一、基于Token进行用户认证
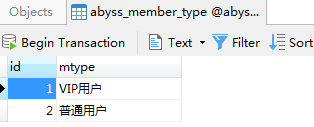
创建相应数据库
class member_type(models.Model):
mtype = models.CharField(max_length=50)
def __unicode__(self):
return self.mtype
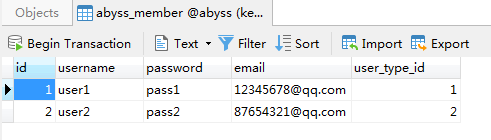
class member(models.Model):
username = models.CharField(max_length=30)
password = models.CharField(max_length=100)
email = models.EmailField()
user_type = models.ForeignKey("member_type")
def __unicode__(self):
return self.username
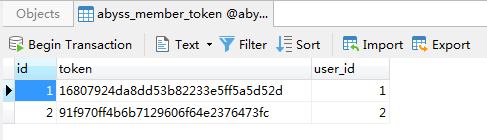
class member_token(models.Model):
user = models.OneToOneField(to=member)
token = models.CharField(max_length=64)
def __unicode__(self):
return self.token
配置路由
from abyss import views
from django.conf.urls import url
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^api/v1/auth$', views.AuthView.as_view(),name='auth'),
url(r'^api/v1/order$', views.OrderView.as_view(),name='order'),
]
在setting文件中,添加rest framework应用
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'rest_framework',
]
配置视图认证
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
from rest_framework import exceptions
from django.http import JsonResponse
from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse
import hashlib
import time
class Myauthentication(BaseAuthentication):
'''认证类'''
def authenticate(self, request):
token = request._request.GET.get("token")
token_obj = models.member_token.objects.filter(token=token).first()
if not token_obj:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed('用户认证失败')
return (token_obj.user, token_obj) # 这里返回值一次给request.user,request.auth
def authenticate_header(self, request):
pass
def make_token(user):
ctime = str(time.time())
hash=hashlib.md5(user.encode("utf-8"))
hash.update(ctime.encode("utf-8"))
return hash.hexdigest()
class AuthView(APIView):
"""登录认证"""
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return super(AuthView,self).dispatch(request,*args, **kwargs)
def get(self,request, *args, **kwargs):
return HttpResponse('get is ok')
def post(self,request, *args, **kwargs):
ret={'code':1000,'msg':"登录成功",'token':None}
try:
user = request._request.POST.get("username")
pwd = request._request.POST.get("password")
obj = models.member.objects.filter(username=user,password=pwd).first()
if not obj:
ret['code'] = 1001
ret['msg'] = "用户名或密码错误"
else:
token = make_token(user)
models.member_token.objects.update_or_create(user=obj,defaults={"token":token})
ret['token'] = token
except exceptions as e:
ret['code'] = 1002
ret['msg'] = "请求异常"
return JsonResponse(ret)
class OrderView(APIView):
"""查看订单信息"""
authentication_classes = [Myauthentication,] #添加认证
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# request.user
# request.auth
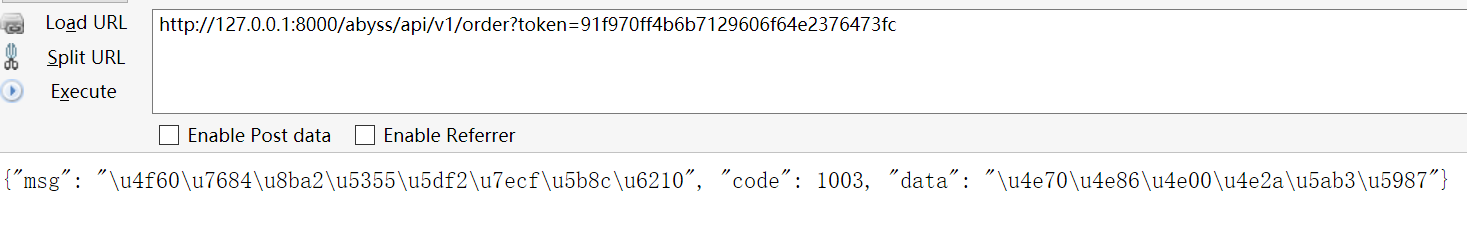
ret = {'code': 1003, 'msg': "你的订单已经完成", 'data': "买了一个媳妇"}
return JsonResponse(ret, safe=True)
登录认证,登录后会生成token值

使用token进行订单查询:
二、全局自定义认证
通过对Django rest framework认证的源码分析知道,可以直接在项目的settings.py配置文件中引入自定义的认证类,即可以对所有的url进行用户认证流程
在应用app目录下创建utils包,在utils包下创建auth.py文件,内容为自定义的认证类
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
from rest_framework import exceptions
from abyss import models
class Myauthentication(BaseAuthentication):
'''认证类'''
def authenticate(self, request):
token = request._request.GET.get("token")
token_obj = models.member_token.objects.filter(token=token).first()
if not token_obj:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed('用户认证失败')
# restframework会将元组赋值给request,以供后面使用
return (token_obj.user, token_obj) # 这里返回值一次给request.user,request.auth
def authenticate_header(self, request):
pass
settings.py中的REST_FRAMEWORK作为key作为配置,所以全局配置示例:
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES':['abyss.utils.auth.Myauthentication',]
}
#其中写认证的类的路径,不要在views中,这里我放在了utils目录下auth.py中
此外,因为开启了全局认证,所以每个接口视图中:authentication_classes = [Myauthentication,] 就不需要设置了。
局部某个视图不需要认证情况,如认证AuthView应该是可以直接访问的,那就如下设置:
authentication_classes = [] #authentication_classes为空,代表不需要认证
三、配置匿名用户
匿名用户配置
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES":['API.utils.auth.Authentication',],
#其中写认证的类的路径,不要在views中,这里我放在了utils目录下auth.py中
"UNAUTHENTICATED_USER": lambda:"匿名",
#匿名用户配置,只需要函数或类的对应的返回值,对应request.user="匿名"
"UNAUTHENTICATED_token": None,
#匿名token,只需要函数或类的对应的返回值,对应request.auth=None
}
四、Django rest framework内置的认证类
1.BaseAuthentication
BaseAuthentication是django rest framework为我们提供了最基本的认证类,正如源码流程一样,该类中其中定义的两个方法authenticate和authenticate_header(认证失败返回的响应头),使用时候重写该两个方法进行认证,正如示例:
class BaseAuthentication(object):
"""
All authentication classes should extend BaseAuthentication.
"""
def authenticate(self, request):
"""
Authenticate the request and return a two-tuple of (user, token).
"""
raise NotImplementedError(".authenticate() must be overridden.")
def authenticate_header(self, request):
"""
Return a string to be used as the value of the `WWW-Authenticate`
header in a `401 Unauthenticated` response, or `None` if the
authentication scheme should return `403 Permission Denied` responses.
"""
pass
其它认证类:
##路径:rest_framework.authentication
BasicAuthentication #基于浏览器进行认证,浏览器弹框
SessionAuthentication #基于django的session进行认证
RemoteUserAuthentication #基于django admin中的用户进行认证,这也是官网的示例
TokenAuthentication #基于drf内部的token认证
五、总结
1.自定义认证类:
继承BaseAuthentication,重写authenticate方法和authenticate_header(pass就可以),authenticate()方法需要有三种情况(返回元祖、出现异常、返回none)。
2.认证配置:
#全局认证
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES":['API.utils.auth.Authentication',]
}
#局部认证
authentication_classes = [BaseAuthentication,]
#是某个视图不进行认证
authentication_classes =[]