一、Mybatis核心对象
1.1SqlSeesionFactory
SqlSessionFactory主要作用是创建时SqlSession。
SqlSessionFactory可通过SqlSessionFactoryBuild构建,
调用器build方法,方法参数为配置文件的输入流。
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; //获取配置文件输入流 InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); //通过配置文件输入流构建sqlSessionFactory, SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
1.2SqlSession
SqlSession负责程序与持久层之间的交互操作。
SqlSession中包含了所有执行SQL语句的方法,
且该对象是线程不安全的。
SqlSession主要方法:
<T> T selectOne(String statement);
执行查询方法,statement代表mapper文件中<select>元素对应的id.
方法结束会返回一个对象。
<T> T selectOne(String statement,Object parameter);
执行查询方法,statement代表mapper文件中<select>元素对应的id,
parameter代表查询语句所需的参数。
<E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter)
与上列函数功能相同,返回的是一个List对象。
int insert(String statement)
statement表示mapper文件中<insert>元素的id,执行插入语句后,返回受影响的行数。
int insert(String statement, Object parameter)
parameter代表插入语句所需的参数对象,结果返回受影响函数。
int update(String statement)
执行更新语句,statement为mapper文件中<update>元素的id,返回受影响函数。
int update(String statement, Object parament);
执行更新语句,parameter为语句所需参数,返回受影响行数。
int delete(String statement)//执行删除语句,statement为<delete>元素id,返回受影响行数
int delete(String statement, Object parameter);执行删除语句,parameter为语句所需参数。
void commit()//提交事务
voidrollBack();//回滚事务。
二、mybatis配置元素
2.1<configuration>
<configuration>根元素,mybatis的其他配置元素都需要在该元素类配置。
2.2<properties>
<properties>:通过外部的配置动态替换内部的配置。
例如:
2.2.1在src目录下新建一个db.properties
#dataSource #Sat Mar 02 13:31:50 CST 2019 jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=123456
2.2.2 在mybatis-config.xml中配置<properties>
<properties resource = "db.properties">
2.2.3 修改mybatis-congfig.xml中的DataSource配置
<dataSource type = "POOLED"> <property name = "driver" value = "${jdbc.driver}" /> <property name = "url" value = "${jdbc.url}" /> <property name = "username" value = "${jdbc.username}" /> <property name = "password" value = "${jdbc.password}" /> </dataSource>
2.3<settings>
<settings>:更改mybatis的运行行为,例如开启二级缓存,开启延迟等。图片来自:https://blog.csdn.net/fageweiketang/article/details/80767532
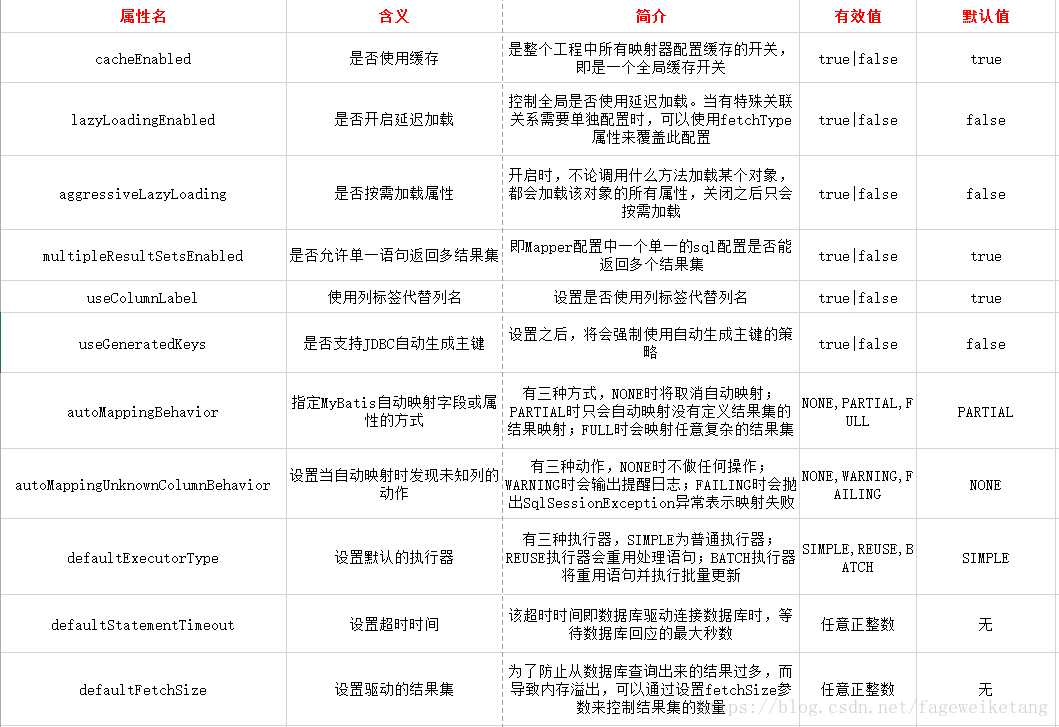
使用时指定属性name和value即可,具体如下:
<settings> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <setting name="multipleResultSetsEnabled" value="true"/>
...
