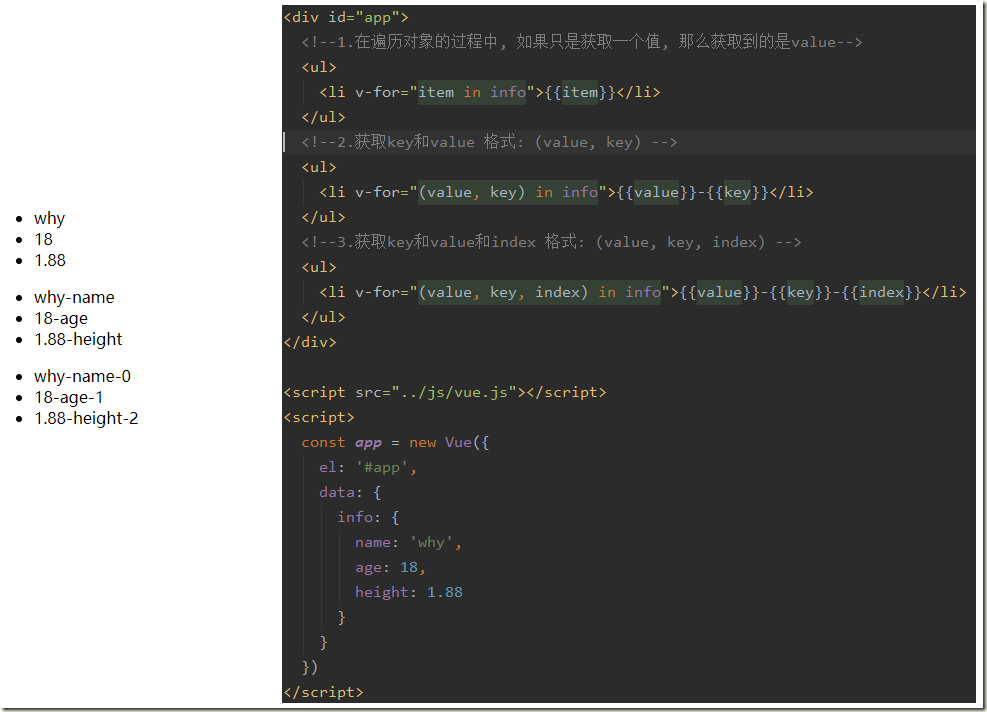
6.1、v-for遍历数组
<div id="app"> <!--1.在遍历的过程中,没有使用索引值(下标值)--> <ul> <li v-for="item in names">{{item}}</li> </ul> <!--2.在遍历的过程中, 获取索引值--> <ul> <li v-for="(item, index) in names"> {{index+1}}.{{item}} </li> </ul> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { names: ['why', 'kobe', 'james', 'curry'] } }) </script>
6.2、v-for遍历对象
6.3、组件key属性
<div id="app"> <ul> <li v-for="item in letters" :key="item">{{item}}</li> </ul> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { letters: ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'] } }) </script>
6.4、响应式方法
<div id="app"> <ul> <li v-for="item in letters">{{item}}</li> </ul> <button @click="btnClick">按钮</button> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { letters: ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'] }, methods: { btnClick() { // 1.push方法 this.letters.push('aaa') this.letters.push('aaaa', 'bbbb', 'cccc') // 2.pop(): 删除数组中的最后一个元素 this.letters.pop(); // 3.shift(): 删除数组中的第一个元素 this.letters.shift(); // 4.unshift(): 在数组最前面添加元素 this.letters.unshift() this.letters.unshift('aaa', 'bbb', 'ccc') // 5.splice作用: 删除元素/插入元素/替换元素 // 删除元素: 第二个参数传入你要删除几个元素(如果没有传,就删除后面所有的元素) // 替换元素: 第二个参数, 表示我们要替换几个元素, 后面是用于替换前面的元素 // 插入元素: 第二个参数, 传入0, 并且后面跟上要插入的元素 this.letters.splice(1, 3, 'm', 'n', 'l', 'x') this.letters.splice(1, 0, 'x', 'y', 'z') // 5.sort() this.letters.sort() // 6.reverse() this.letters.reverse() // 注意: 通过索引值修改数组中的元素 this.letters[0] = 'bbbbbb'; //不是响应式的 this.letters.splice(0, 1, 'bbbbbb') // set(要修改的对象, 索引值, 修改后的值) Vue.set(this.letters, 0, 'bbbbbb') } } })
6.5、小案例
点击选中显示红色,默认第一项显示红色
<div id="app"> <ul> <li v-for="(item, index) in movies" :class="{active: currentIndex === index}" @click="liClick(index)"> {{index+1}}.{{item}} </li> </ul> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { movies: ['海王', '海贼王', '加勒比海盗', '海尔兄弟'], currentIndex: 0 }, methods: { liClick(index) { this.currentIndex = index } } }) </script>
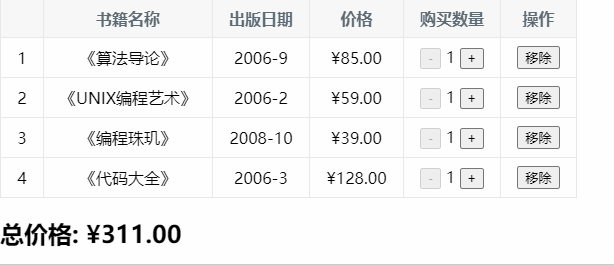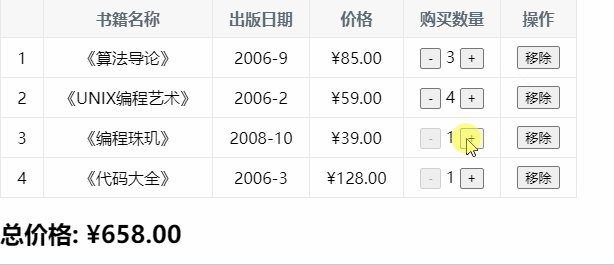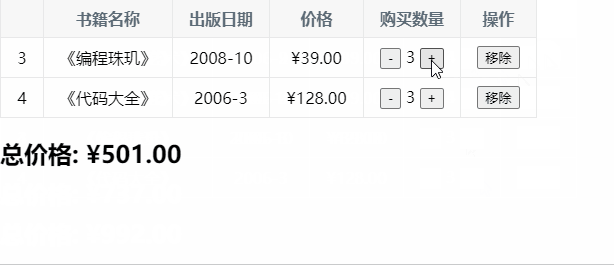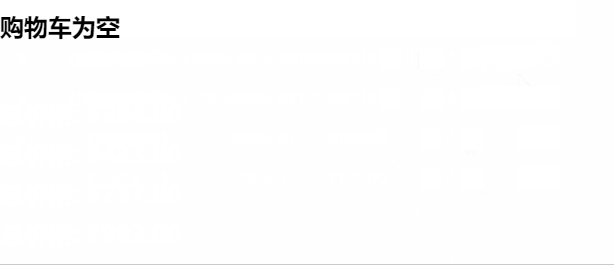
七、图书购物车
