一、UIApplication类
Every app has exactly one instance of UIApplication
每个应用程序都只有一个UIApplication类的实例对象
运行起来的应用程序就是一个UIApplication对象
二、UIApplicationMain
创建UIApplication对象的一个单例对象
The role of your app's application object
.handle the initial routing of incoming user events
处理用户行为的一个循环
.dispatches action messages forwarded to it by control objects(instances of the UIControl class) to appropriate target objects.
将特定的行为分配给特定的目标对象(将不同的事件传递给不同的UI控件)
三、Tasks
Getting the App Instance:获取单例对象
Getting the App Delegate:获取应用程序代理(捕获程序的状态)
Getting App Windows:获取窗口
Controlling and Handling Events:处理事件
Opening a URL Resources:打开外部的APP资源
Configuring the User Notification Setting:配置用户的通知
Registering for Remote Notification:远程通知
Registering for Local Notification:本地通知
Managing Background Execution:管理后台的执行
Managing Home Screen Quick Actions for 3D Touch:快捷方式
Controlling App Appearance:管理程序的外观(状态栏,网络指示,方向)
NSStringFromClass将一个类转换为字符串形式
NSStringFromClass([AppDelegate class])
四、UIApplicationDelegate
The UIApplicationDelegate protocol defines methods that are called by the singleton UIApplication object in response to important events in the lifetime of your app.
响应程序运行过程中发生的一些重要的事件 (程序启动,进入后台,激活,内存吃紧)
The app delegate works alongside the app object to ensure your app interacts properly with the system and with other apps.
应用程序代理和app共同运行,确保程序与系统或者其他色app之间正确地交互
The app delegate is effectively the root object of your app. Like the UIApplication object itself, the app delegate is a singleton object and is always present at runtime.
应用程序代理是程序的root对象,整个程序运行过程中一直都存在
五、App Delegate里面的那些方法应该被实现
The app delegate performs several crucial roles:
- .It contains your app’s startup code.
- 可以在代理里面使用代码进行设置
a.程序加载起来调用的第一个方法(配置,注册服务器信息,读取数据,配置界面)
//还没有运行到内存里面
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application willFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(nullable NSDictionary *)launchOptions NS_AVAILABLE_IOS(6_0);
//加载好了,需要对显示的界面进行配置
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(nullable NSDictionary *)launchOptions NS_AVAILABLE_IOS(3_0);
It responds to key changes in the state of your app. Specifically, it responds to both temporary interruptions and to changes in the execution state of your app, such as when your app transitions from the foreground to the background.
临时打断、状态改变
It responds to notifications originating from outside the app, such as remote notifications (also known as push notifications), low-memory warnings, download completion notifications, and more.
外部通知(消息推送、内存不够、后台下载完成)
registerForRemoteNotificationTypes:
It determines whether state preservation and restoration should occur and assists in the preservation and restoration process as needed.
确定程序的状态(数据)是否应该保存或者恢复
It responds to events that target the app itself and are not specific to your app’s views or view controllers.
响应应用程序本身的事件
application:openURL:options:
You can use it to store your app’s central data objects or any content that does not have an owning view controller.
保存程序当前的核心数据或其他那些没有viewController保存的数据
六、UIResponder
The UIResponder class defines an interface for objects that respond to and handle events.
定义了对象响应和处理事件的接口
所有能够处理事件的UI控件都是直接或者间接继承于UIResponder
两种主要的事件行为:触摸事件和运动事件
There are two general kinds of events: touch events and motion events.
UIEvent
touchesBegan:withEvent:,
touchesMoved:withEvent:,
touchesEnded:withEvent:,
touchesCancelled:withEvent:.
motionBegan:withEvent:,
motionEnded:withEvent:,
motionCancelled:withEvent:.
iOS3.0 canPerformAction:withSender:
iOS4.0 UIResponder added the remoteControlReceivedWithEvent: method for handling remote-control events.
Responder Chain响应者链
辑视图有层级关系,后添加的视图会覆盖前面的视图,当一个事件发生了,最前面的视图会接受到这个事件,如果这个视图不响应,那么继续将事件传递给后面一层,指导UIWindow,如果都不响应,那么事件将会被丢弃,这个过程中,只要有一个响应了,那么这个事件就停止传递了。

七、为什么要使用代理
为了简化代码逻辑
以苹果公司为例,苹果公司自己设计外观和系统,将制造、材料、销售代理出去,就是为了让自己专注于技术层面。
继承也可以实现代理的功能
如果使用继承,相当于苹果公司自己有自己的制造子公司,材料子公司,销售子公司,对于自己的管理加大了难度,并且无法专注于核心竞争力
整个应用程序只有一个代理(默认系统为我们提供了AppDelegate类)
八、UIWindow
manages and coordinates the views an app displays on a device screen
管理和协调设备屏幕上面显示的视图
一个应用程序一般情况下只有一个window
UIWindow的功能
provide an area for displaying its views
提供一片用来显示视图的区域
distribute events to the views.
分发事件给视图
一个UIWindow对象必须设置一个主界面
设置窗口的rootViewController属性
显示窗口
调用makeKeyAndVisible属性
九、UIScreen
A UIScreen object defines the properties associated with a hardware-based display
定义一些基于硬件显示的属性
如何获取设备的主屏幕
[UIScreen mainScreen]
如何获得一个视图的矩形坐标
bounds属性
PS:苹果手机各适配的尺寸
4(320 * 480)
5(320 * 568)
6(375 * 667)
6p(414 * 736)
十、实际操作 自定义一个操作界面
1.先创建一个新的代理 因为所有处理事件的控件都是直接或者间接继承于UIResponder的 所以建的时候 继承的类改为UIResponder如图
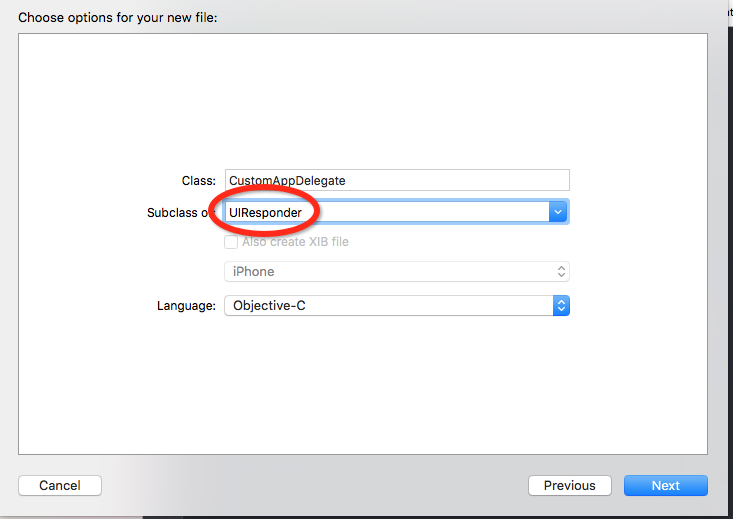
同时应用程序代理是程序的root对象,整个程序运行过程中一直都存在
所以在CustomAppDelegate.h文件中需要服从UIApplicationDelegate协议

我们要实现是一个界面 界面需要通过窗口显示出来 所以我们需要定义一个UIWindow类的变量window作为界面

到了CustomAppDelegate.m文件中
它是程序加载起来之后调用的第一个代理方法 包括加载配置文件、加载数据、打开数据库、配置启动界面
加载好了,需要对显示的界面进行配置
需要调用UIApplication中的didFinishLaunchingWithOptions这个方法

.h文件中我们定义了window变量 这里我们就要创建一个窗口

设置窗口的背景颜色 有专门的UIColor类可以选择颜色

我们还可以设置窗口的大小

如果这个时候我们就让程序显示这个窗口 系统会报错


通过错误原因 我们发现 虽然有了窗口 系统提示我们缺少了主界面
原因是:窗口是用来存放视图的,而一个视图对应一个界面,我们刚才没有创建任何界面 所以显示的时候出错了
所以有了窗口之后 我们还需要创建一个界面 所以我们先新建一个用来定义界面的文件

然后我们创建一个界面 同时将这个界面作为窗口的主界面
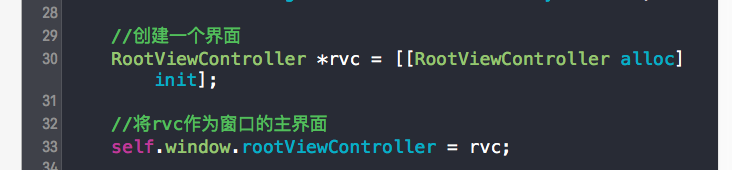
然后我们运行一下 就得到想要的界面了 如下图

但是我们都知道苹果手机运行程序的时候一般只有一个界面 所以我们需要将这个界面适配成全屏的
我们可以用下面的代码获取设备屏幕的尺寸

在运行一次就得到全屏的界面了