</settings>
2.4<typeAliases>:为配置文件中的java了设置别名。
<typeAliases> <typeAlias> alias = "user" type = "com.xxx.xxx.User" /> </typeAliases>
将com.xxx.xxx.User起一个别名uesr。如果alias缺省,则会自动将类名首字母小写后作为别名。
<typeAliases> <package name = "com.xx.xxx"/> </typeAliases>
自动扫描指定包下所有类,自动将类名首字母为小写作为别名。
例如com.xxx.xxx.User的别名为user。
可以使用注解指定别名
@Alias("author")
public class Author {
...
}
mybatis默认别名:
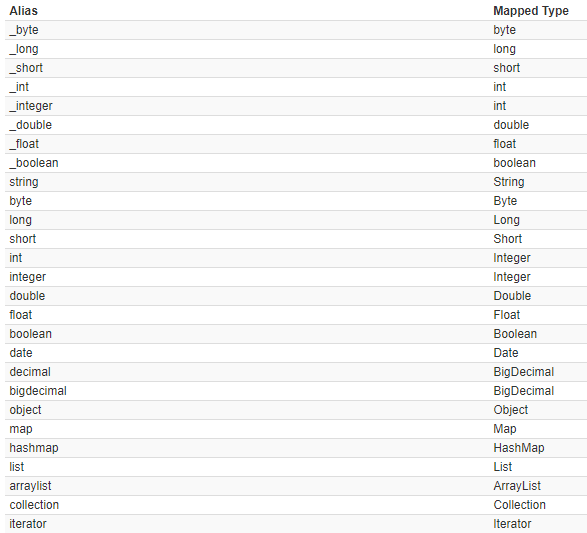
2.5<typeHandlers>
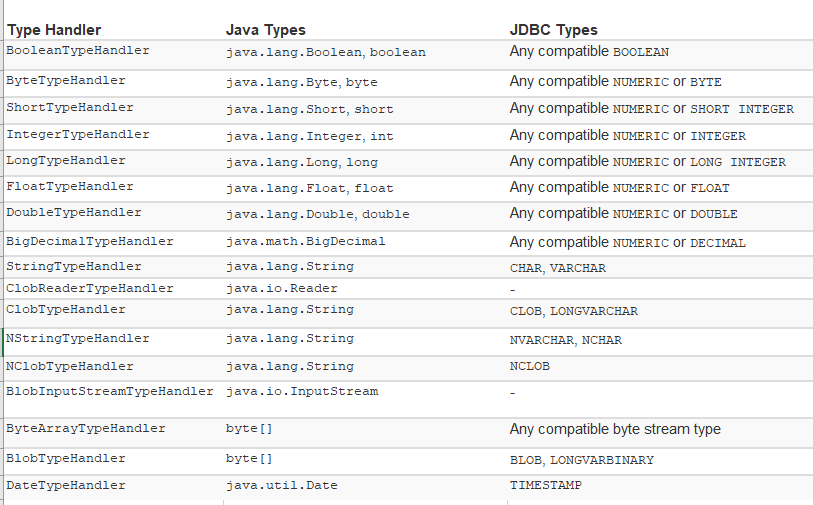

2.6<objectFactory>
每次MyBatis创建结果对象的新实例时,都会使用ObjectFactory实例来执行此操作。
2.7<plugins>
MyBatis允许在映射语句的执行过程中的某一点进行拦截调用。
2.8<environments>
<environments>主要对环境进行配置,内部可包含多个<environment>,其实就是数据源的配置,MyBatis允许配置多个数据源。
<environment>中不同的id区分不同的数据源,需要注意的是每一个数据库都对应一个SqlSessionFactory实例。如果有两个
数据库则需要构建两个实例。
构建不同的SqlSessionFactory实例,通过<environment>的id区分。
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader, environment);
例如配置如下:
<environments default = "mysql"> <!-- 配置id为SQL的数据库环境 --> <environment id = "my"> <!--区分不同数据库,构建不同的SqlSessionFactory--> <!-- 设置事务管理类型为JDBC --> <transactionManager type = "JDBC"/> <!-- 设置数据源 --> <dataSource type = "POOLED"> <property name = "driver" value = "${jdbc.driver}" /> <property name = "url" value = "${jdbc.url}" /> <property name = "username" value = "${jdbc.username}" /> <property name = "password" value = "${jdbc.password}" /> </dataSource> </environment>
<environment id= "you">
...
