1, char a[] = "hello";
char c[] = {'h','e','l','l','o'};
int b[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
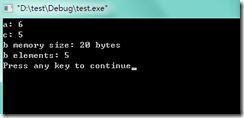
数组是开辟一块连续的内存空间,数组本身的标识符(也就是通常所说的数组名)代表整个数组,可以使用sizeof来获得数组所占据内存空间的大小(注意,不是数组元素的个数,而是数组占据内存空间的大小,这是以字节为单位的)。举例如下:
// test.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char a[] = "hello";
char c[] = {'h','e','l','l','o'};
int b[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
printf("a: %d ", sizeof(a));
printf("c: %d ", sizeof(c));
printf("b memory size: %d bytes ", sizeof(b));
printf("b elements: %d ", sizeof(b)/sizeof(int));
return 0;
}
数组a为字符型,后面的字符串实际上占据6个字节空间(注意最后有一个�标识字符串的结束)。从后面sizeof(b)就可以看出如何获得数组占据的内存空间,如何获得数组的元素数目。至于int数据类型分配内存空间的多少,则是编译器相关的。gcc默认为int类型分配4个字节的内存空间。