---恢复内容开始---
1.昨日内容回顾
编译型:一次性将全部代码翻译成二进制文件。 c c++
优点:运行效率高
缺点:开发效率慢,不能跨平台。
解释型:当程序运行时,从上至下一行一行的解释成二进制
优点:开发速度快,可跨平台
缺点:运行效率低
pyrhon2和python3宏观上的区别:
python2x源码,重复率高,不规范 python崇尚的是简单优美清晰,所以龟叔创建了python3,规范化。
在python2首行输入; #-*-encoding:utf-8-*- 解决python2中中文报错的问题
变量;由数字,字母和下划线任意组合,且不能以数字开头
具有可描述性
不能用python中的关键字,中文,拼音
常量: 约定俗成 不可更改 全部是大写字母
注释:单行注释用# 多行注释用三引号
用户交互 input():
输出的数据类型全部是str
基础数据类型:bool
int + - * / // % **
str 加引号的都是字符串 可以和int相乘
if条件语句
嵌套if
if条件:
if条件:
结果
else:
结果
while条件:
结果
break中断循环,continue跳过当前循环
2.作业题
1.使用while循环输入123456 8910
1 #使用while循环输入123456 8910 2 count=0 3 while count<10: 4 count+=1 5 if count==7: 6 print(" ") 7 continue 8 print(count)
2.输出1到100内所有奇数
1 count=1 2 while count<100: 3 print(count) 4 count+=2
count=1 while count<100: if count % 2==1: print(count) count+=1
3.求1-2+3-4...99所有数的和
sum=0 count=0 while count<100: if count%2==1: sum=sum+count else: sum=sum-count count+=1 print(sum)
4.用户登录三次机会:
i=1 while i<=3: username=input("请输入你的名字:") passwoed=input("请输入你的密码:") if username=="咸鱼哥" and passwoed=="123": print("登陆成功") break else: print("登陆失败") continue i+=1
i=1 while i<=3: username=input("请输入你的名字:") passwoed=input("请输入你的密码:") if username=="咸鱼哥" and passwoed=="123": print("登陆成功") break else: print("登陆失败") print("您还有%d次机会" % (3 - i)) i += 1
3.pycharm安装
4.格式化输出:
%s %d %%
转义;想要在格式化输出中表示单纯的%号,输入应该是%%,%后的都转义了
name=input("请输入你的名字") age=input("请输入你的年龄") height=input("请输入你的身高") usg='''--------------info of %s-------------- name:%s age:%s height:%s ------------------------------------------ '''%(name,name,age,height) print(usg)
5.while else break continue pass
当循环被break打断时,就不会执行else结果
break

count=0 while count<6: count+=1 if count==3: break print("loop",count) else: print("循环正常执行完了")
continue
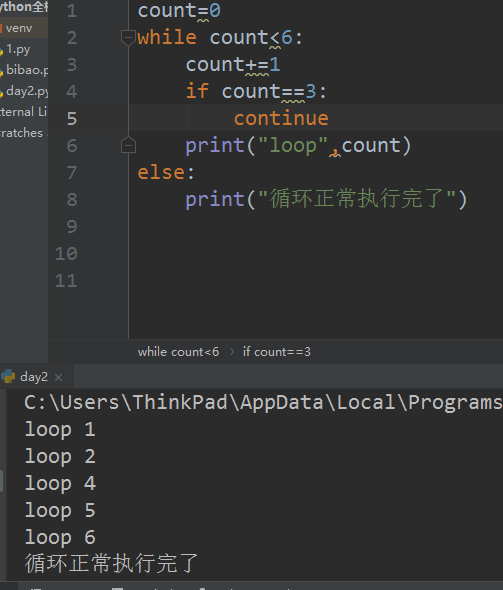
pass

6.逻辑运算符:
针对逻辑运算的进一步研究:
1,在没有()的情况下not 优先级高于 and,and优先级高于or,即优先级关系为( )>not>and>or,同一优先级从左往右计算
print(3>4or 4<3 and 1==1) print(1<2 and 3<4 or 4>5 and 2<1) print(not 2>1 and 3<4 or 4>5 and 2>1 and 9>8 or 7<6) False True False
x or y, x为真,值就是x,x为假,值就是y
x and y,x为真,值是y,x为假,值是x
print(1 or 2) print(3 or 2) print(0 or 100) 1 3 100
print(0 or 1-4) print(2 or 1<3) print(1<3 or 0) print(9 or 1>3 and 2 or 0) print(1>2 and 3 or 4 and 3<2) -3 2 True 9 False
数字转换成bool值
非零是True bool()括号里面只能输入一个数字
bool值抓换成数字时 True 为1 False 为0
print(bool(2)) print(bool(-2)) print(bool(0)) print(int(True)) print(int(False)) True True False 1 0
Python运算符优先级
以下表格列出了从最高到最低优先级的所有运算符:
| 运算符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ** | 指数 (最高优先级) |
| ~ + - | 按位翻转, 一元加号和减号 (最后两个的方法名为 +@ 和 -@) |
| * / % // | 乘,除,取模和取整除 |
| + - | 加法减法 |
| >> << | 右移,左移运算符 |
| & | 位 'AND' |
| ^ | | 位运算符 |
| <= < > >= | 比较运算符 |
| <> == != | 等于运算符 |
| = %= /= //= -= += *= **= | 赋值运算符 |
| is is not | 身份运算符 |
| in not in | 成员运算符 |
| not and or | 逻辑运算符 |
---恢复内容结束---