</environment> </environments>
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; //获取配置文件输入流 InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); //通过配置文件输入流构建sqlSessionFactory, SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream,"my");//不同的id区分数据库
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream,"you");//不同的id区分数据库
2.9<transactionManager>
在MyBatis中可以配置两种事务管理类型,一种是JDBC、一种是MANAGED。
JDBC:这种配置只是直接使用JDBC提交和回滚功能。它依赖从数据源检索到的连接来管理事务的范围。
MANAGED:此配置几乎不起作用。它从不提交或回滚连接。相反,它允许容器管理事务的整个生命周期
(例如,JEE应用程序服务器上下文)。默认情况下,它会关闭连接。但是,有些容器并不期望这样做,
因此如果需要阻止它关闭连接,请将“closeConnection”属性设置为false。
<transactionManager type="MANAGED"> <property name="closeConnection" value="false"/> </transactionManager>
注:如果计划将MyBatis与Spring一起使用,则无需配置任何TransactionManager,因为Spring模块将设置一个覆盖以前任何设置的配置。
2.10<dataSource>
<dataSource>:dataSource元素用于配置JDBC连接资源对象,使用标准的JDBC数据资源接口。
该元素有三种数据源类型(UNPOOLED、POOLED、JNDI)
UNPOOLED:每次请求数据源时,该数据源的实现只需打开和关闭一个连接。虽然速度有点慢,
但对于不需要立即可用连接性能的简单应用程序来说,这是一个不错的选择。
因此对于某些人来说,池可能不那么重要,这种配置将是理想的。
属性配置:
driver:JDBC驱动的java类,(例如com.mysql.jdbc.Driver)
url:数据库的连接地址。
username:数据库登录名
password:登录密码
defaultTransactionlsolationLevel:默认的连接事务隔离级别。
POOLED:他实现了连接池JDBC连接对象,以避免创建新连接实例所需的初始连接和身份验证时间。
这是一种流行的并发Web应用程序实现最快响应的方法。
属性配置:
除了上述五个配置外,该类型还支持如下配置:
poolMaximumActiveConnections :这是可以在任何给定时间存在的活动(即正在使用)连接数。默认值:10
poolMaximumIdleConnections :任意给定时间能够存在的空闲连接数。
poolMaximumCheckoutTime:
poolTimeToWait 使池有机会打印日志状态,并在连接花费异常长的情况下重新尝试获取连接
(以避免在池配置错误的情况下永远无提示地失败)。默认值:20000ms(即20秒)
poolMaximumLocalBadConnectionTolerance 如果获得一个坏的连接,它还有机会重新尝试获得另一个有效的连接。
但重试时间不应超过该属性设置的值。
poolPingQuery :ping查询被发送到数据库,以验证连接是否处于良好的工作状态,并准备好接受请求。
默认值是“no ping query set”,这将导致大多数数据库驱动程序失败,并显示一条错误消息。
poolPingEnabled :可以启用或禁止ping query,如果启用,还必须使用有效的SQL语句设置PoolpingQuery属性.默认为false.