html代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css"> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <div v-if="books.length"> <table> <thead> <tr> <th></th> <th>书籍名称</th> <th>出版日期</th> <th>价格</th> <th>购买数量</th> <th>操作</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr v-for="(item,index) in books"> <td>{{item.id}}</td> <td>{{item.name}}</td> <td>{{item.date}}</td> <td>{{item.price | showPrice}}</td> <td> <button @click="decrement(index)" v-bind:disabled="item.count <= 1">-</button> {{item.count}} <button @click="increment(index)">+</button> </td> <td> <button @click="removeHandle(index)">移除</button> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> <h2>总价格: {{totalPrice | showPrice}}</h2> </div> <h2 v-else>购物车为空</h2> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script src="main.js"></script> </body> </html>
css:
table { border: 1px solid #e9e9e9; border-collapse: collapse; border-spacing: 0; } th,td { padding: 8px 16px; border: 1px solid #e9e9e9; text-align: center; } th { background-color: #f7f7f7; color: #5c6b77; font-weight: 600; }
vue:
const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { books: [ { id: 1, name: '《算法导论》', date: '2006-9', price: 85.00, count: 1 }, { id: 2, name: '《UNIX编程艺术》', date: '2006-2', price: 59.00, count: 1 }, { id: 3, name: '《编程珠玑》', date: '2008-10', price: 39.00, count: 1 }, { id: 4, name: '《代码大全》', date: '2006-3', price: 128.00, count: 1 }, ] }, computed: { totalPrice() { // 1.普通的for循环 // let totalPrice = 0 // for (let i = 0; i < this.books.length; i++) { // totalPrice += this.books[i].price * this.books[i].count // } // return totalPrice // 2.for (let i in this.books) // let totalPrice = 0 // for (let i in this.books) { // const book = this.books[i] // totalPrice += book.price * book.count // } // return totalPrice // 3.for (let i of this.books) // let totalPrice = 0 // for (let item of this.books) { // totalPrice += item.price * item.count // } // return totalPrice //4.使用reduce高阶函数 return this.books.reduce(function (preValue, book) { return preValue + book.price * book.count },0) } }, methods: { increment(index) { this.books[index].count++ }, decrement(index) { this.books[index].count-- }, removeHandle(index) { this.books.splice(index, 1) } }, filters: { showPrice(price) { return '¥' + price.toFixed(2); } } })