IO流基础
1.1 相对路径
相对路径:此时是相当于当前工程的路径。
绝对路径:在windows下一个有盘符的完全路径。
工作中使用相对路径,在linux下没有c盘,d盘。
1.2 Java字符串的编码与解码
编码encode:将字符串转换为字节数组。
译码decode:将字节数组转换为字符串。
请你说一下什么是乱码:编码的格式和解码的格式不一致。
(UTF-8中文字符占3个字节,GBK中文字符占二个字节)
package com.hujesse.IO;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Gbkencode {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
byte[] bytes = "好噶".getBytes("GBK");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
System.out.println(new String(bytes, "GBK"));
}
}
// toString()中参数有offset,count,which means从offset偏移量开始解码,解码长度为count。
1)数组下标为什么从0开始?
下标最精确的意思是"偏移量offset",对数组第二个元素,它对第一个元素偏移量为1----
1.3try with resources
JDK7的一个新特性。弱化了finally,java程序在运行时能自动关闭资源
场景:使用Scanner完成数据的输入,如何使用try with resource关闭资源
目的:解决传统的try{}catch(){}finally(){}

try(定义要关闭的资源){
容易出现异常的代码块
}catch(){
异常处理
}
//IDEA可以帮你解决什么代码可以放进try()中,不能会报红
// 实现了AutoCloseable(Scince JDK7,自动关闭资源的接口)的类就可以,Scanner继承了
//Closeable implements AutoCloseable
package com.hujesse.IO;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class endocing01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);){
System.out.println(scanner.next());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//jVM运行程序自动帮你关闭资源
}//finally {
//scanner.close();
//}
}
}
2 IO流介绍
I:input
O:output
Stream:是一个在二个设备之间进行数据传输的一个管道;作用:在设备之间进行数据传输的。

3 IO流的体系结构
1)按照流向分为二大类
输入流
输出流
2)按照数据类型可分为二大类
字节流bytes
字节输入流InputStream
字节输入流OutPutStream
字符流char(占二字节)
字符输入流Reader
字符输出流Writer
4 字节流(重点)
InputStream是所有字节输入流的父类,它是一个抽象类,它定义了抽象方法由子类实现,它的子类如下:
AudioInputStream(读取音频文件的输入流),ByteArrayInputStream(字节数组的输入流),FilterInputStream,FileInputStream重点,ObjectInputStream(读取对象的输入流),StringBufferInputStream(字符串缓冲区输入流).
OutputStream
* @see java.io.BufferedOutputStream
* @see java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream
* @see java.io.DataOutputStream
* @see java.io.FilterOutputStream
* @see java.io.FileOutputStream
* @see java.io.ObjectOutputStream

4.1FileOutputStream
构造方法:
1 new FileOutputStream(String name) 创建基于磁盘的字节输出对象,以字符串参数表示磁盘的路径。(绝对路径)
2 new FileOutputStream(File File)--- 以File参数表示磁盘的路径,例如File(“路径”)(相对路径)
FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append)创建文件输出流以写入由指定的 File对象表示的文件。true:在原有内容追加内容,不会复牌。默认为false。
| Constructor and Description |
|---|
FileOutputStream(File file)创建文件输出流以写入由指定的 File对象表示的文件。 |
FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append)创建文件输出流以写入由指定的 File对象表示的文件。true:在原有内容追加内容,不会复牌。默认为false。 |
FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj)创建文件输出流以写入指定的文件描述符,表示与文件系统中实际文件的现有连接。 |
FileOutputStream(String name)创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件。 |
FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append)创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件。 |
他有一下成员方法:
void |
close()关闭此文件输出流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源。 |
|---|---|
protected void |
finalize()清理与文件的连接,并确保当没有更多的引用此流时,将调用此文件输出流的 close方法。 |
FileChannel |
getChannel()返回与此文件输出流相关联的唯一的FileChannel对象。 |
FileDescriptor |
getFD()返回与此流相关联的文件描述符。 |
void |
write(byte[] b)将 b.length个字节从指定的字节数组写入此文件输出流。 |
void |
write(byte[] b, int off, int len)将 len字节从位于偏移量 off的指定字节数组写入此文件输出流。 |
void |
write(int b)将指定的字节写入此文件输出流。 |
场景:创建FileOutputStream

fos相当于是这个管道对象。
package com.hujesse.IO;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class OutputStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File("aa.txt"));
fileOutputStream.write("helloFile".getBytes());
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
// write(byte[],offset,len)
4.1追加写和换行写
追加写
FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append)创建文件输出流以写入由指定的 File对象表示的文件。true:在原有内容追加内容,不会复牌。默认为false
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File("aa.txt"),true);
换行写
win系统下换行符为
unix linux下
mac
package com.hujesse.IO;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class enterAsentence {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("a.txt"));
fos.write("hello".getBytes());
fos.write("
".getBytes());
fos.write("hello".getBytes());
fos.close();
}
}
4.2需要注意的问题
1) 工作中不要在类方法上throws Excepction --altho it looks clean.But the class(main) counld't throws Exceptions to uper class. aye. because the class is the most small unit. we better use try & catch
2) 不要在try里面写close(),the errors may accure Excepction before the function of close(),then program stop, the close()would never use;
the best solution is using try catch resources
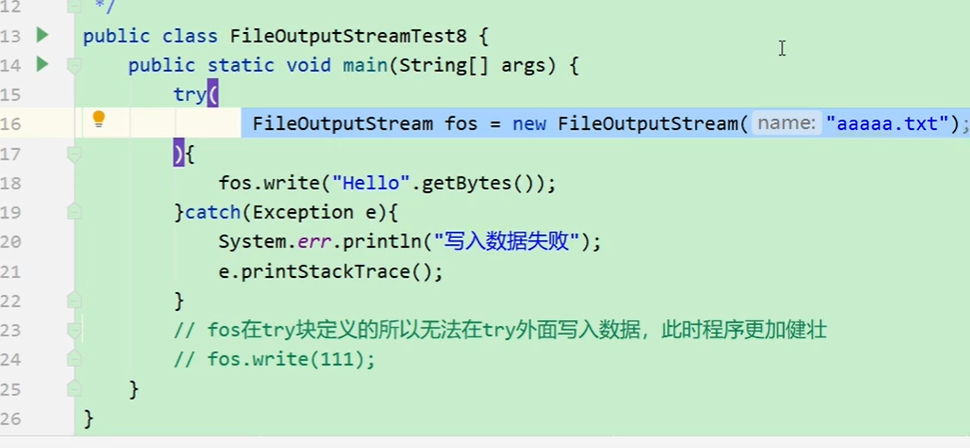
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("a.txt"));
===》
OutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("a.txt"));
编译看左边,运行看右边
多态 继承
5FileInputStream

| Constructor and Description |
|---|
FileInputStream(File file)通过打开与实际文件的连接创建一个 FileInputStream ,该文件由文件系统中的 File对象 file命名。 |
FileInputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj)创建 FileInputStream通过使用文件描述符 fdObj ,其表示在文件系统中的现有连接到一个实际的文件。 |
FileInputStream(String name)通过打开与实际文件的连接来创建一个 FileInputStream ,该文件由文件系统中的路径名 name命名。 |
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
int |
available()返回从此输入流中可以读取(或跳过)的剩余字节数的估计值,而不会被下一次调用此输入流的方法阻塞。 |
void |
close()关闭此文件输入流并释放与流相关联的任何系统资源。 |
protected void |
finalize()确保当这个文件输入流的 close方法没有更多的引用时被调用。 |
FileChannel |
getChannel()返回与此文件输入流相关联的唯一的FileChannel对象。 |
FileDescriptor |
getFD()返回表示与此 FileInputStream正在使用的文件系统中实际文件的连接的 FileDescriptor对象。 |
int |
read()从该输入流读取一个字节的数据。 |
int |
read(byte[] b)从该输入流读取最多 b.length个字节的数据为字节数组。 |
int |
read(byte[] b, int off, int len)从该输入流读取最多 len字节的数据为字节数组。 |
long |
skip(long n)跳过并从输入流中丢弃 n字节的数据。 |
对于read()方法,再次调用read()方法返回-1,表示已经读取到文件末尾了。
场景:读取当前目录下的一个文本文件
package com.hujesse.IO;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class FileInputStreamTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (InputStream fin = new FileInputStream(new File("a.txt"));
) {
//用来存储读取的数据
byte [] buffer = new byte[3];
// read返回读取的有效字节
int len = fin.read(buffer);
System.out.println(len);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(buffer));
// 译码将字节数组转换为字符串
System.out.println(new String(buffer));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
6文件的拷贝

场景:把D盘的一张图片拷贝到当前目录下:
package com.hujesse.IO;
import java.io.*;
public class CopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(
InputStream fin=new FileInputStream(new File("D:\timg.jpg"));
OutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("copy.jpg"));
){
int data = 0;
/**
* fin.read()使用输入管道读取数据
* data接受读取的数据
* 当data=-1,停止读取
*/
while((data=fin.read())!=-1){
// 读取的数据使用输出管道write()写入到目的路径
fos.write(data);
}
}catch (Exception e){
System.err.println("拷贝失败");
e.printStackTrace();
} }}
优化:
package com.hujesse.IO;
import java.io.*;
public class CopyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(
InputStream fin=new FileInputStream(new File("D:\timg.jpg"));
OutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("copy2HadImproved.jpg"));
){
byte []buffer = new byte[1024];
/**
* fin.read(buffer)使用输入管道读取数据,每次读取1024字节
* buffer接受读取的数据
* 当len=-1,停止读取
*/
int len ;
while((len=fin.read(buffer))!=-1){
// 最后一次读取可能读不到1024个,所以需要用这个方法。
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
}catch (Exception e){
System.err.println("拷贝失败");
e.printStackTrace();
} }}
小结:使用FileInputStream读取数据核心方法read()方法
使用FileOutputStream写数据核心方法write()方法。
helped by caojie
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV155411n7EV?p=7