广度优先搜索算法(Breadth-First Search),又称为"宽度优先搜索"或"横向优先搜索"主要可以解决两类问题:
·是否存在从起点到终点的路径
·找出从起点到终点的最短路径a
算法描述:
1 int bfs(){ 2 初始化 首结点入队(首指针为0,尾指针为1) 3 while(首指针小于尾指针){ 4 首指针后移一位 5 for(;;) { 产生子结点 6 if() { 判断子结点是否满足条件 7 if(){ 如果结点未与之前产生过重复 8 尾指针后移 9 存入新的结点 (提供结点的父结点和层数) 10 if(){ 如果新结点是目标节点 11 输出并退出 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 } 16 } 17 }
值得注意的是,广搜的过程中每生成一个子结点,都要提供指向他们的父结点的指针和层数,以免找到解的时候找不到来时的路径。
广度优先搜索在访问完该层的所有结点后,才开始访问下一层
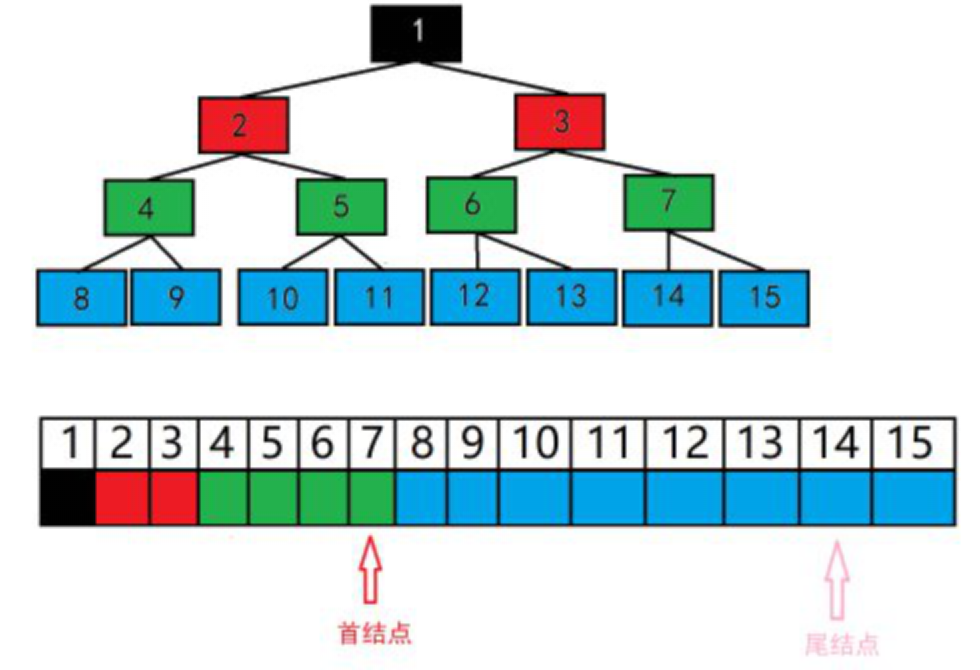
关于从搜索树通过队列存入数组的思想:
广搜一定要将生成的结点与之前的比较,以免出现重复的节点,浪费时间和空间,还有可能陷入死循环!
八字码问题
Description
The 15-puzzle has been around for over 100 years; even if you don't know it by that name, you've seen it. It is constructed with 15 sliding tiles, each with a number from 1 to 15 on it, and all packed into a 4 by 4 frame with one tile missing. Let's call the missing tile 'x'; the object of the puzzle is to arrange the tiles so that they are ordered as:
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 x
where the only legal operation is to exchange 'x' with one of the tiles with which it shares an edge. As an example, the following sequence of moves solves a slightly scrambled puzzle:
1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8 5 6 7 8 5 6 7 8 5 6 7 8
9 x 10 12 9 10 x 12 9 10 11 12 9 10 11 12
13 14 11 15 13 14 11 15 13 14 x 15 13 14 15 x
r-> d-> r->
The letters in the previous row indicate which neighbor of the 'x' tile is swapped with the 'x' tile at each step; legal values are 'r','l','u' and 'd', for right, left, up, and down, respectively.
Not all puzzles can be solved; in 1870, a man named Sam Loyd was famous for distributing an unsolvable version of the puzzle, and
frustrating many people. In fact, all you have to do to make a regular puzzle into an unsolvable one is to swap two tiles (not counting the missing 'x' tile, of course).
In this problem, you will write a program for solving the less well-known 8-puzzle, composed of tiles on a three by three
arrangement.
Input
You will receive a description of a configuration of the 8 puzzle. The description is just a list of the tiles in their initial positions, with the rows listed from top to bottom, and the tiles listed from left to right within a row, where the tiles are represented by numbers 1 to 8, plus 'x'. For example, this puzzle
1 2 3
x 4 6
7 5 8
is described by this list:
1 2 3 x 4 6 7 5 8
Output
You will print to standard output either the word ``unsolvable'', if the puzzle has no solution, or a string consisting entirely of the letters 'r', 'l', 'u' and 'd' that describes a series of moves that produce a solution. The string should include no spaces and start at the beginning of the line.
Sample Input
2 3 4 1 5 x 7 6 8
Sample Output
ullddrurdllurdr
这道题的思路大概是这样子
1.读入到a数组内
2.输出一下a数组 做一个子程序 print2
3.定义一下宽搜的节点
1)首先有一个a棋盘(是一个二维数组)
2)移动空位,记住空位的位置x,y
3)记录深度(你走了几步)叫dep
4)父节点,打方案用,走法dd
4.定义队列大数组结构体data1 100000 一个头指针op,尾指针cl
5.偏移量,空位的移动方案d[5]结构体d[1].x d[1].y偏移
6.初始化队列 首节点入队(初始状态) 写一个拷贝子程序
7.做一个棋盘之间的复制 copy(a,b) 把a棋盘的值拷贝到b棋盘
8.判断两个棋盘的值是否相同
9.判断队列中棋盘是否存在 exist(a) a棋盘在我的data1数组中从1到cl是否存在
10.输出方案的子程序print1
11.写宽搜的框架
但这个时候问题来了,单项搜索的效率太低了!!!如果要走20步,程序需要运行8秒多!!!
这个时候,我们会发现题目中给出了终态! 在这种情况下,同样的搜索从初态和终态出发各搜索一半状态,产生两棵深度减半的搜索树,在中间交会、组合成最终的答案。
这种算法的时间复杂度只有O(2N/2log2n/2)=O(N*2N/2)!!!
这道题是不是完美地解决了??
等等! 还有unsolvable的判断!但是这道题不能用搜索来判断是否有解------无解的时候程序将无限的搜索下去!!
这个时候就需要事先判断八个数字的排列了。
我们会用到置换:
在组合数学中,置换一词的传统意义是一个有序序列,其中元素不重复,但可能有阙漏。例如1,2,4,3可以称为1,2,3,4,5,6的一个置换,但是其中不含5,6。此时通常会标明为“从n个对象取r个对象的置换”。
轮换长度为偶数的轮换称为偶轮换,反之则为奇轮换;由此可定义任一置换的奇偶性,并可证明:一个置换是偶置换的充要条件是它可以由偶数个换位生成。偶轮换在置换群中构成一个正规子群,称为交错群。
(摘自百度百科)
也就是说,我们可以统计排列中逆序的次数(即后一项小于前一项,0不计),如果有奇数次,则无解。
举个栗子叭
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
5 |
4 |
7 |
|
0 |
8 |
6 |
4<5 , 6<7 , 6<8 一共有三次逆序,所以无解.
双向搜索代码
1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 #include<cstring> 5 using namespace std; 6 int a[4][4]={},c[4][4]={},x1,y1,x,y,op=0,cl=1,op1=0,cl1=1,dep=0,dep1=0; //op1 cl1表示由答案开始搜索的队列 7 int ii,jj; 8 int a1[10]={}; //用于判断unsolvable 9 char k,answer[100]; 10 int ans[4][4]={{1,2,3,0},{4,5,6,0},{7,8,0,0},{0,0,0,0}}; 11 void input(int a[4][4]){ 12 for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ 13 for(int j=0;j<3;j++){ 14 cin>>k; 15 if(k=='x') {a[i][j]=0;x=i;y=j;} 16 else { 17 a[i][j]=k-'0'; 18 a1[i*3+j]=a[i][j]; 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 void print2(int a[4][4]){ 24 for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ 25 for(int j=0;j<3;j++) 26 printf("%d ",a[i][j]); 27 printf(" "); 28 } 29 } 30 void copy(int a[4][4],int b[4][4]){ 31 for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ 32 for(int j=0;j<3;j++) 33 b[i][j]=a[i][j]; 34 } 35 } 36 bool same(int a[4][4],int b[4][4]){ 37 for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ 38 for(int j=0;j<3;j++) 39 if(b[i][j]!