17.01 ArrayList集合的toString()方法源码解析
代码:
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add("hello");
c.add("world");
c.add("java");
System.out.println(c);
输出c时默认调用的是c的toString()方法
A:Collection c = new ArrayList();
这是多态,所以输出c的 toString()方法,其实是输出ArrayList的toString()方法
B:看 ArrayList 的 toString()方法
在ArrayList里面却没有发现toString()。应该去父类查找→ AbstractList → AbstractCollection
C:toString()的方法源码
1 public String toString()
2 {
3 Iterator<E> it = iterator(); //集合本身调用迭代器方法,得到集合迭代器
4 if (! it.hasNext())
5 return "[]";
6
7 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
8 sb.append('[');
9 for (;;)
10 {
11 E e = it.next(); //e=hello,world,java
12 sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e);
13 if (! it.hasNext())
14 //[hello, world, java]
15 return sb.append(']').toString();
16 sb.append(',').append(' ');
17 }
18 }
17.02 Set集合概述及特点
Set接口概述:一个不包含重复元素的 collection
特点:
无序(存入与取出的顺序不一致)
唯一(存入集合的元素唯一)
17.03 HashSet存储字符串并遍历
HashSet类概述:不保证 set 的迭代顺序,特别是它不保证该顺序恒久不变。此类允许使用 null 元素。
例:
1 public class Practice
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 HashSet<String> hs = new HashSet<String>();
6 hs.add("hello");
7 hs.add("world");
8 hs.add("world");
9 hs.add("java");
10
11 for (String s : hs)
12 {
13 System.out.println(s);
14 }
15 }
16 }
运行结果:
hello java world
17.04 HashSet保证元素唯一性的源码解析
1 interface Collection
2 {...}
3
4 interface Set extends Collection
5 {...}
6
7 class HashSet implements Set
8 {
9 private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
10 private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;
11
12 public HashSet()
13 {
14 map = new HashMap<>();
15 }
16
17 public boolean add(E e)
18 { //e=hello,world
19 return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
20 }
21 }
22
23 class HashMap implements Map
24 {
25 public V put(K key, V value)
26 { //key=e=hello,world
27
28 //看哈希表是否为空,如果空,就开辟空间
29 if (table == EMPTY_TABLE)
30 {
31 inflateTable(threshold);
32 }
33
34 //判断对象是否为null
35 if (key == null)
36 return putForNullKey(value);
37
38 int hash = hash(key); //和对象的hashCode()方法相关
39
40 //在哈希表中查找hash值
41 int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
42 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next)
43 {
44 //这次的e其实是第一次的world
45 Object k;
46 if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
47 {
48 V oldValue = e.value;
49 e.value = value;
50 e.recordAccess(this);
51 return oldValue;
52 //走这里其实是没有添加元素
53 }
54 }
55
56 modCount++;
57 addEntry(hash, key, value, i); //把元素添加
58 return null;
59 }
60
61 transient int hashSeed = 0;
62
63 final int hash(Object k)
64 { //k=key=e=hello,
65 int h = hashSeed;
66 if (0 != h && k instanceof String)
67 {
68 return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
69 }
70
71 h ^= k.hashCode(); //这里调用的是对象的hashCode()方法
72
73 // This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
74 // constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
75 // number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
76 h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
77 return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
78 }
79 }
通过查看add方法的源码,知道这个方法底层依赖两个方法:hashCode()和equals()。
判断元素唯一性的方式:通过对象的hashCode和equals方法来完成元素唯一性
如果对象的hashCode值不同,那么不用判断equals方法,就直接存储到哈希表中。
如果对象的hashCode值相同,那么要再次判断对象的equals方法是否为true。
如果为true,视为相同元素,不存。如果为false,那么视为不同元素,就进行存储。
如果类没有重写这两个方法,默认使用的Object()。一般来说不会相同。
17.05 HashSet存储自定义对象并遍历
1 public class Practice
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 HashSet<Student> hs = new HashSet<Student>();
6
7 hs.add(new Student("小明",23));
8 hs.add(new Student("旺财",12));
9 hs.add(new Student("旺财",12));
10 hs.add(new Student("小强",24));
11 hs.add(new Student("小明",22));
12 hs.add(new Student("小红",22));
13
14 for(Student s : hs)
15 {
16 System.out.println(s.getName()+":"+s.getAge());
17 }
18 }
19 }
17.06 HashSet保证元素唯一性的代码体现