JNDI:可以在EJB或者引用服务器等容器中使用,容器可以集中或在外部配置数据源,然后放置一个JNDI上下文引用。
配置属性:
initial_context:主要用于在InitialContext中寻找上下文,该属性为可选属性。
data_source:此属性表示引用数据源实例位置的上下文路径。
2.11<mappers>
定义了映射SQL语句后,需要告诉MyBtis在哪里找到映射文件,<mappers>就是提供这样的功能。
可以通过一下方法告知映射文件位置:
2.11.1使用类路径相关资源

2.11.2使用URL路径
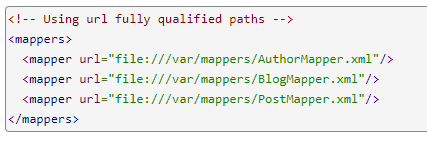
2.11.3使用接口类
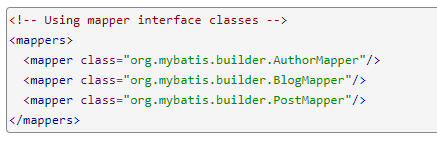
2.11.4将包下所有接口注册为映射
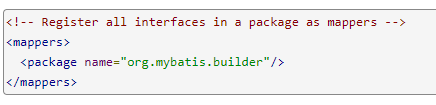
三、映射文件配置元素
3.1 <select>
<select>元素主要用于编写查询语句,可指定属性:
id:唯一标识符,代表该语句。
parameterType:传递的参数类型。
resultType:返回值类型。
flushCache:设置是否清空缓存,默认为fasle。
userCache:是否开启缓存,默认为true.
timeout:设置超时时间。
fetchSize:指定获取记录的总条数。
statementType:指定语句的类型.(例如Statement,PreparedStatement...)
resultSetType:表示结果集类型。
<select id="findCustomerById" parameterType = "Integer" resultType = "com.mybatis.first.Customer"> select * from t_customer where id = #{id} </select>
参数类型为Integer,返回值类型为Customer,#{}类似占位符,#{id}代表为其设置的参数。
3.2<insert>
该元素用于映射插入语句,返回一个数字表示插入的行数。
属性:
keyProperty:(仅对update、insert有效)将插入或删除语句的返回值赋给PO类的某个属性。
useGeneratedKeys:获取数据库主键(数据库内部自动增加的字段),默认为fasle.
两者需要配合使用,设置useGeneratedKeys=“true”并将keyProperty设置为目标属性。
<!-- 添加用户 --> <insert id = "addCustomer" parameterType = "com.mybatis.first.Customer" keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true"> insert into t_customer(username, jobs,phone) value(#{username}, #{jobs}, #{phone}) </insert>
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; public class MybatisTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; //获取配置文件输入流 InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); //通过配置文件输入流构建sqlSessionFactory, SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream,"my"); //通过sqlSessionFactory获取sqlSession,true代表设置为自动提交。 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); //执行CustomerMapper.xml文件中,id为xxxCustomer的语句,参数为Integer对象。 Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setJobs("student"); customer.setPhone("135xxxx9876"); customer.setUsername("zrx"); int customers = sqlSession.insert("com.mybatis.mapper.CustomerMapper.addCustomer", customer); System.out.println(customer.getId()); System.out.println(customers); //如果没有设置自动提交,使用insert、update、delete时需要使用sqlSession.commit()手动提交。 sqlSession.close(); } }

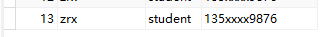
对于不支持主键自动增长的数据库,可通过如下方式实现主键自动增长。
<!-- 添加用户 --> <insert id = "addCustomer" parameterType = "com.mybatis.first.Customer" > <selectKey keyProperty = "id" resultType = "Integer" order = "BEFORE"> select if(max(id) is null,1,max(id) + 1) as newId from t_customer </selectKey> insert into t_customer(id,username, jobs,phone) value(#{id},#{username}, #{jobs}, #{phone}) </insert>
寻找表中最大id,如果为空则设置为1,不为空则设置为最大id+1。
order属性可设置为:BEFORE,AFTER。BEFORE代表在执行语句之前执行
<selectKey>,AFTER代表在<selectKey>之后执行语句。
3.3 update和delete
update和delete的属性与上述语句中属性基本一样。
<update id = "updateCustomer" parameterType = "com.xxx.xxx.Customer" flushCache = "true" statementType = "PREPARED" timeout = "20"> ...... </update>
<delete id = "updateCustomer" parameterType = "com.xxx.xxx.Customer" flushCache = "true" statementType = "PREPARED" timeout = "20"> ...... </delete>
3.4<sql>
<sql>元素用于定义可重用的SQL代码片段,然后在其他语句中应用这个定义的片段。
例如:
<sql id = "customerColumns"> id,username,jobs,phone </sql> <select> select <include refid = "customerColumns"/> from t_customer where id = #{id} </select>
其实还可以更灵活的使用<sql>元素:
<sql id = "customerColumns"> id,username,jobs,phone </sql> <sql id = "tablename"> ${prefix}customer </sql> <sql id = "someinclude"> from <include refid = "${include_target}"/> </sql> <sql> <select id = "findCustomerById" parameterType = "Integer" resultType = "com.xxx.xxx.Customer"> select <include refid = "customerColumns"/> <include refid = "someinclude"> <property name = "prefix" value = "t_"/> <property name = "include_target" value = "tablename"/> </include> where id = #{id} </select>
首先<insert>中首先包含"customerColumns",语句就变成了select id,username,jobs,phone
然后再包含"someinclude", someinclude中首先有from,然后又包含了refid = ${include_targer},
${include_targer}即获取include_target属性的值,就变成了refid = "tablename".