=a[i][j]) return false; 40 } 41 return true; 42 } 43 44 struct node1{ 45 int x,y; 46 }d[5]={{0,0},{-1,0},{+1,0},{0,-1},{0,+1}}; 47 struct node2{ 48 int m[4][4]; 49 int dep; //结点深度 50 int dd; //行走方向 51 int x,y; //坐标 52 int fa; //父结点下标 53 }data1[100001]; 54 struct node3{ 55 int m[4][4]; 56 int dep; //结点深度 57 int dd; //行走方向 58 int x,y; //坐标 59 int fa; //父结点下标 60 }data2[100001]; 61 bool exist(int a[4][4]){ 62 for(int i=0;i<=cl;i++){ 63 if(same(data1[i].m,a)) return false; 64 } 65 return true; 66 } 67 bool exist1(int a[4][4]){ 68 for(int i=0;i<=cl1;i++){ 69 if(same(data2[i].m,a)) return false; 70 } 71 return true; 72 } 73 void print1(int cl, int cl1){ 74 int kk=cl,num=0; 75 while(dep--){ 76 if(data1[kk].dd==1) answer[num++]='u'; 77 else if(data1[kk].dd==2) answer[num++]='d'; 78 else if(data1[kk].dd==3) answer[num++]='l'; 79 else if(data1[kk].dd==4) answer[num++]='r'; 80 kk=data1[kk].fa; 81 } 82 for(int i=num-1;i>=0;i--) printf("%c",answer[i]); 83 kk=cl1; num=0; 84 while(dep1--){ 85 if(data2[kk].dd==1) answer[num++]='u'; 86 else if(data2[kk].dd==2) answer[num++]='d'; 87 else if(data2[kk].dd==3) answer[num++]='l'; 88 else if(data2[kk].dd==4) answer[num++]='r'; 89 kk=data2[kk].fa; 90 } 91 for(int i=0;i<num;i++) printf("%c",answer[i]); 92 printf(" "); 93 } 94 95 int main(){ 96 // freopen("Eight.in","r",stdin); 97 //输入 98 input(a); 99 //特判 100 if(same(a,ans)){ 101 printf("%d ",0); 102 return 0; 103 } 104 int sum1=0; 105 for(int i=1;i<9;i++) 106 if (a1[i]!=0){ 107 for (int j=i+1; j<9; ++j) 108 if (a1[i]>a1[j] && a1[j]!=0) { 109 ++sum1; 110 } 111 } 112 113 if (sum1%2==0){ 114 printf("unsolvable "); 115 return 0; 116 } 117 118 //首结点入队 119 data1[1].dd=0; 120 data1[1].dep=1; 121 data1[1].x=x; 122 data1[1].y=y; 123 data1[1].fa=-1; 124 copy(a,data1[1].m); 125 126 data2[1].dd=0; 127 data2[1].dep=1; 128 data2[1].x=2; 129 data2[1].y=2; 130 data2[1].fa=-1; 131 copy(ans,data2[1].m); 132 //宽搜 133 while(op<=cl){ 134 135 op++; op1++; 136 if(dep!=data1[op].dep){ 137 for(int i=1;i<=cl;i++){ 138 for(int j=1;j<=cl1;j++){ 139 if(data1[i].dep==dep){ 140 if(same(data1[i].m,data2[j].m)){ 141 print1(i,j); return 0; 142 } 143 } 144 } 145 } 146 } 147 dep=data1[op].dep; 148 for(int i=1;i<=4;i++){ 149 x=data1[op].x+d[i].x; 150 y=data1[op].y+d[i].y; 151 if(x>=0 && x<3 && y>=0 && y<3){ 152 //printf(" %d %d %d ",op,x,y); 153 //移动后的棋盘存给c 154 copy(data1[op].m,c); 155 c[data1[op].x][data1[op].y]=c[x][y]; 156 c[x][y]=0; 157 if(exist(c)){ 158 cl++; 159 data1[cl].dd=i; 160 data1[cl].dep=dep+1; 161 data1[cl].x=x; 162 data1[cl].y=y; 163 data1[cl].fa=op; 164 copy(c,data1[cl].m); 165 } 166 } 167 } 168 dep1=data2[op1].dep; 169 for(int i=1;i<=4;i++){ 170 x=data2[op1].x+d[i].x; 171 y=data2[op1].y+d[i].y; 172 if(x>=0 && x<3 && y>=0 && y<3){ 173 copy(data2[op1].m,c); 174 c[data2[op1].x][data2[op1].y]=c[x][y]; 175 c[x][y]=0; 176 if(exist1(c)){ 177 cl1++; 178 data2[cl1].dd=i; 179 data2[cl1].dep=dep1+1; 180 data2[cl1].x=x; 181 data2[cl1].y=y; 182 data2[cl1].fa=op; 183 copy(c,data2[cl1].m); 184 } 185 } 186 } 187 } 188 return 0; 189 }