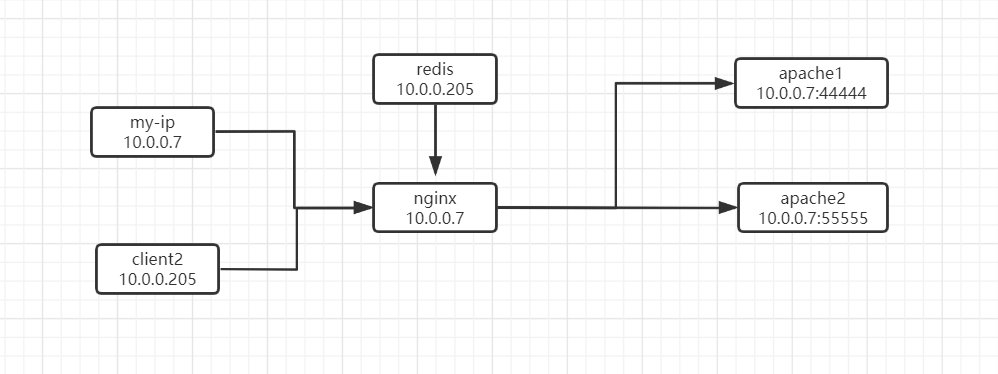
1.灰度发布拓扑图,公司本地访问服务进灰度环境,其他的访问原来生产。
2.nginx.conf的配置
[root@VM_0_7_centos conf]# cat nginx.conf worker_processes 1; error_log logs/error.log; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include vhost/*.conf; server { listen 22222; server_name 10.0.0.7 www.a.com localhost; #charset koi8-r; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; default_type 'text/plain'; location /test { content_by_lua_file /Users/chenguowei/local/openresty/nginx/lua_conf/huidu.lua; } location @client1 { proxy_pass http://client1; } location @client2 { proxy_pass http://client2; } } }
3.nginx的lua脚本
当来源的IP是myip时,就进灰度,其他的进生产环境。如果有密码加一句 在red:auth("密码") 即可。 参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42085428/article/details/104898500
[root@VM_0_7_centos ~]# cat /Users/chenguowei/local/openresty/nginx/lua_conf/huidu.lua local redis = require "resty.redis" local cache = redis.new() cache:set_timeout(60000) local ok, err = cache.connect(cache, "10.0.0.205", 6379)
cache:auth("密码") if not ok then ngx.say("failed to connect: redis", err) return end local local_ip = ngx.req.get_headers()["X-Real-IP"] if local_ip == nil then local_ip = ngx.req.get_headers()["x_forwarded_for"] end if local_ip == nil then local_ip = ngx.var.remote_addr end local intercept = cache:get("myip") if intercept == local_ip then ngx.exec("@client2") return end ngx.exec("@client1") --之前不能有任何的ngx.say()函数执行过,否则请求会出错 local ok, err = cache:close() if not ok then ngx.say("failed to close: ", err) return end
4.redis设置我的IP
[root@VM_0_42_centos src]# ./redis-cli -h 10.0.0.205 -p 6379 10.0.0.205:6379> set myip 10.0.0.7 OK 10.0.0.205:6379>
参考: https://blog.csdn.net/gochenguowei/article/details/85041578