tablename中同样先获取prefix属性的值(${prefix})“t_”,于是语句最后就变成了:
select id,username,jobs,phone from t_customer where id = #{id}。
3.5<resultMap>
<resultMap>主要用于建立数据库中列名与POJO类属性的映射关系,
当列名与POJO类属性同名时,MyBatis会自动填充。但如果不同名时,
需要指定映射关系,MyBatis才会对其填充。
属性:
id:<resutlMap>的唯一标识符
type:需要映射的POJO类。
子元素:
id:指定主键与POJO属性之间映射,property指定POJO类属性名,column指定列名。
result:指定列名和POJO类属性映射,property指定POJO类属性名,column指定列名。
Customer.java
public class Customer { private Integer id; private String username; private String jobs; private String phone; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getJobs() { return jobs; } public void setJobs(String jobs) { this.jobs = jobs; } public String getPhone() { return phone; } public void setPhone(String phone) { this.phone = phone; } @Override public String toString() { return "Customer [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", jobs=" + jobs + ", phone=" + phone + "]"; } }
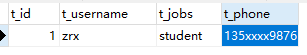
创建t_custoemr表:
CREATE TABLE `t_customer` ( `t_id` int(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `t_username` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, `t_jobs` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, `t_phone` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`t_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=16 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;

CustomerMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace = "com.mybatis.mapper.CustomerMapper" >
<!--结果映射,将列名与Customer属性建立映射关系--> <resultMap type="com.mybatis.first.Customer" id="re"> <id property="id" column="t_id"/> <result property = "username" column="t_username"/> <result property = "jobs" column="t_jobs"/> <result property="phone" column="t_phone" /> </resultMap> <!--查找所有用户--> <select id="findAllCustomer" resultMap="re"> select * from t_customer </select> <!-- 添加用户 --> <insert id = "addCustomer" parameterType = "com.mybatis.first.Customer" > <selectKey keyProperty = "id" resultType = "Integer" order = "BEFORE"> select if(max(t_id) is null,1,max(t_id) + 1) as newId from t_customer </selectKey> insert into t_customer(t_id,t_username, t_jobs,t_phone) value(#{id},#{username}, #{jobs}, #{phone}) </insert> </mapper>
测试:
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; public class MybatisTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; //获取配置文件输入流 InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); //通过配置文件输入流构建sqlSessionFactory, SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream,"my"); //通过sqlSessionFactory获取sqlSession,true代表设置为自动提交。 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); //执行CustomerMapper.xml文件中,id为xxxCustomer的语句,参数为Integer对象。 Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setJobs("student"); customer.setPhone("135xxxx9876"); customer.setUsername("zrx"); int num = sqlSession.insert("com.mybatis.mapper.CustomerMapper.addCustomer",customer); List<Customer> customers = sqlSession.selectList("com.mybatis.mapper.CustomerMapper.findAllCustomer", customer); for(Customer temp : customers) { System.out.println(customers); } //如果没有设置自动提交,使用insert、update、delete时需要使用sqlSession.commit()手动提交。 sqlSession.close(); } }

参考资料: