对于vue这类mvvm框架来说,其核心就是组件与数据,因此做好相应的数据管理极为重要。这里分享下vuex数据模块化管理的方法,有利于搭建便于维护、协作的vue项目。
vuex管理基本方法和使用
模块化的概念已经在js、css中大量的用到,已不再陌生,其可增加代码的复用、扩展性、维护性等,对于一个大型的系统来说,必不可少。这里也希望提供一种有效的模块化数据管理方式,让协作变的更为高效。
- 首先看看vuex的四个对象
state: {}, // 存储数据的状态
getters: {}, // 获取vuex数据(state)的统一接口
mutations: {}, // 存vuex数据(state)的统一接口
actions: {}, // vuex内的异步操作接口
- 再看某种应用方式
项目有两个模块,一个home页面,一个poetry页面,对应不同的vuex数据模块,其vuex的管理方式如下:
// home.js
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {...},
mutations: {...}
})
// poetry.js
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {...},
getters: {...}
})
// vuex调用
if (pathname.indexOf('/home') >= 0) {
store = require('/vuex/home').default
} else if (pathname.indexOf('/poetry') >= 0) {
store = require('/vuex/home').default
}
由于每个单页对应会生成一个全新的vuex,这样就会造成vuex数据的丢失(单页跳转、回退时),这就是没有实现vuex的模块化管理及数据共享共享。那么怎么样进行模块化管理呢?
简单的vuex模块化
简单的vuex管理代码如下:
// home.js
...
export default {
state,
getters,
actions,
mutations
}
// poetry.js
...
同home.js~~
// index.js
...
import common from './common'
import home from './home'
import poetry from './poetry'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {},
modules: {
common,
home,
poetry
}
})
// 调用方法如下
import store from 'src/store/index'
如此,vuex模块化后的结构如下:

图一 vuex模块化的结构
一个独立项目,仅有一处进行new Vuex操作,防止vuex丢失。但上图的方法,可以实现简单项目的管理,在多人协作下仍然存在数据操作隐患。首先来看下重名状态下,各个属性的表现。
方法重名的表现及带来的问题
重名的情况下,state会自动根据模块确认命名空间(独立的属性调用)。再看getters、mutations、actions,其与state不同,会引发重名问题,具体表现如下:
-
getters
在重名的情况下,仅首先注册的getters会生效,同时报错,提示重名。
错误如下:

图二 getters重名报错图
-
mutations/action
在重名情况下,多个重名方法都将被调用。(以mutations为例)
this.updateInitInfo('poetry string’) // home.js const mutations = { updateInitInfo(state, string) { state.initInfo = string console.log('home update', string) } } // poetry.js const mutations = { updateInitInfo(state, string) { state.pageName = string console.log('poetry update', string) } }在poetry中调用,执行结果如下:
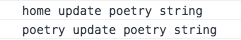
图3 mutations的重命名执行结果
由图3,可以得出结论,方法会按序执行,且无报错和警告。
对于这类方法的重名调用,比较难察觉,多人协作时,较容易出现数据共享错误,所以需要用另外的方法来加强配置,使得强调 单一调用 的协作场景,也可以高效的展开。
vuex数据模块化管理方案
vuex自带模块化方法,为namespaced:true。通过对模块进行命名空间设置,就能分模块进行管理。
-
目录结构
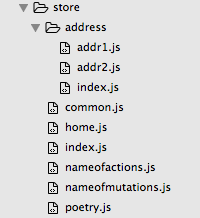
图4 vuex的目录结构
其中address模块的增加,是为了适应更为复杂的应用需求。相关设置代码如下:
// address/index.js
import addr1 from './addr1'
import addr2 from './addr2'
import addrList from './addrList'
export default {
namespaced: true,
modules: {
addr1,
addr2,
addrList
}
}
// home.js
const state = {
initInfo: 'hello hity'
}
const getters = {
initInfo(state, getters) {
return state.initInfo
}
}
const actions = {
getInfo({commit, state}) {
commit('updateInitInfo', 'getInfo')
}
}
const mutations = {
updateInitInfo(state, string) {
state.initInfo = string
console.log('home update', string)
}
}
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
getters,
actions,
mutations
}
// index.js
......
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {},
modules: {
common,
home,
poetry,
address
}
})
运行结果vuex视图如下:

图5 vuex运行后的结构图
由上图可见,通过命名空间设置的getters、mutaions、actions都可以生成自己独有的方法名,从而实现模块化。这样的方法名,如何调用呢?调用方法有如下几种[以贴出代码的home模块为例]:
// xxx.vue中调用
a、通过store直接调用:
state:this.$store.state.home.initInfo
getters: this.$store.getters['home/initInfo']
mutations: this.$store.commit('home/updateInitInfo', 'set home init info')
actions: this.$store.dispatch('home/getInfo')
b、配合vuex的createNamespacedHelpers方法使用
import { createNamespacedHelpers } from 'vuex'
const { mapActions, mapState, mapMutations, mapGetters } = createNamespacedHelpers('home')
computed: {
...mapState({
initInfoState: state => state.initInfo
}),
...mapGetters([
'initInfo'
])
},
methods: {
...mapMutations([
'updateInitInfo'
]),
...mapActions([
'getInfo'
])
}
c、使用原始的mapX方法
import { mapActions, mapState, mapMutations, mapGetters } from 'vuex'
computed: {
...mapState({
initInfoState: state => state.home.initInfo
}),
...mapGetters('home', [
'initInfo'
])
}
methods: {
...mapMutations('home', [
'updateInitInfo'
]),
...mapActions('home', [
'getInfo'
])
}
从vuex运行后的结构图可以看出,state的模块名成为其属性名,从而实现模块化;而getters、mutations、actions的模块名,则成为方法名的前缀,通过'/'分隔,从而实现模块化。从调用方法上可以看出,更容易看出两者的区别。如果你的代码是从非模块化,到模块化的改造,且都是使用的mapX方法进行方法管理,那么使用方案b的state方法,结合方案c的mapGetters、mapMutations、mapActions,将使得改造成本最小化。
tips:使用vuex的项目,建议使用mapX方法进行统一的管理,对vuex的调用较为直观,也便于将来的扩展和改造。