上例中重复元素被存入到了集合中,因为Student没有重写hashCode和equals方法,默认使用的Object()的hashCode和equals方法,一般来说结果不会相同,所以存入到了集合中,Student类应重写hashCode和equals方法(自动生成)。
1 @Override
2 public int hashCode()
3 {
4 final int prime = 31;
5 int result = 1;
6 result = prime * result + age;
7 result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
8 return result;
9 }
10
11 @Override
12 public boolean equals(Object obj)
13 {
14 if (this == obj)
15 return true;
16 if (obj == null)
17 return false;
18 if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
19 return false;
20 Student other = (Student) obj;
21 if (age != other.age)
22 return false;
23 if (name == null)
24 {
25 if (other.name != null)
26 return false;
27 } else if (!name.equals(other.name))
28 return false;
29 return true;
30 }
17.07 LinkedHashSet的概述和使用
LinkedHashSet类概述:
元素有序唯一:由链表保证元素有序、由哈希表保证元素唯一
例:
1 public class Practice
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 LinkedHashSet<String> hs = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
6 hs.add("hello");
7 hs.add("world");
8 hs.add("world");
9 hs.add("java");
10
11 for(String s : hs)
12 {
13 System.out.println(s);
14 }
15 }
16 }
运行结果:
hello world java
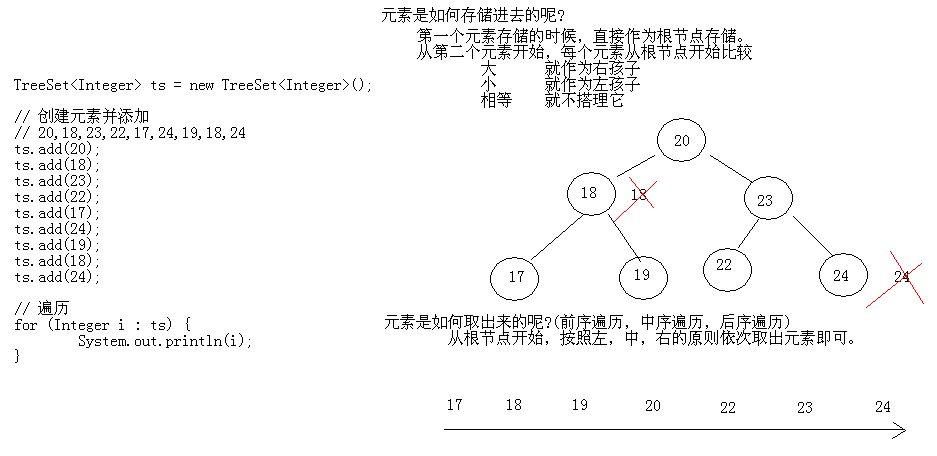
17.08 TreeSet存储Integer类型的元素并遍历
TreeSet类概述:使用元素的自然顺序对元素进行排序,或者根据创建 set 时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
例:
1 public class Practice
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 TreeSet<Integer> ts = new TreeSet<Integer>();
6 ts.add(20);
7 ts.add(18);
8 ts.add(23);
9 ts.add(22);
10 ts.add(17);
11 ts.add(24);
12 ts.add(19);
13 ts.add(18);
14
15 for(Integer i : ts)
16 {
17 System.out.print(i+" ");
18 }
19 }
20 }
运行结果:
17 18 19 20 22 23 24
17.09 TreeSet保证元素排序的源码解析
1 interface Collection {...}
2
3 interface Set extends Collection {...}
4
5 interface NavigableMap {}
6
7 class TreeMap implements NavigableMap
8 {
9 public V put(K key, V value)
10 {
11 Entry<K,V> t = root;
12 if (t == null)
13 {
14 compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
15
16 root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
17 size = 1;
18 modCount++;
19 return null;
20 }
21 int cmp;
22 Entry<K,V> parent;
23 // split comparator and comparable paths
24 Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
25 if (cpr != null)
26 {
27 do
28 {
29 parent = t;
30 cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
31 if (cmp < 0)
32 t = t.left;
33 else if (cmp > 0)
34 t = t.right;
35 else
36 return t.setValue(value);
37 } while (t != null);
38 }
39 else
40 {
41 if (key == null)
42 throw new NullPointerException();
43 Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
44 do
45 {
46 parent = t;
47 cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
48 if (cmp < 0)
49 t = t.left;
50 else if (cmp > 0)
51 t = t.right;
52 else
53 return t.setValue(value);
54 } while (t != null);
55 }
56 Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
57 if (cmp < 0)
58 parent.left = e;
59 else
60 parent.right = e;
61 fixAfterInsertion(e);
62 size++;
63 modCount++;
64 return null;
65 }
66 }
67
68 class TreeSet implements Set
69 {
70 private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m;
71
72 public TreeSet()
73 {
74 this(new TreeMap<E,Object>());
75 }
76
77 public boolean add(E e)
78 {
79 return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
80 }
81 }
真正的比较是依赖于元素的compareTo()方法,而这个方法是定义在 Comparable里面的。
所以,要想重写该方法,就必须是先实现 Comparable接口。这个接口表示的就是自然排序。
17.10 TreeSet保证元素唯一性和自然排序的原理和图解
17.11 TreeSet存储自定义对象并遍历练习1
Student类实现自然排序接口Comparable,重写compareTo()方法
1 @Override
2 public int compareTo(Student s)
3 {
4 //主要条件,按年龄排
5 int num = this.age - s.age;
6 //次要条件,年龄相同按姓名排
7 int num2 = (num == 0)?this.name.compareTo(s.name):num;
8 return num2;
9 }
17.12 TreeSet存储自定义对象并遍历练习2
Student类实现自然排序接口Comparable,重写compareTo()方法
1 @Override
2 public int compareTo(Student s)
3 {
4 // 主要条件 姓名的长度
5 int num = this.name.length() - s.name.length();
6 // 姓名的长度相同,比较姓名的内容是否相同
7 int num2 = num == 0 ? this.name.compareTo(s.name) : num;
8 // 姓名的长度和内容相同,比较年龄是否相同,继续判断年龄
9 int num3 = num2 == 0 ? this.age - s.age : num2;
10 return num3;
11 }
17.13 TreeSet保证元素唯一性和比较器排序的原理及代码实现
1 // 比较器排序,让集合具备比较性,匿名内部类实现
2 TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(new Comparator<Student>()
3 {
4 @Override
5 public int compare(Student s1, Student s2)
6 {
7 // 姓名长度
8 int num = s1.getName().length() - s2.getName().length();
9 // 姓名内容
10 int num2 = num == 0 ? s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()) : num;
11 // 年龄
12 int num3 = num2 == 0 ? s1.getAge() - s2.getAge() : num2;
13 return num3;
14 }
15
16 });
17.14 TreeSet对元素排序的总结
唯一性:根据比较的返回的是否是0来决定
排序: 1.自然排序,一个类的元素想要进行自然排序就必须实现自然排序接口Comparable(元素具备比较性)
2.比较器排序,让集合的构造方法接收一个比较器接口的子类对象Comparator(集合具备比较性)
17.15 产生10个1-20之间的随机数要求随机数不能重复案例简洁版
编写一个程序,获取10个1至20的随机数,要求随机数不能重复。
1 public class Practice
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 // 创建随机数对象
6 Random r = new Random();
7
8 // 创建一个Set集合
9 HashSet<Integer> ts = new HashSet<Integer>();
10
11 // 判断集合的长度是不是小于10
12 while (ts.size() < 10)
13 {
14 int num = r.nextInt(20) + 1;
15 ts.add(num);
16 }
17
18 // 遍历Set集合
19 for (Integer i : ts)
20 {
21 System.out.println(i);
22 }
23 }
24 }
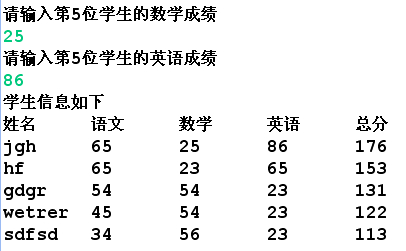
17.16 键盘录入学生信息按照总分排序后输出在控制台案例
Student类
1 public class Student
2 {
3 private String name;
4 private int chinese;
5 private int math;
6 private int english;
7 public Student(String name, int chinese, int math, int english)
8 {
9 super();
10 this.name = name;
11 this.chinese = chinese;
12 this.math = math;
13 this.english = english;
14 }
15 public String getName()
16 {
17 return name;
18 }
19 public void setName(String name)
20 {
21 this.name = name;
22 }
23 public int getChinese()
24 {
25 return chinese;
26 }
27 public void setChinese(int chinese)
28 {
29 this.chinese = chinese;
30 }
31 public int getMath()
32 {
33 return math;
34 }
35 public void setMath(int math)
36 {
37 this.math = math;
38 }
39 public int getEnglish()
40 {
41 return english;
42 }
43 public void setEnglish(int english)
44 {
45 this.english = english;
46 }
47
48 public int getSum()
49 {
50 return this.chinese+this.english+this.math;
51 }
52 }
测试类
1 public class Practice
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(new Comparator<Student>()
6 {
7 @Override
8 public int compare(Student s1, Student s2)
9 {
10 //按总分比较
11 int num1 = s2.getSum() - s1.getSum();
12 //总分相同按语文成绩比较
13 int num2 = num1==0?s1.getChinese() - s2.getChinese():num1;
14 //语文成绩相同按数学成绩比较
15 int num3 = num2==0?s1.getMath() - s2.getMath():num2;
16 //数学成绩相同按英语成绩比较
17 int num4 = num3==0?s1.getChinese() - s2.getChinese():num3;
18 //英语成绩相同按姓名比较
19 int num5 = num4==0?s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()):num4;
20 return num5;
21 }
22 });
23 for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
24 {
25 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
26 System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"位学生的姓名");
27 String name = sc.nextLine();
28 System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"位学生的语文成绩");
29 String chinese = sc.nextLine();
30 System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"位学生的数学成绩");
31 String math = sc.nextLine();
32 System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"位学生的英语成绩");
33 String english = sc.nextLine();
34
35 Student s = new Student(name, Integer.parseInt(chinese), Integer.parseInt(math), Integer.parseInt(english));
36 ts.add(s);
37 }
38 System.out.println("学生信息如下");
39 System.out.println("姓名 语文 数学 英语 总分");
40 for(Student s:ts)
41 {
42 System.out.println(s.getName()+" "+s.getChinese()+" "+s.getMath()+" "+s.getEnglish()+" "+s.getSum());
43 }
44 }
45 }
运行结果: